Table 1.
Details on woodchuck hepatitis virus (WHV) infection in 20 adult woodchucks at the time of acquisition of circulating lymphoid cells analysed in the cytotoxicity assays
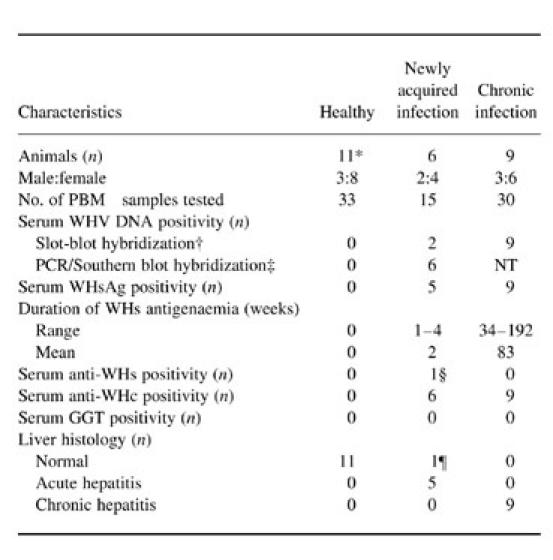
*Includes six animals that were subsequently inoculated with WHV and developed preacute or acute WHV infection.
†Approximate sensitivity 106–107 WHV genome copies/ml.
‡Amplified by nested polymerase chain reaction (PCR) with WHV core gene-specific primers and detected by Southern blot hybridization; approximate sensitivity 10–102 WHV genome copies/ml.
§One animal became anti-WHV surface (WHs)-reactive 5 weeks after inoculation with WHV following a 3-week period of WHsAg positivity (see Fig. 4a; 838/AH animal).
¶After WHV inoculation, one animal remained WHsAg non-reactive and had normal liver histology at the time of cytotoxicity assay despite the presence of WHV DNA and anti-WHV core (WHc) in the serum (see Fig. 4a; 821/preAH animal).
NT, Not tested.
