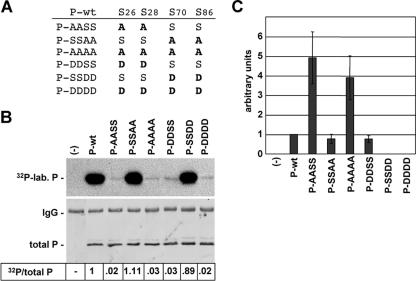
FIG. 1.
Phosphorylation and cofactor activity of BDV-P mutants lacking the major or minor phosphate acceptor sites. (A) BDV-P mutants harboring amino acid substitutions at the major (S26/28) and minor (S70/86) phosphorylation sites. (B) To determine the extent of phosphorylation of P-wt and P mutants, these proteins were transiently expressed in HEK 293T cells in the presence of 32P-labeled orthophosphate, immunoprecipitated, separated by SDS-PAGE using a 15% gel, and transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane. The upper panel represents an autoradiography showing the levels of radioactive labeled P (32P-lab. P). The lower panel shows the detection of total P by P-specific antiserum. The immunoglobulin G (IgG) heavy chain detected by the secondary antibody is indicated. Numbers give the ratio of 32P-labeled P proteins (32P) to levels of total P detected by Western blot analysis. The ratio of 32P/total P observed with P-wt was set to 1. −, no transfection of expression plasmids. (C) To determine the activity of the P mutants in supporting viral polymerase, a T7-based BDV minireplicon assay was performed. BSR-T7/5 cells were transfected with the BDV minigenome CAT reporter construct, the expression constructs for N and L, and plasmids encoding P-wt or mutant proteins as well as a plasmid constitutively expressing luciferase, which served to normalize variation in transfection efficiency. Minireplicon activity was analyzed by CAT enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Mean values of at least four independent assays are shown. −, complete reaction mixtures without P served as a negative control reaction.