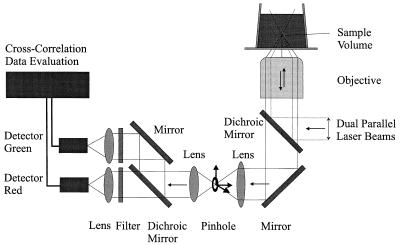
Figure 2.
The dual-color FCS setup. Two parallel laser beams of an argon-ion laser (488 nm, 0.1 mW) and a helium-neon laser (633 nm, 0.05 mW) pass through a water-immersion microscope objective (×40, 1.2 NA) in an epi-illumination arrangement resulting in two superimposed focal spots in the sample, forming a confocal volume element in the femtoliter range. The emitted fluorescence light is collected by the microscope objective, separated from the excitation light by a dichroic mirror, and focused onto a pinhole by a lens. The pinhole, with an adjustable diameter, is located in the image plane of this lens and can be adjusted in the x-y-z axes. Fluorescence emission is parallelized, separated by a dichroic mirror into a green and a red fraction and refocused on two avalanche photo diodes.