Fig. 4.
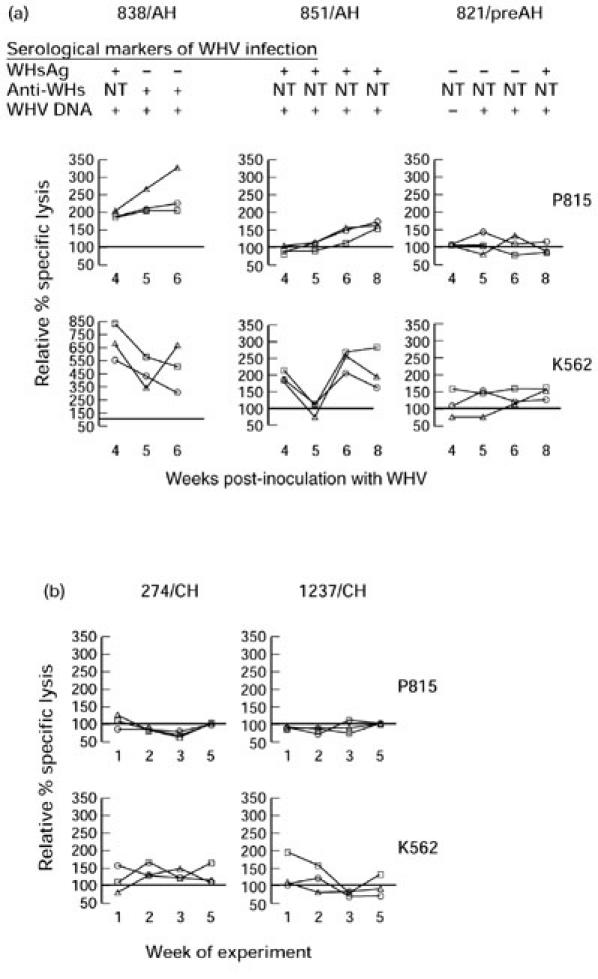
Profiles of peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC)-induced cytotoxicity toward P815 or K562 target cells determined in individual woodchucks during newly acquired and advanced chronic woodchuck hepatitis virus (WHV) infections. Sequential PBMC samples collected from three woodchucks between weeks 4 and 8 after WHV inoculation (a) and serial PBMC samples from two WHV surface antigen (WHsAg)+ animals with chronic WHV hepatitis (b) were tested in parallel at given time points for cytotoxicity against Fas-positive P815 or Fas-negative K562 cells at E:T ratios of 50:1 (○), 25:1 (□) and 12.5:1 (Δ). Points represent the means of duplicate evaluations and are shown as a percentage of the cytotoxicity exhibited by PBMC from healthy animals against a given cell target and tested in the same assay. The results on serum WHsAg and anti-WHs reactivities and WHV DNA detection are presented for animals with newly acquired WHV infection in (a). All animals chronically infected with WHV (b) were WHsAg- and WHV DNA-positive at all time points tested.
