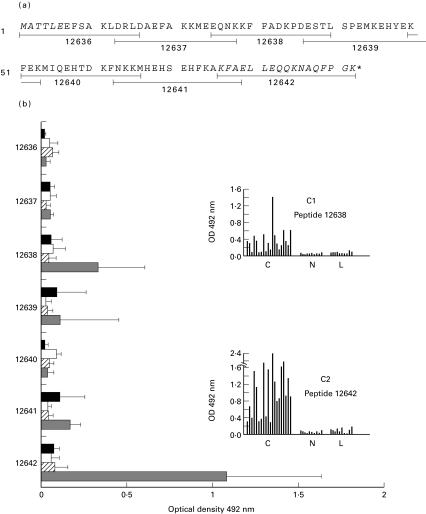
Fig. 3.
Reactivity of sera from Chagas' disease, leishmaniasis, tuberculosis and malaria patients against the synthetic peptides, 16-mer long overlapped by four residues, covering the entire T. cruzi KMP11 protein. (a) Amino acid sequence of the T. cruzi KMP11 protein. The amino acids absent in the amino (KMP11-at) and carboxyl-terminal (KMP11-ct) truncated KMP11 proteins are indicated in italic. The synthetic peptide sequences are underlined and indicated by consecutive numbers (12636–12642). (b) The horizontal bars represent the absorbance values of the 5 sera from chagasic ( ), VL (
), VL ( ), tuberculosis (▪) and malaria (□) patients, respectively, minus the mean absorbance of 5 healthy donors sera (OD492nm = 0·061) plus three standard deviations (SD = 0·008) for each peptide and sera group. (C1 and C2) Histograms with the values of the reactivities of 20 sera from Chagas' disease patients, 10 sera with visceral leishmaniasis and 10 healthy donors sera used as control, against the synthetic peptides 12638 and 12642 which correspond, respectively, to the central and carboxyl-terminal regions of the T. cruzi KMP11 protein. The sera were assayed at 1 : 200 dilution. None of the used sera recognized the KLH protein.
), tuberculosis (▪) and malaria (□) patients, respectively, minus the mean absorbance of 5 healthy donors sera (OD492nm = 0·061) plus three standard deviations (SD = 0·008) for each peptide and sera group. (C1 and C2) Histograms with the values of the reactivities of 20 sera from Chagas' disease patients, 10 sera with visceral leishmaniasis and 10 healthy donors sera used as control, against the synthetic peptides 12638 and 12642 which correspond, respectively, to the central and carboxyl-terminal regions of the T. cruzi KMP11 protein. The sera were assayed at 1 : 200 dilution. None of the used sera recognized the KLH protein.