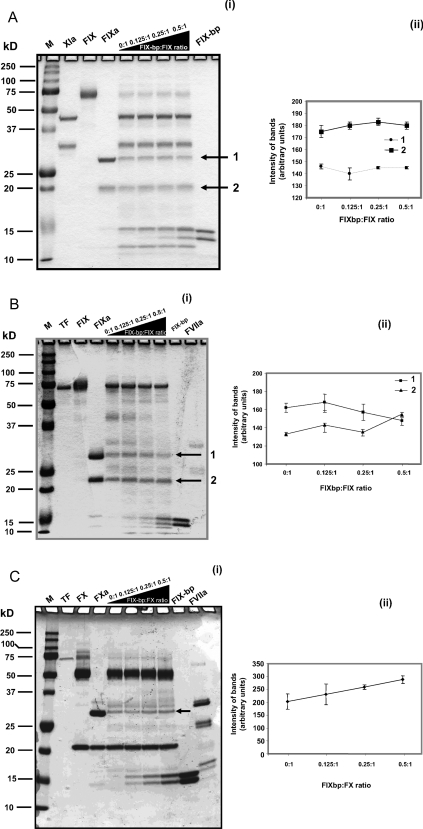
Figure 2. In vitro intrinsic and extrinsic cleavage assays.
(a) In vitro intrinsic cleavage assay. (i) The intrinsic cleavage (conversion of Factor IX into IXa by Factor XIa) reaction was carried out in binding buffer (50 mM Hepes, 1 mM MgCl2 and 5 mM CaCl2) with 4.4 μM of Factor IX mixed with 620 nM of Factor XIa, at ambient temperature for 30 min. Similar reactions were also carried out in the presence of the IX-bp (550, 1100 and 2200 nM). For identification, each protein was loaded as a marker. Cleavage products are indicated by arrows. (ii) The intensities of cleavage products 1 and 2 were quantified using the ImageJ software. The average from two experiments is indicated with error bars. (b) In vitro extrinsic cleavage assay. (i) The extrinsic cleavage assay (conversion of Factor IX into IXa by lipidated tissue vactor and Factor VIIa) was carried out in binding buffer, 4.4 μM of Factor IX mixed with 500 pM of tissue factor and 800 nM of Factor VIIa, at ambient temperature for 24 h. Similar reactions were also carried out in the presence of IX-bp (550, 1100 and 2200 nM). For identification, each protein was loaded as a marker. Cleavage products are indicated by arrows. (ii) The intensities of cleavage products 1 and 2 were quantified using the ImageJ software. The average from two experiments is indicated with error bars. (c) In vitro extrinsic cleavage assay. (i) Similar to Figure 2(b), but conversion of Factor X into Xa is assayed. In this case, one cleavage product (indicated by an arrow) was quantified. (ii) The intensity of the cleaved product was quantified using the ImageJ software. The average from two experiments is indicated with error bars. FIX-bp, IX-bp.