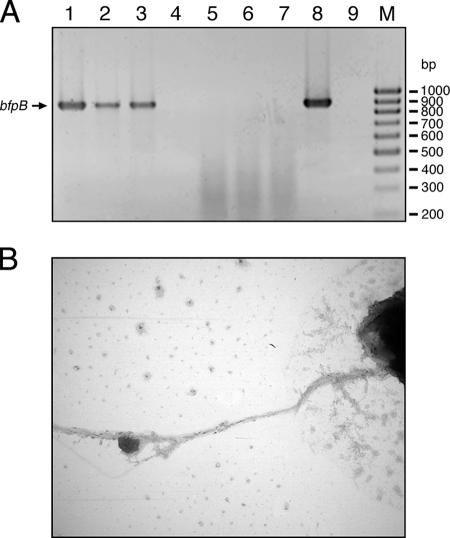
FIG. 5.
Verification of BFP pheno- and genotypes of intermediate pathogens. BFP expression was confirmed by detection of bfpB cDNA by RT-PCR (A) and by electron microscopy analysis (B). Whole RNAs of strains 265-1 (LEE negative, EAF positive), 4932-53 (LEE negative, EAF positive), E2348/69 (LEE positive, EAF positive), and 3431-4/86 (LEE positive, EAF negative) were isolated and transcribed to cDNAs. Transcription of bfpB could be detected for strain 265-1 (A, lane 1), 4932-53 (A, lane 2), and E2348/69 (A, lane 3). Strain 3431-4/86 cDNA (A, lane 4) did not yield a PCR product, like the negative controls with mRNAs of strains 265-1 (A, lane 5), 4932-53 (A, lane 6), and E2348/69 (A, lane 7) as the template and the sample without a template (A, lane 9). The positive control with genomic DNA of strain E2348/69 (A, lane 8) as the template produced the expected 910-bp PCR product. Lane M contained molecular size markers. (B) Production of BFP was visualized by electron microscopy analysis of strain 265-1 (magnification, ×21,000).