Abstract
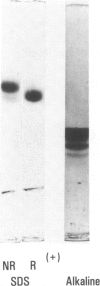
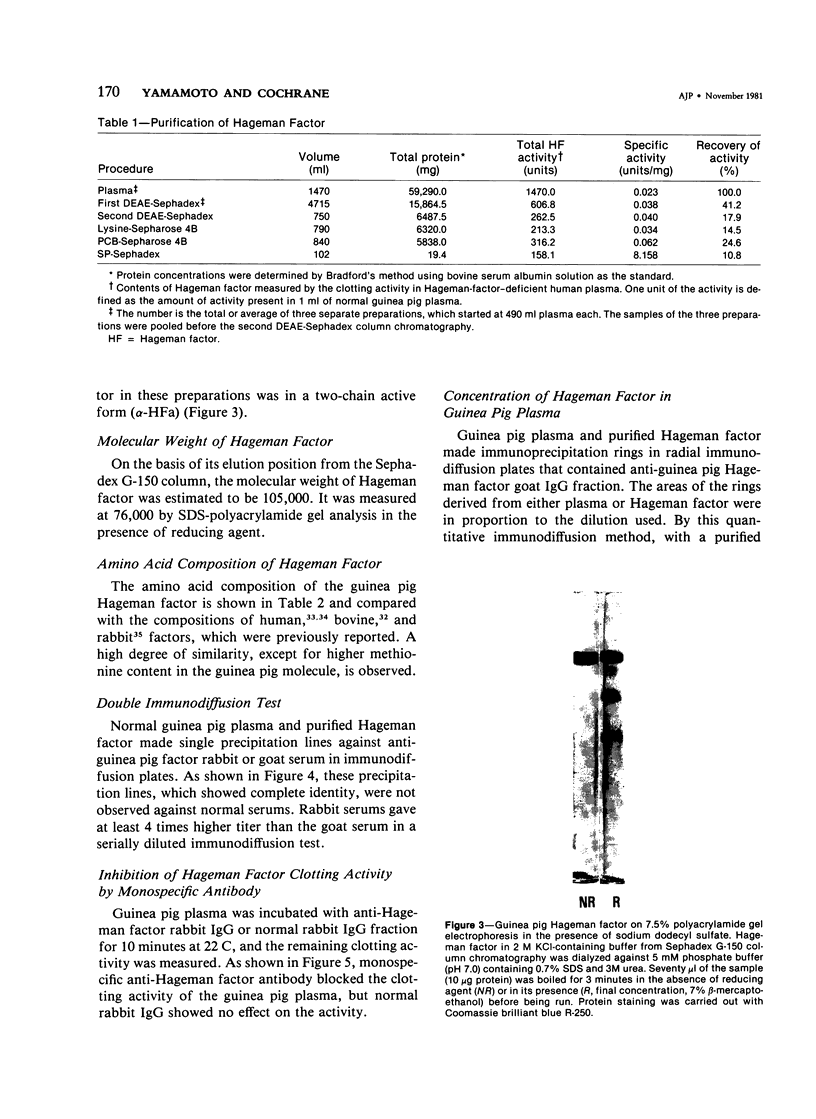
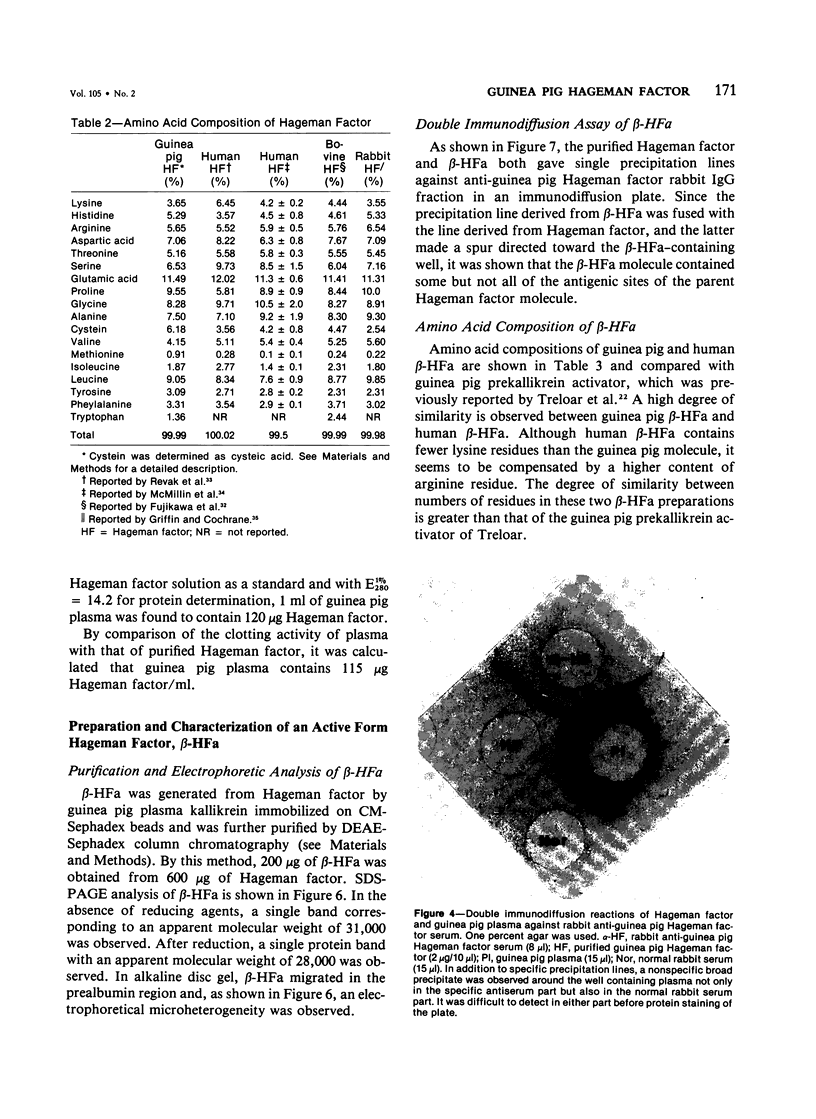
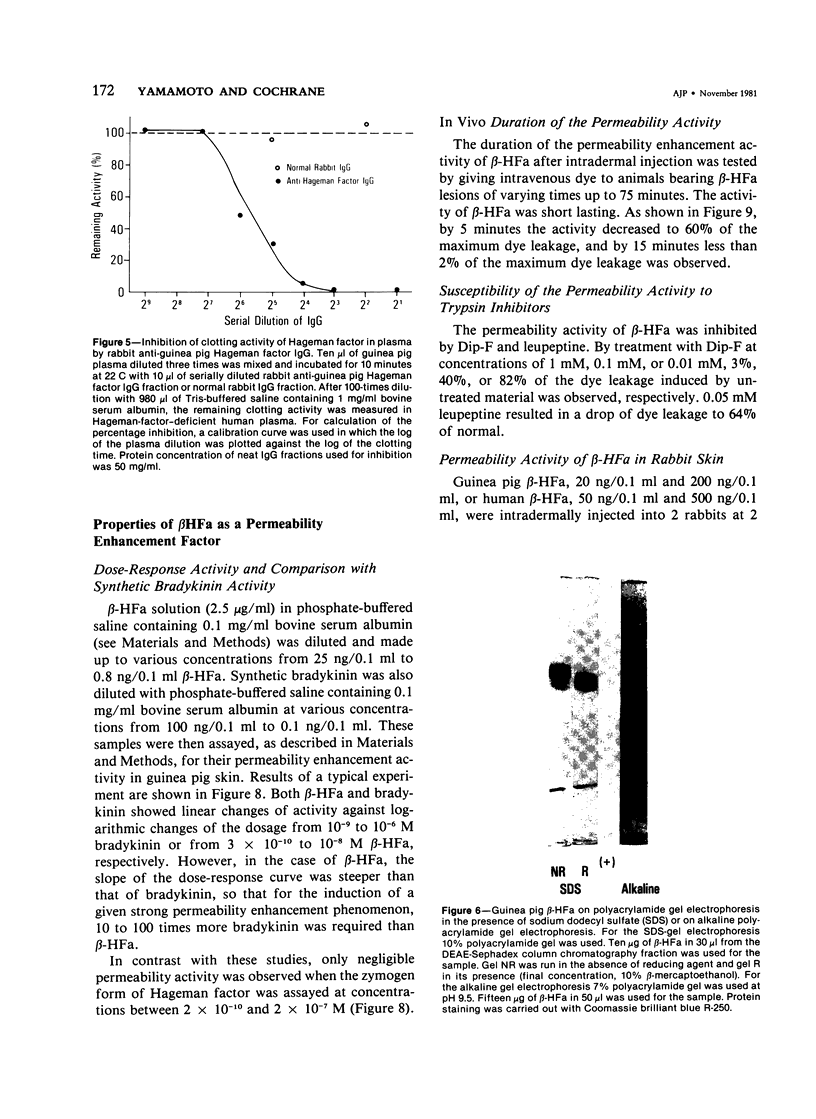
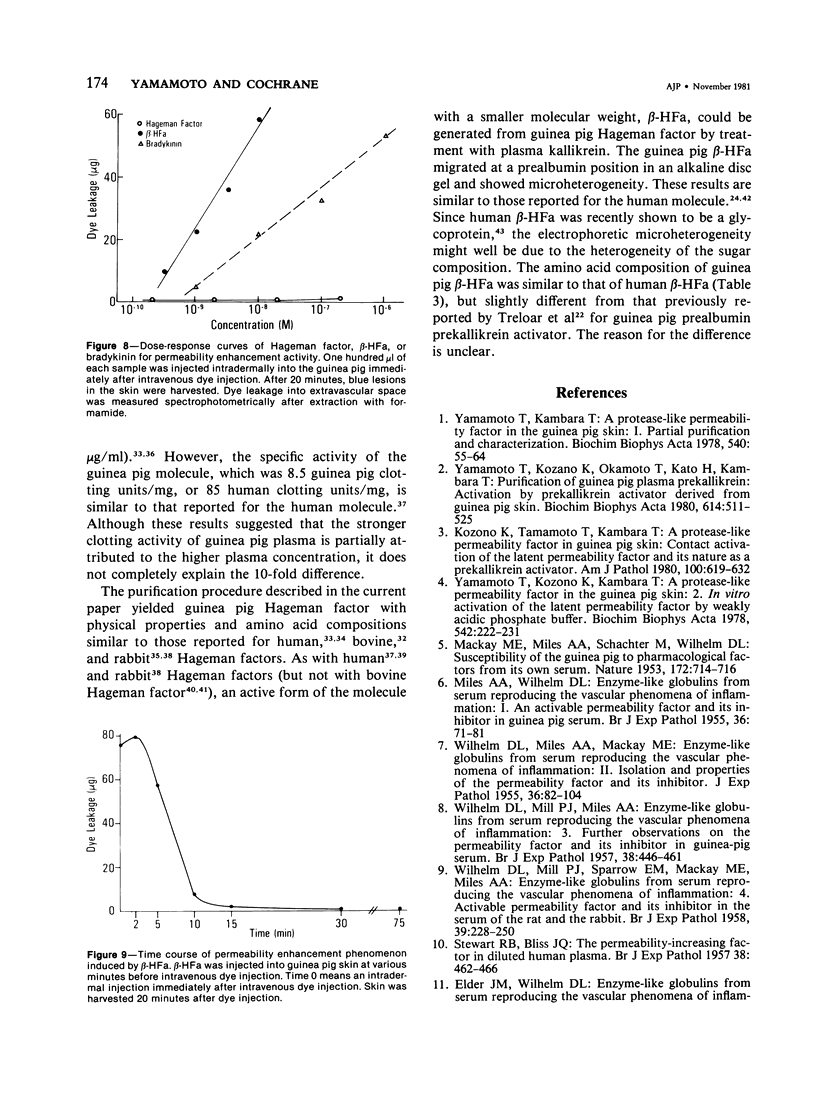
Hageman factor was purified from guinea pig plasma by successive column chromatography. The guinea pig Hageman factor appeared homogeneous as a single-chain protein on polyacrylamide gels in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) and beta-mercaptoethanol. The apparent molecular weight was 76,000 daltons by SDS--polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and 105,000 daltons by gel filtration with a Sephadex G-150 column. Amino acid composition of the guinea pig Hageman factor was similar to that reported for human, bovine, and rabbit Hageman factors. The purified guinea pig Hageman factor, as well as guinea pig plasma, showed strong clotting time correction activity in Hageman-factor--deficient human plasma. The activity could be blocked by the IgG fraction of antiserums against guinea pig Hageman factor raised in rabbits or a goat. The concentration of Hageman factor in guinea pig plasma was determined to be 120 microgram/ml by quantitative radial immunodiffusion assay. The 28,000-dalton active form of Hageman factor (beta-HFa) was prepared from guinea pig Hageman factor by treatment with plasma kallikrein. beta-HFa caused an increase in vascular permeability when injected into guinea pig skin at concentrations as low as 3 x 10(-10) M (0.8 ng). Native, or zymogen Hageman factor did not cause an increase in permeability at concentrations of up to 2 x 10(-7) M. The increased permeability induced by beta-HFa was short lasting, with about a 50% decrease in activity apparent within 6 minutes after intradermal injection. The permeability enhancement activity of beta-HFa was inhibited by pretreatment of beta-HFa with diisopropylfluorophosphate. It may be concluded that active Hageman factor in the interstitial space of guinea pigs acts as a vascular permeability factor of far greater potency than bradykinin.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cochrane C. G., Wuepper K. D. The first component of the kinin-forming system in human and rabbit plasma. Its relationship to clotting factor XII (Hageman Factor). J Exp Med. 1971 Oct 1;134(4):986–1004. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.4.986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELDER J. M., WILHELM D. L. Enzyme-like globulins from serum reproducing the vascular phenomena of inflammation. V. Activable permeability factor in human serum. Br J Exp Pathol. 1958 Aug;39(4):335–342. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujikawa K., Heimark R. L., Kurachi K., Davie E. W. Activation of bovine factor XII (Hageman factor) by plasma kallikrein. Biochemistry. 1980 Apr 1;19(7):1322–1330. doi: 10.1021/bi00548a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujikawa K., Kurachi K., Davie E. W. Characterization of bovine factor XIIa (activated Hageman factor). Biochemistry. 1977 Sep 20;16(19):4182–4188. doi: 10.1021/bi00638a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujikawa K., Walsh K. A., Davie E. W. Isolation and characterization of bovine factor XII (Hageman factor). Biochemistry. 1977 May 17;16(10):2270–2278. doi: 10.1021/bi00629a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hojima Y., Tankersley D. L., Miller-Andersson M., Pierce J. V., Pisano J. J. Enzymatic properties of human Hageman factor fragment with plasma prekallikrein and synthetic substrates. Thromb Res. 1980 May 1;18(3-4):417–430. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(80)90337-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugli T. E., Moore S. Determination of the tryptophan content of proteins by ion exchange chromatography of alkaline hydrolysates. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 10;247(9):2828–2834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston A. R., Cochrane C. G., Revak S. D. The relationship between PF-DIL and activated human Hageman factor. J Immunol. 1974 Jul;113(1):103–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAGEN L. J., LEDDY J. P., BECKER E. L. THE PRESENCE OF TWO PERMEABILITY GLOBULINS IN HUMAN SERUM. J Clin Invest. 1963 Aug;42:1353–1361. doi: 10.1172/JCI104819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan A. P., Austen K. F. A pre-albumin activator of prekallikrein. J Immunol. 1970 Oct;105(4):802–811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellermeyer R. W., Ratnoff O. D. Abolition of the permeability-enhancing properties of Hageman factor by specific antiserum. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 Sep;70(3):365–371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozono K., Yamamoto T., Kambara T. A proteaselike permeability factor in guinea pig skin: contact activation of the latent permeability factor and its nature as a prekallikrein activator. Am J Pathol. 1980 Sep;100(3):619–632. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKAY M. E., MILES A. A., SCHACHTER M., WILHELM D. L. Susceptibility of the guinea pig to pharmacological factors from its own serum. Nature. 1953 Oct 17;172(4381):714–716. doi: 10.1038/172714b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARGOLIS J. Activation of a permeability factor in plasma by contact with glass. Nature. 1958 Mar 1;181(4609):635–636. doi: 10.1038/181635a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILES A. A., WILHELM D. L. Enzyme-like globulins from serum reproducing the vascular phenomena of inflammation. I. An activable permeability factor and its inhibitor in guinea-pig serum. Br J Exp Pathol. 1955 Feb;36(1):71–81. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillin C. R., Saito H., Ratnoff O. D., Walton A. G. The secondary structure of human Hageman factor (factor XII) and its alteration by activating agents. J Clin Invest. 1974 Dec;54(6):1312–1322. doi: 10.1172/JCI107877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OUCHTERLONY O. Diffusion-in-gel methods for immunological analysis. Prog Allergy. 1958;5:1–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oishi S., Webster M. E. Vascular permeability factors (PF/Nat and PF/Dil)--their relationship to Hageman factor and the kallikrein-kinin system. Biochem Pharmacol. 1975 Mar 1;24(5):591–598. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(75)90179-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RATNOFF O. D., MILES A. A. THE INDUCTION OF PERMEABILITY-INCREASING ACTIVITY IN HUMAN PLASMA BY ACTIVATED HAGEMAN FACTOR. Br J Exp Pathol. 1964 Jun;45:328–345. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revak S. D., Cochrane C. G., Bouma B. N., Griffin J. H. Surface and fluid phase activities of two forms of activated Hageman factor produced during contact activation of plasma. J Exp Med. 1978 Mar 1;147(3):719–729. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.3.719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revak S. D., Cochrane C. G., Johnston A. R., Hugli T. E. Structural changes accompanying enzymatic activation of human Hageman factor. J Clin Invest. 1974 Sep;54(3):619–627. doi: 10.1172/JCI107799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revak S. D., Cochrane C. G. The relationship of structure and function in human Hageman factor. The association of enzymatic and binding activities with separate regions of the molecule. J Clin Invest. 1976 Apr;57(4):852–860. doi: 10.1172/JCI108361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEWART P. B., BLISS J. P. The permeability-increasing factor in diluted human plasma. Br J Exp Pathol. 1957 Aug;38(4):462–466. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi Y., Movat H. Z. Conversion of Hageman factor (factor XII) of the guinea pig to prekallikrein activator and inhibition of the formed kallikrein by a natural plasma inhibitor. Eur J Immunol. 1972 Aug;2(4):345–349. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830020409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temme H., Jahrreiss R., Habermann E., Zilliken F. Aktivierung von Gerinnungs- und Kininsystem durch eine Plasmaesterase (Hageman-Faktor) Reinigung und Wirkungsbedingungen. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1969 Apr;350(4):519–521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treloar M. P., Pyle H., Ozge-Anwar A. H., Takeuchi Y., Movat H. Z. Isolation of prekallikrein activator from guinea pig serum or plasma adsorbed to immune precipitates or celite: possible relationship to Hageman factor. Eur J Immunol. 1972 Aug;2(4):338–345. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830020408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udaka K., Takeuchi Y., Movat H. Z. Simple method for quantitation of enhanced vascular permeability. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Apr;133(4):1384–1387. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILHELM D. L., MILES A. A., MACKAY M. E. Enzyme-like globulins from serum reproducing the vascular phenomena of inflammation. II. Isolation and properties of the permeability factor and its inhibitor. Br J Exp Pathol. 1955 Feb;36(1):82–104. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILHELM D. L., MILL P. J., MILES A. A. Enzyme-like globulins from serum reproducing the vascular phenomena of inflammation. III. Further observations on the permeability factor and its inhibitor in guinea-pig serum. Br J Exp Pathol. 1957 Aug;38(4):446–461. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILHELM D. L., MILL P. J., SPARROW E. M., MACKAY M. E., MILES A. A. Enzyme-like globulins from serum reproducing the vascular phenomena of inflammation. IV. Activable permeability factor and its inhibitor in the serum of the rat and the rabbit. Br J Exp Pathol. 1958 Jun;39(3):228–250. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuepper K. D., Miller D. R., Lacombe M. J. Flaujeac trait. Deficiency of human plasma kininogen. J Clin Invest. 1975 Dec;56(6):1663–1672. doi: 10.1172/JCI108248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuepper K. D. Prekallikrein deficiency in man. J Exp Med. 1973 Dec 1;138(6):1345–1355. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.6.1345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Kambara T. A protease-like permeability factor in the guinea pig skin. 1. Partial purification and characterization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Apr 19;540(1):55–64. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90434-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Kozono K., Kambara T. A protease-like permeability factor in the guinea pig skin. 2. In vitro activation of the latent form permeability factor by weakly acidic phosphate buffer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Aug 17;542(2):222–231. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Kozono K., Okamoto T., Kato H., Kambara T. Purification of guinea-pig plasma prekallikrein. Activation by prekallikrein activator derived from guinea-pig skin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Aug 7;614(2):511–525. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(80)90240-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]