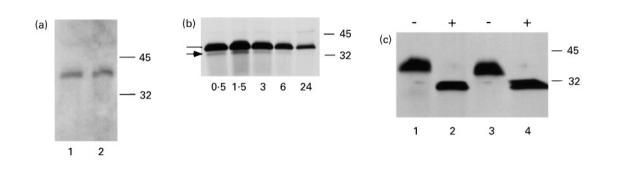
Fig. 3.
Characterization of rPR3 secreted into the media supernatants of stably transfected 293 cells. (a) Immunoblot of proteins contained in media supernatants of 293 cells expressing rPR3-S176A (lane 1) and δ-rPR3-S176A (lane 2) separated by SDS–PAGE (12% gel, non-reducing conditions). Detection of the rPR3 variants with the PR3-specific MoAb MCPR3-2 reveals an electrophoretic mobility consistent with a molecular mass of about 38 kD. (b) 293 cells expressing rPR3-S176A were pulse-labelled with 35S-methionine/35S-cysteine and subsequently incubated with normal growth medium for the time periods (hours of chase) indicated at the bottom of the panel. Labelled proteins secreted into the media supernatants were immunoprecipitated with the rabbit anti-PR3 serum and separated by SDS–PAGE (12% gel) under reducing conditions. The bulk of the newly synthesized rPR3 was secreted into the media within 90 min. The majority of the immunoprecipitated material has an apparent molecular mass of 34–36 kD (line). The minor immunoprecipitated 32-kD band (arrow) was also an N-terminally unprocessed rPR3-S176A isoform (confirmed by radiosequencing). (c) Media supernatants from metabolically labelled HMC-1/PR3-S176A cells and from 293 cells expressing rPR3-S176A were immunoprecipitated with the rabbit anti-PR3 serum and divided into two equal aliquots each, which were incubated with (+) or without (–) N-glycosidase F under identical conditions followed by SDS–PAGE (12% gel, reducing conditions) and autoradiography. N-glycosidase F digestion resulted in removal of all N-linked sugar moeities and a drop of the molecular mass to 29 kD. Comparison of rPR3-S176A expressed in HMC-1 cells (lanes 1 and 2) to that expressed in 293 cells (lanes 3 and 4) indicates that the glycosylation of the rPR3 secreted into the media supernatants of these two cell types is similar.