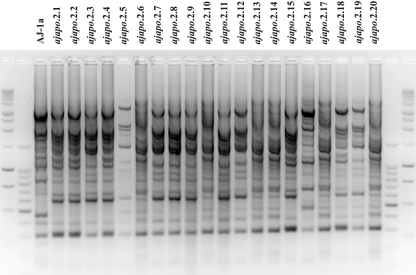
FIG. 2.
rep-PCR genomic profiling of strains from A. japonicum specimen Ajapo.2. Three distinct strain types were identified: (i) strains ajapo.2.1 to ajapo.2.5, ajapo.2.7 to ajapo.2.9, ajapo.2.11, ajapo.2.12, ajapo.2.15, ajapo.2.18, and ajapo.2.19 (strains ajapo.2.1 and ajapo.2.19 [identified as P. mandapamensis] represent the minor genetic variation among these 13 strains); (ii) ajapo.2.6, ajapo.2.10, ajapo.2.13, ajapo.2.14, ajapo.2.17, ajapo.2.20 (with identical rep-PCR profiles, represented by ajapo.2.6 [P. mandapamensis]); and (iii) ajapo.2.16 (P. leiognathi). Included for comparison is strain AJ-1a from the study of Fukasawa et al. (14), identified here as P. mandapamensis. Flanking unlabeled lanes are 1-kb and 100-bp DNA size standard ladders.