Fig. 1. Grk expression in cuff mutant egg chambers.
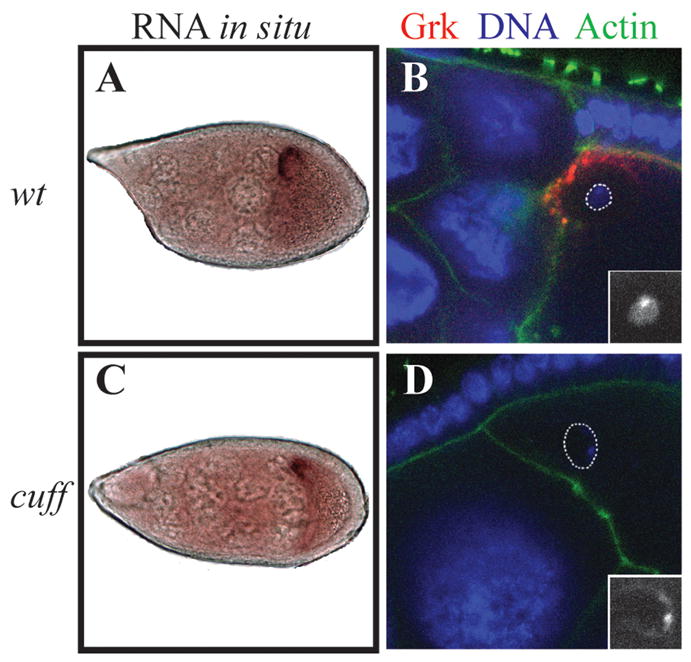
grk RNA in situ hybridization (A, C) and Grk antibody staining (B, D).
(A, B) Cuff heterozygous females were used as wild type control: In Stage 9 wild type egg chambers, grk transcripts form a tight cap around the oocyte nucleus at the dorsal cortex (A). Grk protein is translated from the localized mRNA, and is also restricted to the dorsal anterior region of the oocyte (B). At this stage of oogenesis, the chromatin of the oocyte nucleus forms a compact, round structure termed the karyosome (B inset).
(C, D) cuff WM25/KG05951. In Stage 9 cuff mutant egg chambers, grk transcript localization appears mostly normal (C), however, in 10–40% of the egg chambers, Grk protein is undetectable (D). Some 10–20% of the oocyte nuclei at this stage also assume a defective morphology. Often, the DNA seems to localize to the periphery of the nucleus (D inset). In B and D, the oocyte nucleus is marked by dotted lines.
