Fig. 2.
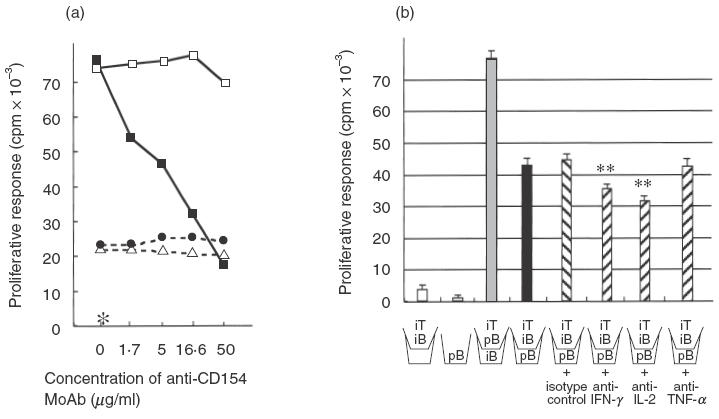
B cell proliferative responses to autoreactive Th1 lines. (a) Anti-CD154 MoAb (MR1) dramatically inhibited B cell proliferation induced by the CD154-intact line (5-1), but not that by the CD154-deficient line (G1 or P5). (b) A membrane insert (\_/) was used to prevent contact by T cell line (P5) with B cells. Irradiated (1500 rad) T cells, which do not proliferate themselves, enhanced purified B cell proliferation. Irradiated (3000 rad) B cells are thought to promote cytokine production from the T cell line as an APC. CD154-deficient lines induce B cell proliferation both in a contact-dependent and -independent manner; however, contact-independent B cell proliferation (black bar) was not inhibited at all by anti-TNF-α MoAb, but was inhibited by anti-IFN-γ or IL-2 MoAb (hatched bar). Concentration of MoAb or isotype control: 25 µg/ml. This figure shows the representative results of three experiments. iT; irradiated T cells (P5), pB; purified B cells, iB; irradiated B cells. **P <0·01 (versus isotype control). (a) □, 5-1 (with hamster IgG); •, G1; ▵, P5; ▪, 5-1; *B cells alone.
