Fig. 3.
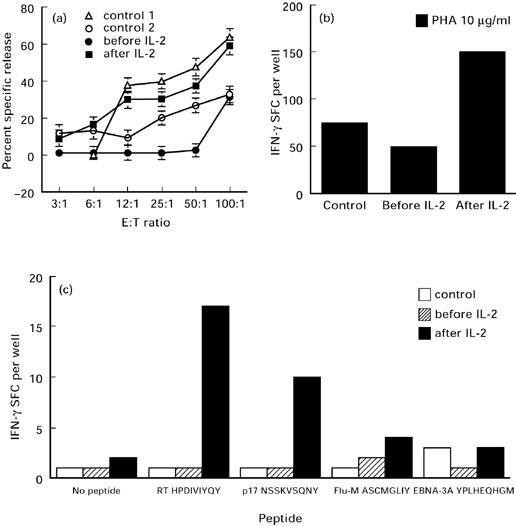
IL-2 increases natural killer (NK) activity and induces non-specific and HIV-1 peptide-specific IFN-γ-secreting cells. (a) Measurement of the NK-mediated cytotoxicity by patient's NK cells before (•) and after (▪) IL-2 immunotherapy, and by uninfected controls (open symbols); s.d. of the mean for each effector cell dilution was < 5%. (b) ELISPOT assay measuring IFN-γ release in response to phytohaemagglutinin (PHA) by peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) obtained before and after IL-2 immunotherapy. The data represent average values at each point and variation among duplicates was < 10%. (c) ELISPOT assays measuring IFN-γ release in response to HLA-B35-restricted peptides. Patient cells obtained before and after IL-2 immunotherapy, and HLA-B35 uninfected donor cells were stimulated with or without HLA-B35-restricted peptides: (i) HIV-RT: HPDIVIYQY; (ii) HIV-p17: NSSKVSQNY; (iii) Flu-M: ASCMGLIY; (iv) EBV-EBNA3A: YPLHEQHGM. Patient 3 HLA phenotype: A1/24, B35/61, Bw6 C4/1202 DR4/7 DRB4-53 DQB0601; uninfected donor HLA phenotype: A11/33 B7/35 Bw6 C4/1202 DR1/1303 DRB3-52 DRB4-53 DQ5/7.
