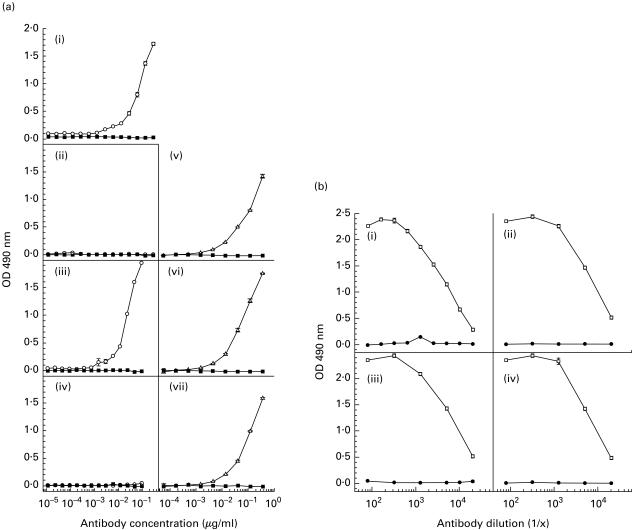
Fig. 3. (a).
ELISA titrations showing the reactivity of purified MoAb 3B9 (○) and isotype control MUI-1 MoAb (▪) to βA4[35–43] peptide (i), βA4[1–40] (ii), βA4[1–42] (iii) and βA4[1–43] (iv). In these experiments the WO2 MoAb was used as a positive control for peptide binding [21]. (v,vi,vii) Reactivity of MoAb WO2 (Δ) and the isotype control MUI-1 MoAb (▪) to βA4[1–40], βA4[1–42] and βA4[1–43], respectively. (b) ELISA titrations showing the reactivity of polyclonal mouse anti-βA4[34–40] antiserum (○) and preimmune serum (•) to βA4[34–40] peptide (i), βA4[1–40] (ii), βA4[1–42] (iii) and βA4[1–43] (iv).