FIGURE 2.
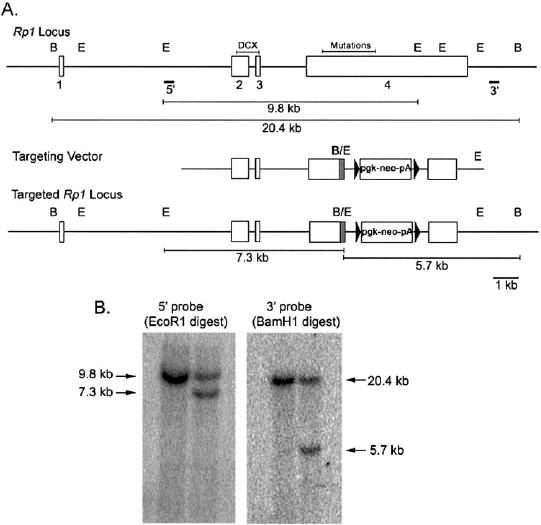
Targeted disruption of the Rp1gene in mice. (A)Maps of the wild-type Rp1locus, the targeting vector, and the targeted Rp1locus are shown. The exons of the Rp1gene are shown as open boxes. The DCX domain encoded by exons 2 and 3 is indicated, as is the region that contains all pathologic mutations at the beginning of exon 4. The map of the targeting vector shows the portion of exon 4 after Arg662 of the mouse Rp1coding sequence that is replaced with a neomycin resistance gene cassette (pgk-Neo-pA). A 10-amino-acid myctag coding sequence (shaded area)was placed at the C-terminal end of the truncated Rp1gene. The 5′ and 3′ probes used for Southern blot analyses are shown. The locations of EcoRI (E) and BamHI (B) are indicated, as are the expected sizes of the restriction fragments for the wild-type and targeted loci. (B)Southern blot analysis of EcoRI and BamHI digested genomic DNA isolated from control (left)and targeted (right)ES cells. The 7.3-kb band detected with the 5′ probe, and the 5.7-kb band detected with the 3′ probe confirm correct recombination at the Rp1locus.
