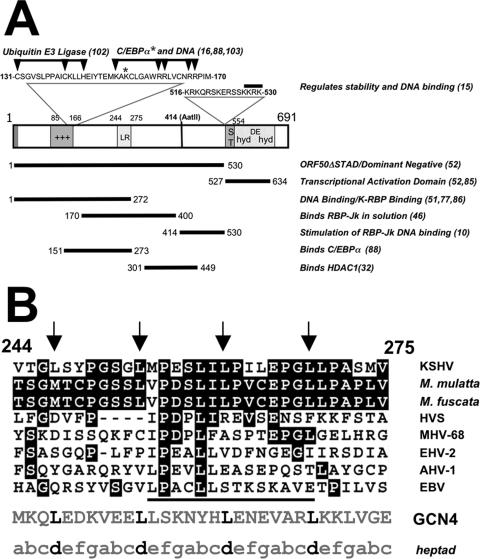
FIG. 1.
Primary amino acid sequence of KSHV ORF50/Rta protein. (A) Structure/function map of ORF50/Rta. A schematic of the primary amino acid sequence of the FL ORF50/Rta protein is shown. The numbers on the diagram refer to amino acid positions; the numbers to the right in parentheses indicate references. The bars with arrowheads indicate the positions of single-amino acid mutations that eliminate ubiquitin E3 ligase activity and binding to C/EBPα and DNA. The bars underneath ORF50 represent domains with functions identified in the list at the right. See the text for the relevant references. Abbreviations: NLS, nuclear localization sequence; AatII, position of truncation of cDNA by restriction digestion by the AatII enzyme; ST, serine/threonine-rich sequence; hyd, hydrophobic; DE, acidic amino acid-rich; HDAC1, histone deacetylase 1. Symbols: *, location of single-amino-acid mutation that eliminates binding to C/EBPα; +++, basic amino acid-rich sequence. (B) Alignment of KSHV ORF50/Rta LR with other gammaherpesvirus ORF50 proteins. Numbers refer to the animo acid position. Arrows point to leucines in the heptapeptide repeat. White lettering on a black background indicates amino acid identity. The bar under the viral sequences indicates the core of highest identity among all the indicated proteins. “heptad” indicates the lettering of canonical amino acid positions in heptad repeats. Abbreviations: M. mulatta, Macaca mulatta (either RRV/H26-95 or RRV/17577 isolates); M. fuscata, Macaca fuscata (GenBank accession number NC_007016) (S. G. Hansen, N. Avery, M. K. Axthelm, and S. W. Wong, unpublished data); HVS, herpesvirus saimiri; MHV-68, murine gammaherpesvirus 68; EHV-2, equine herpesvirus 2; AHV-1, alcelaphine herpesvirus 1; EBV, Epstein-Barr virus; GCN4, S. cerevisiae GCN4 leucine zipper.