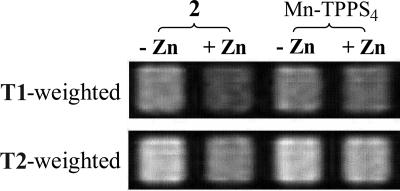
Fig. 6.
Zn2+-induced relaxation rate change in buffered solution as measured by MRI. Solutions of 2 or Mn-TPPS4 in 25 mM Pipes buffer at pH 7.0 were arrayed in microtiter plates. A spin echo pulse sequence was used to acquire an MRI image. From left to right: 2 without zinc, 2 with 1 mM Zn2+, Mn-TPPS4 without zinc, and Mn-TPPS4 with 1 mM Zn2+. (Upper) T1-weighted image (TR = 175 ms; TE = 10 ms), 200 μM CAs. (Lower) T2-weighted image (TR = 2,000 ms; TE = 240 ms), 500 μM CAs with 100 mM KCl. The solutions containing 2 show that the presence of zinc lowers the MR signal intensity in both the T1- and T2-weighted images. These results indicate a decrease in the T1 relaxation rate and an increase in the T2 relaxation rate, respectively, under the described conditions. By comparison, the MR signal for Mn-TPPS4 is relatively zinc-independent.