Fig. 1.
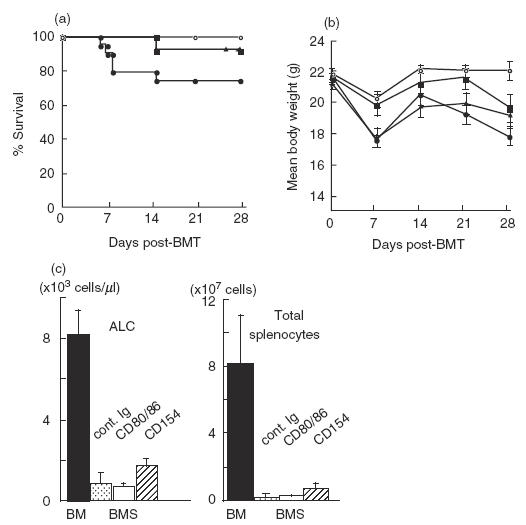
Effects of treatment with either anti-CD154 or anti-CD80/86 MoAbs in a complete allogeneic GVHD model. Each group of sublethally (6·5Gy) irradiated BALB/c mice received 2·0 × 106 splenocytes and 2·5 × 107 TCD-BM cells from wild-type B6 mice, and treated with either control reagents (BMS, •) anti-CD80/86 (RM80/PO3) MoAbs (BMS CD80/86, ▪), or anti-CD154 (MR1) MoAb (BMS CD154, ▴). One group of mice received TCD-BM cells alone (BM, ○). Each group consists of 8–19 mice. Survival rates (a) and mean body weight (b) are plotted. Data shown are representative of three experiments. BM versus BMS, P = 0·013, BMS CD80/86 versus BMS, P = 0·043, BMS CD154 versus BMS, P = 0·043. (c) Peripheral blood cells and splenocytes were analysed at day 28 post-BMT. ALC; absolute lymphocyte count. Splenocytes were stained with FITC-anti-CD4, PE-anti-CD8 and PerCP-anti-CD3 MoAbs. CD3+, CD3+4+ and CD3+8+ cells were counted as donor T, CD4+ T, CD8+ T cells, respectively. More than 99% of splenocytes were H-2d− donor-derived cells in all groups. Data represent the mean ± s.d. from five mice in each group. *Statistically different (P < 0·05).
