Fig. 1.
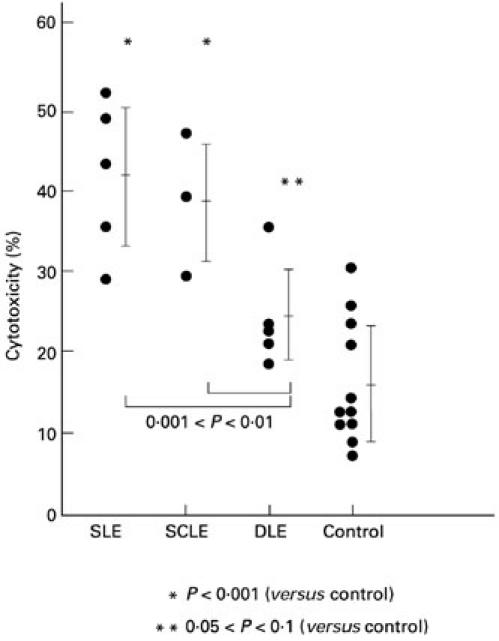
Autologous combinations of targets and serum from lupus patients but not normal controls enhance antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) of irradiated keratinocytes. In this assay ADCC (cytotoxicity percentage) was measured using an acridine orange/ethidium bromide assay in 24 h cytotoxicity experiments. Each circle represents an individual data point, and the lines and brackets indicate the mean ± s.d. Each data point is an ADCC experiment containing autologous cultured keratinocytes (T) and sera (A) from one subject plus a standard homologous mononuclear effector (E). The keratinocytes and sera were from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus (SCLE), or discoid lupus erythematosus (DLE) or from normal controls. The keratinocytes were irradiated with 100 mJ/cm2 of UVB light 24 h before addition of sera and effectors. The percentage cytotoxicity was determined by the following formula comparing different combinations of T, A and E. ADCC of irradiated targets = (TUVRAE − TUVRE) − (TAE − TE), where TUVR are targets irradiated with UVB 24 h before the experiment was performed, and T are keratinocytes which were sham-irradiated. Irradiated targets incubated with anti-SS-A/Ro antibody did show some cytotoxicity without added mononuclear effectors, but it represented only a fraction of the cytotoxicity observed with antibody plus effectors (data not shown). Statistical significance of different comparisons is indicated by P values.
