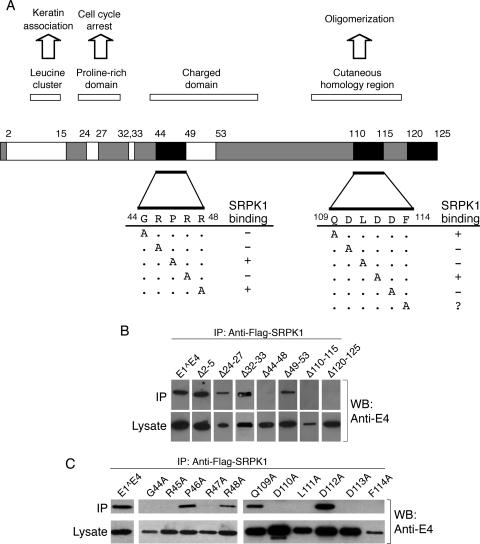
FIG. 4.
Mapping the domains within HPV1 E1^E4 that mediate the association with SRPK1. Anti-Flag immunoprecipitations (IP) from lysates prepared from 293T cells coexpressing Flag-SRPK1 and mutant HPV1 E1^E4 proteins were performed to identify key residues in HPV1 E1^E4 necessary for SRPK1 binding. (A) A diagrammatic summary of the data from the immunoprecipitation experiments is shown. The white domains correspond to regions within E1^E4 that are not required for the interaction with Flag-SRPK1, and the black domains identify residues found necessary for the association to occur. Alanine-scanning mutagenesis of residues in regions 44 to 48 and 109 to 114 involved in SRPK1 binding identified individual amino acids that are key participants in the association. +, binding; −, no binding. The relationship of the different domains to known E1^E4 functions and sequence characteristics is also shown. (B) Western blot (WB) analysis of immunoprecipitations between Flag-SRPK1 and E1^E4 proteins containing various deletions. (C) Western blot analysis of immunoprecipitations between alanine point substitutions and Flag-SRPK1. All of these mutants aside from F114A are expressed to a similar or greater level than the wild-type E1^E4. Analysis of the immunoprecipitations indicate that the amino acids G44, R45, R47, D110, L111, and D113 are each required to maintain the association of HPV1 E1^E4 with Flag-SRPK1.