Fig. 3.
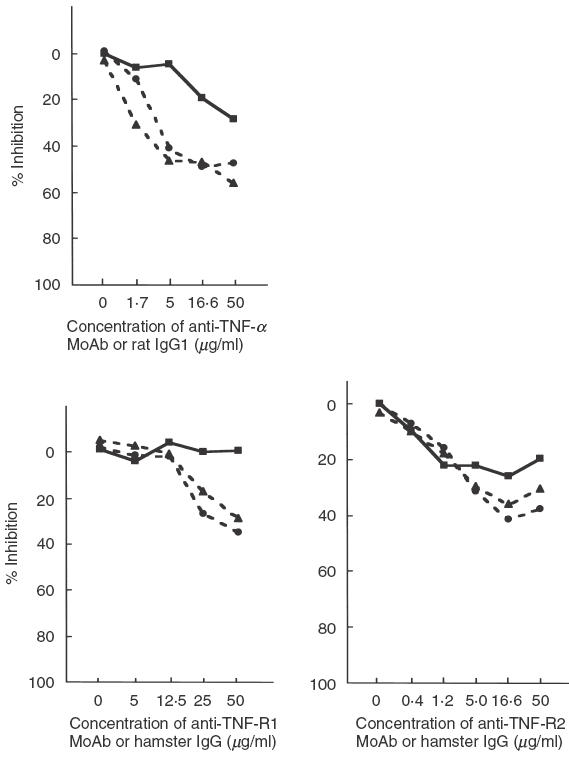
Inhibition by anti-TNF-α/TNF-R MoAb of B cell proliferative responses to CD154-intact (5-1) or -deficient (G1 and P5) Th1 cell lines. Anti-TNF-α MoAb and anti-TNF-R2 MoAb partially inhibit B cell proliferative responses, and are therefore thought to be mediated via contact-dependent T cell help. Anti-TNF-R1 MoAb also seems to block proliferation by G1 and P5, although a high concentration (>25 µg/ml) was required. Rat IgG1 and hamster IgG constitute isotype controls of anti-TNF-α and anti-TNF-R1 or R2 MoAb, respectively. % Inhibition = (1-{[3H]-thymidine uptake with blocking MoAb (cpm)/[3H]-thymidine uptake with isotype control(cpm)}) × 100. Mean cpm of triplicate cultures was used for calculations; s.d. for each experiment was less than 10%. ▪, 5-1; •, G1; ▴, P5.
