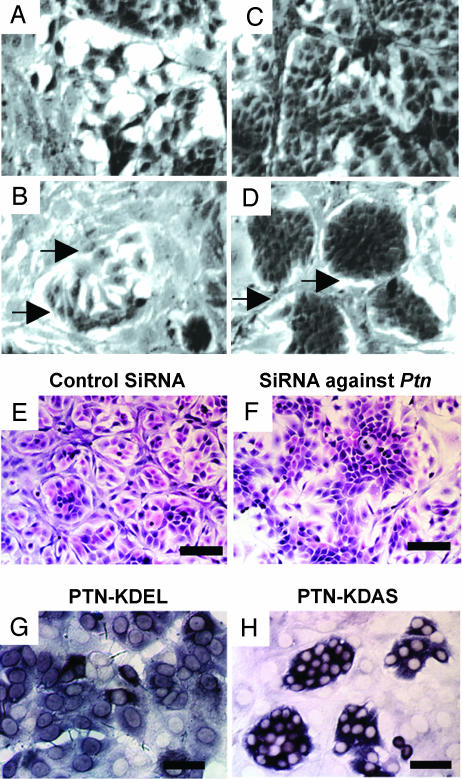
Fig. 3.
MCF-7 cells stably transfected with Ptn (MCF-7-Ptn) cells form epithelial islands in coculture with NIH 3T3 cells that depend on Ptn expression and PTN secretion. Representative images are shown. (A and B) Epithelial island formation. Cocultures of equal numbers of MCF-7-mock cells (A) or MCF-7-Ptn cells (B) with NIH 3T3 cells in logarithmic phase observed by using phase-contrast microscopy. (C and D) Cocultures of equal numbers of MCF-7-mock (C) or MCF-7-Ptn cells (D) with NIH 3T3 cells at confluence. Arrows point to acellular areas surrounding epithelial islands. Phase-contrast microscopy. (Scale bar: 100 μm.) (E and F) Loss of epithelial island formation by knockdown of Ptn expression. siRNA reduces epithelial island formation in cocultures of MCF-7-Ptn with NIH 3T3 cells (F), but MCF-7-Ptn cells with a control (scrambled) siRNA formed clearly defined epithelial islands (E). H&E-stained slides. (Scale bar: 200 μm.) (G and H) Anti-human Ptn in situ hybridization of MCF-7-Ptn-KDEL and MCF-7-Ptn-KDAS cells in coculture with NIH 3T3 cells. (H and G) Epithelial islands form when MCF-7-Ptn-KDAS (H) but not MCF-7-Ptn-KDEL (G) cells are cocultured with NIH 3T3 cells. (Scale bar: 100 μm.)