Fig. 6.
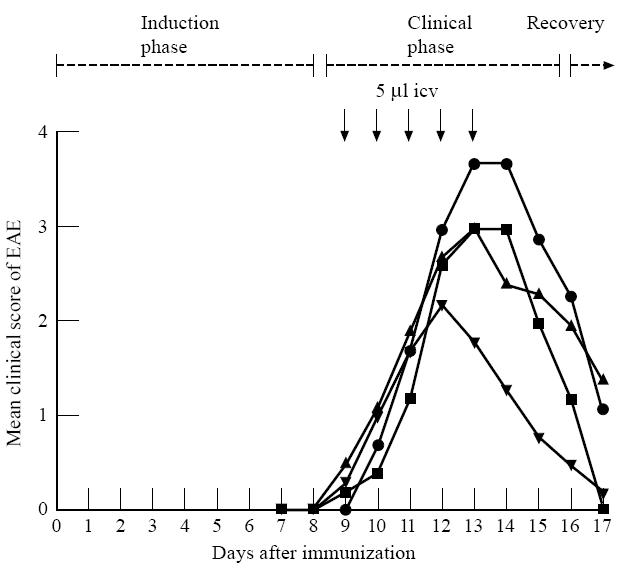
Effects of repeated intracerebroventricular (icv) injections of annexin-1 (1–188) or anti-annexin-1 MoAbs on EAE (experiment 3). EAE was induced by subcutaneous injection of myelin basic protein (MBP). Non-cannulated controls (•): rats that did not receive an icv cannula and that were not treated after induction of EAE (n = 7). Other groups of rats received icv cannulas and were treated once daily icv with annexin-1 (1–188) (2.15 μg in 5 μl in 2.5 min, n = 6; ▾), a MoAb against annexin-1 (5 μg in 5 μl in 2.5 min, n = 5; ▪) or saline (vehicle controls, 5 μl in 2.5 min, n = 7; ▴), at 9–13 days after induction of EAE. Note that the neurological symptoms of EAE were most severe in intact non-cannulated rats.
