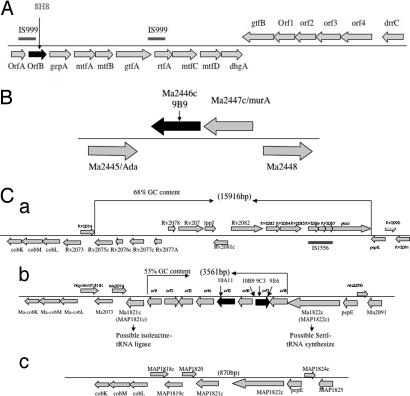
Fig. 1.
Chromosome regions. (A) Organization of the chromosome region inactivated in the 8H8 clone of M. avium involved in the glycosylation of the lipopeptide core. (B) Organization of the chromosome region inactivated in the M. avium 9B9 clone. The M. avium gene names correspond to MAP numbers from M. avium subsp. paratuberculosis genome sequence. (C) Genetic organization of M. avium 104 PI associated with low invasion of macrophages and virulence in mice. The M. avium 104 (b) sequence and gene organization of this region is presented in the comparison with M. tuberculosis H37Rv (a) and M. avium subsp. paratuberculosis (c) similar loci. Numbers in parentheses indicate the approximate size of the different regions in above-mentioned mycobacterial species. The gene name or corresponding Rv or MAP numbers from M. tuberculosis H37Rv and M. avium subsp. paratuberculosis genome sequence is shown above the construct. Unknown M. avium genes are presented as ORFs 1–8. The arrows on the genes indicates the location of disrupted genes by the insertion of Tn5367 transposon.