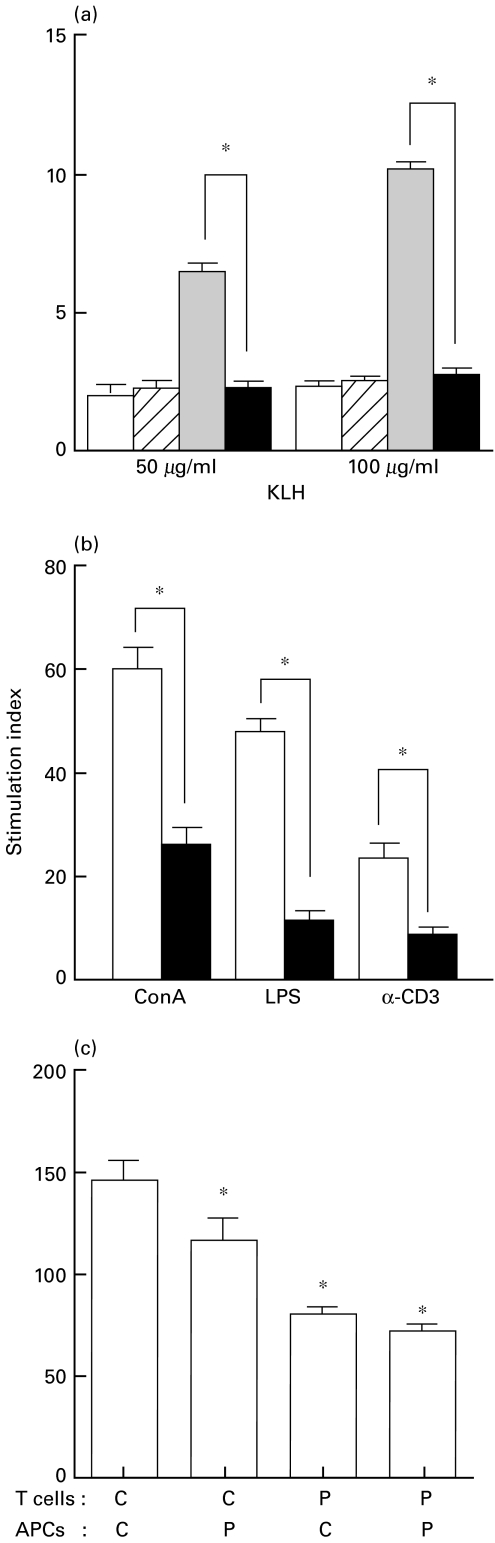
Fig. 2.
Effect of phenytoin treatment on splenocyte proliferative response. a, KLH-specific proliferative response of splenocytes from phenytoin-treated mice. Splenocytes (2 × 105) were cultured with 50 or 100 µg/ml KLH for 3 days. Control mice (n = 5, □), phenytoin-treated mice (n = 5, □/), control mice with KLH-immunization (n = 5,  ), phenytoin-treated mice with KLH-immunization (n = 5, ▪). b, Effect of phenytoin treatment on splenocyte proliferative response to mitogens. Splenocytes from control (□) or phenytoin-treated (▪) mice were cultured with ConA, LPS or anti-CD3 antibody for 3 days and their response was evaluated by [3H]-thymidine incorporation. c, Effect of phenytoin treatment on accessory cell funciton. Purified T cells (2 × 105) and spleen adherent cells (5 × 104) from control (C) (n = 3) and phenytoin-treated mice (P) (n = 3) were cultured with ConA for 3 days. The cells were labelled with 0·5 µCi [3H]-thymidine for the last 18 h, harvested and [3H]-thymidine incorporated by splenocytes was counted. Results are expressed as mean ± SE of stimulation index. *significantly decreased from the control group.
), phenytoin-treated mice with KLH-immunization (n = 5, ▪). b, Effect of phenytoin treatment on splenocyte proliferative response to mitogens. Splenocytes from control (□) or phenytoin-treated (▪) mice were cultured with ConA, LPS or anti-CD3 antibody for 3 days and their response was evaluated by [3H]-thymidine incorporation. c, Effect of phenytoin treatment on accessory cell funciton. Purified T cells (2 × 105) and spleen adherent cells (5 × 104) from control (C) (n = 3) and phenytoin-treated mice (P) (n = 3) were cultured with ConA for 3 days. The cells were labelled with 0·5 µCi [3H]-thymidine for the last 18 h, harvested and [3H]-thymidine incorporated by splenocytes was counted. Results are expressed as mean ± SE of stimulation index. *significantly decreased from the control group.