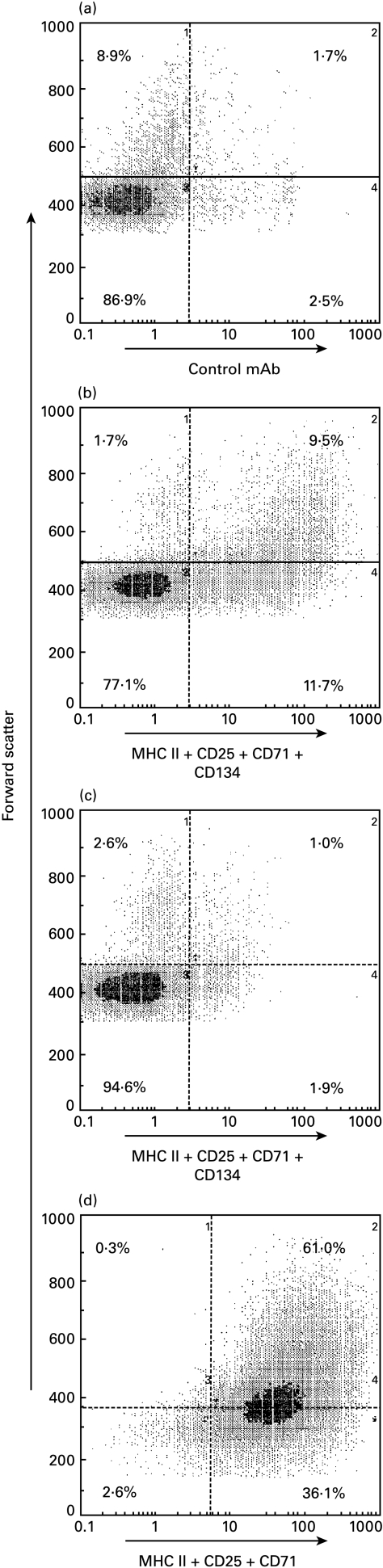
Fig. 3.
The surface antigen phenotype of purified thoracic duct (TD) CD4+ T cells and of the same cells after a secondary depletion of cells expressing the activation markers MHCII, CD25, CD71 and CD134 using immunomagnetic beads and a cocktail of the MoAbs against these markers. The cells were analysed by flow cytometry and the fluorescent intensity is shown plotted against forward light scatter, an index of cell size. TD lymphocytes pooled from four arthritic donor rats were depleted of B cells and CD8+ cells (see Materials and methods). The purified CD4+ T cells were stained with (a) negative control MoAb 1B5 or (b) a mixture of MoAbs against MHC II, CD25, CD71 and CD134. (c) Cells remaining after depletion of those cells expressing the above activation markers (see Materials and methods). The remaining cells were re-stained with the mixture of depleting antibodies. (D). Flow cytometric analysis of CD4+ T cells selected positively on the basis of their activated phenotype. CD4+ T cells were prepared by negative selection (see Materials and methods) from TD lymphocytes pooled from four arthritic donor rats. They were then stained with a mixture of MoAbs against MHCII, CD25 and CD71. After positive selection of the labelled cells using a Dynal rabbit antimouse IgG1 CELLection kit (see Materials and methods), they were re-stained with the same mixture of MoAbs.