Fig. 4.
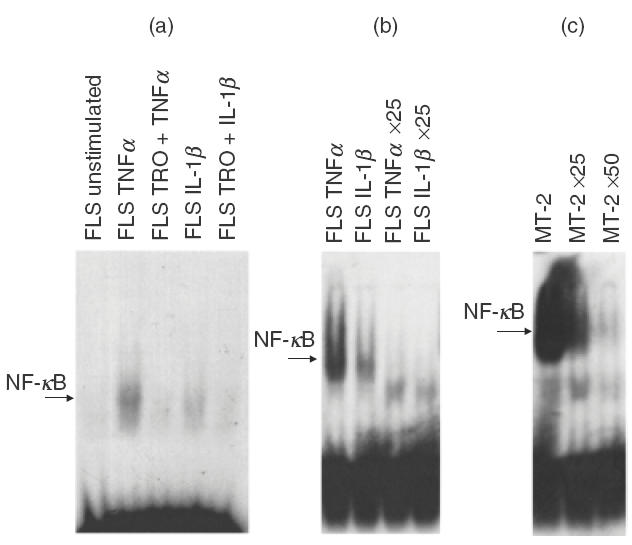
Troglitazone inhibits NF-κB nuclear activity in FLS. FLS were cultured with or without 10 μm troglitazone for 24 h, and further incubated in the presence or absence of TNF-α (200 IU/ml) or IL-1β (20 IU/ml) for 30 min. After incubation, nuclear NF-κB DNA binding activity in FLS was investigated by EMSA. (a) Representative experiment using FLS isolated from RA patients. Note the lack of basal NF-κB nuclear activity in FLS; however, NF-κB activity was induced in FLS cells treated with TNF-α and IL-1β. The latter response was abrogated by pretreatment of troglitazone (10 μm). TRO: pretreated with 10 μm of troglitazone for 24 h. Results shown are representative data of six experiments. (b) Inhibition of NF-κB nuclear activity in TNF-α- and IL-1β-treated FLS by adding excess cold oligonucleotide. ×25 : Addition of 25 times the high molar concentration of cold oligonucleotide. Results shown are representative data of three experiments. (c) Positive control for NF-κB nuclear activity determined in MT-2 cells. Note the detection of NF-κB nuclear activity in MT-2 cells, which was clearly inhibited by adding excess cold oligonucleotide (×25 : addition of 25 times the high molar concentration of cold oligonucleotide; ×50 : addition of 50 times the high molar concentration of cold oligonucleotide).
