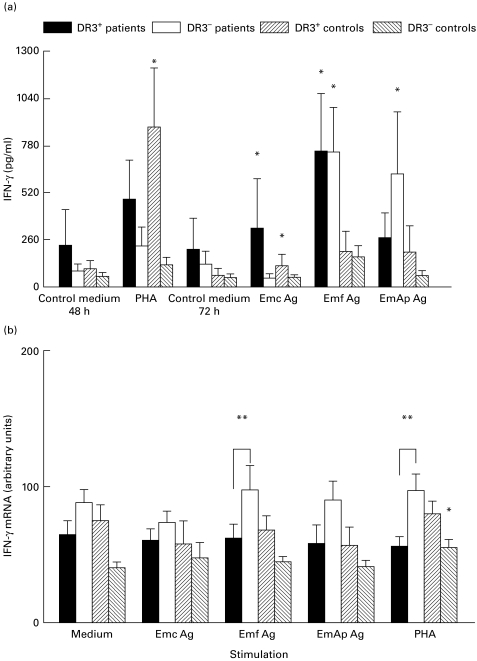
Fig. 3.
Secretion of IFN-γ (a) and IFN-γ mRNA expression (b) in peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) cultures. IFN-γ protein and mRNA levels were assessed in PBMC cultures from alveolar echinococcosis (AE) patients and healthy subjects with or without the HLA-DR3, DQ2, B8 haplotype, after cell stimulation with phytohaemagglutinin (PHA) or Echinococcus multilocularis antigens. Cultures without any stimulation served as controls. Cytokine secretion was measured using an ELISA assay. Values are means ± s.e.m. IFN-γ mRNA expression was semiquantified by densitometric analysis after polymerase chain reaction amplification of cDNA with specific primer pairs. Results are expressed as arbitrary units as described in PATIENTS and METHODS. *P < 0·05: statistically significant difference for cytokine protein or cytokine mRNA level between non-stimulated and stimulated cells in each group (Wilcoxon signed-rank test); **P < 0·05: statistically significant difference for cytokine protein or mRNA level between cell cultures from DR3+ and DR3− AE patients (Mann–Whitney U-test). Control medium, no stimulation; Emc Ag, stimulation with the crude extract antigen of E. multilocularis; Emf Ag, stimulation with the vesicular fluid purified antigen; EmAp Ag, stimulation with the alkaline phosphatase of E. multilocularis; PHA, stimulation with the non-specific mitogen, phytohaemagglutinin.