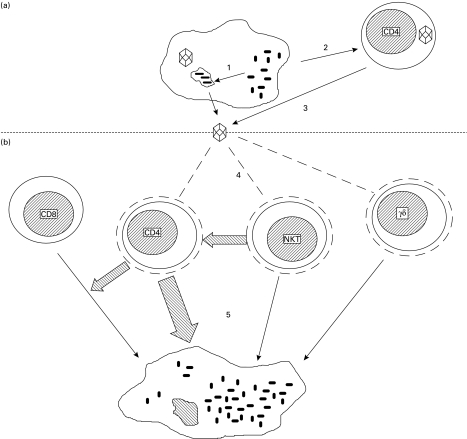
Fig. 1.
Reciprocal enhancement of replication in HIV and Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) co-infection. (a) MTB infection increases HIV production from co-infected macrophages (1) and activates and causes proliferation of CD4+ T cells (2), which creates more optimal conditions for HIV production from infected lymphocytes (3). (b) HIV reduces circulating CD4+, γδ and natural killer (NK) T cells through a variety of mechanisms (4), which normally kill MTB-infected macrophages (5).