Figure 3.
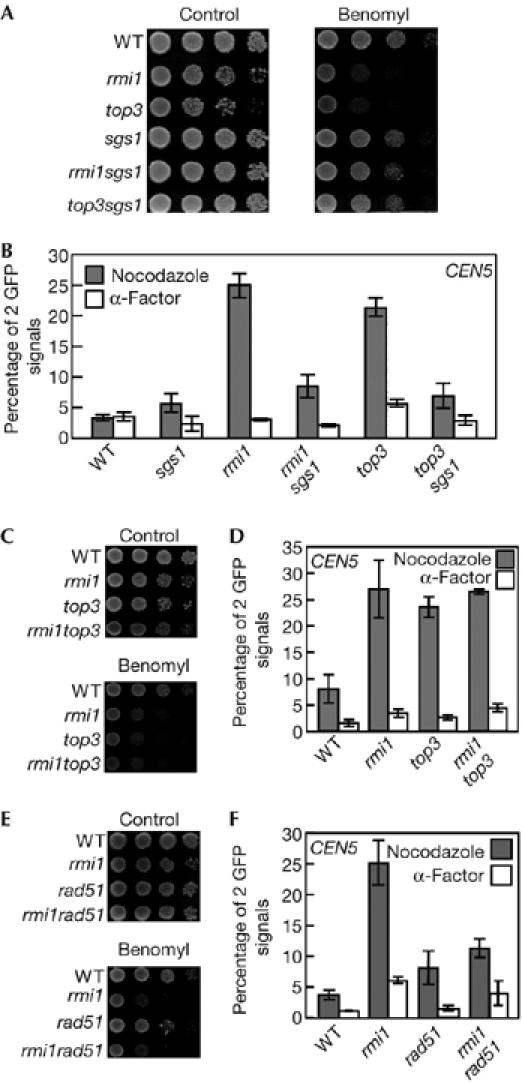
Deletion of SGS1 or RAD51 suppresses cohesion defects in rmi1 and top3 cells. (A,C,E) Serial tenfold dilutions of log phase cultures of (A) wild-type (YPH1477), rmi1 (YPH1477r1), top3 (YPH1477t3), sgs1 (YPH1477s1), rmi1sgs1 (YPH1477r1s1) and top3sgs1 (YPH1477t3s1) cells, (C) of wild-type (YPH1477), rmi1 (YPH1477r1), top3 (YPH1477t3) and rmi1top3 (YPH1477r1t3) cells, and (E) of wild-type (YPH1477), rmi1 (YPH1477r1), rad51 (YPH1477r51) and rmi1rad51 (YPH1477r1r51) cells were spotted onto growth plates containing 0, 20 (A,E) or 22 μg/ml (C) benomyl, incubated at 30°C for 3 days and then photographed. (B,D,F) The same combination of cells in (A), (C) and (E) were used. Cells were arrested in M-phase with nocodazole or in G1 phase with α-factor and then fixed with paraformaldehyde. One hundred cells of each strain were scored for number of cells with two green fluorescent protein (GFP) signal foci. The data shown represent the average of three experiments. Bars indicate standard deviation. WT, wild type.
