Abstract
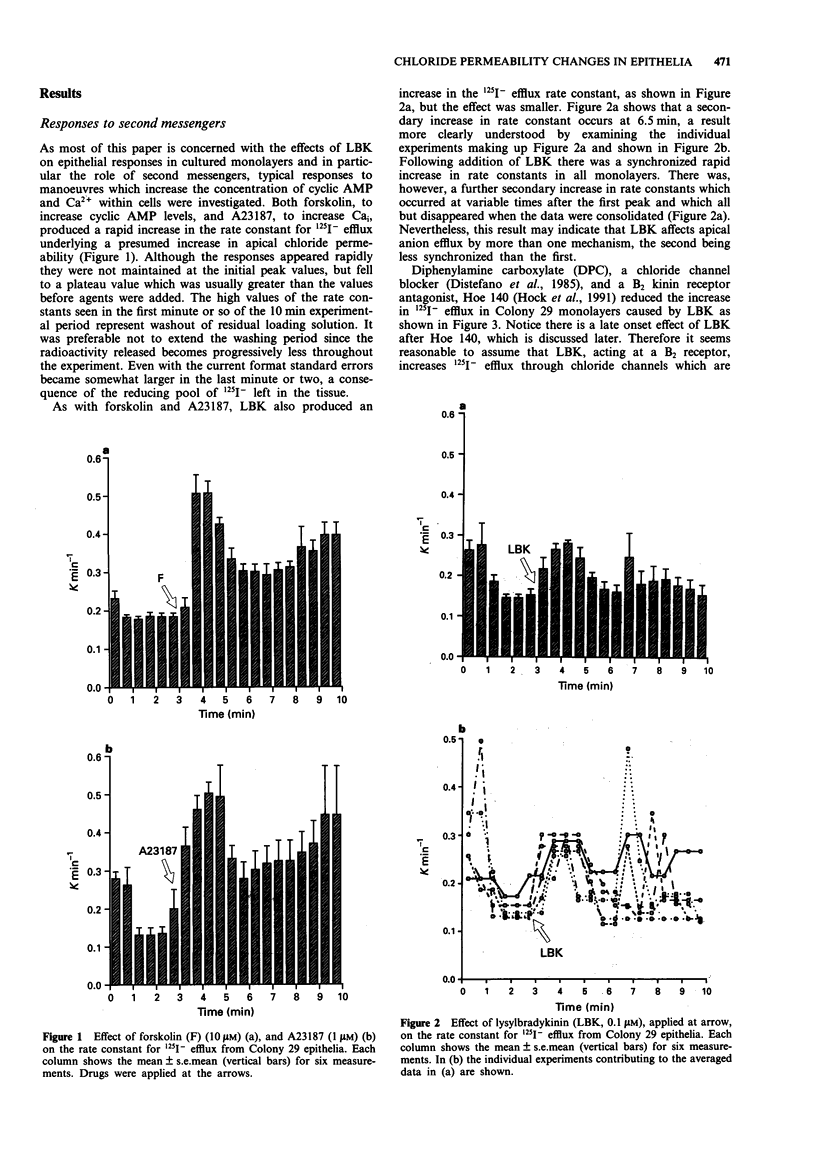
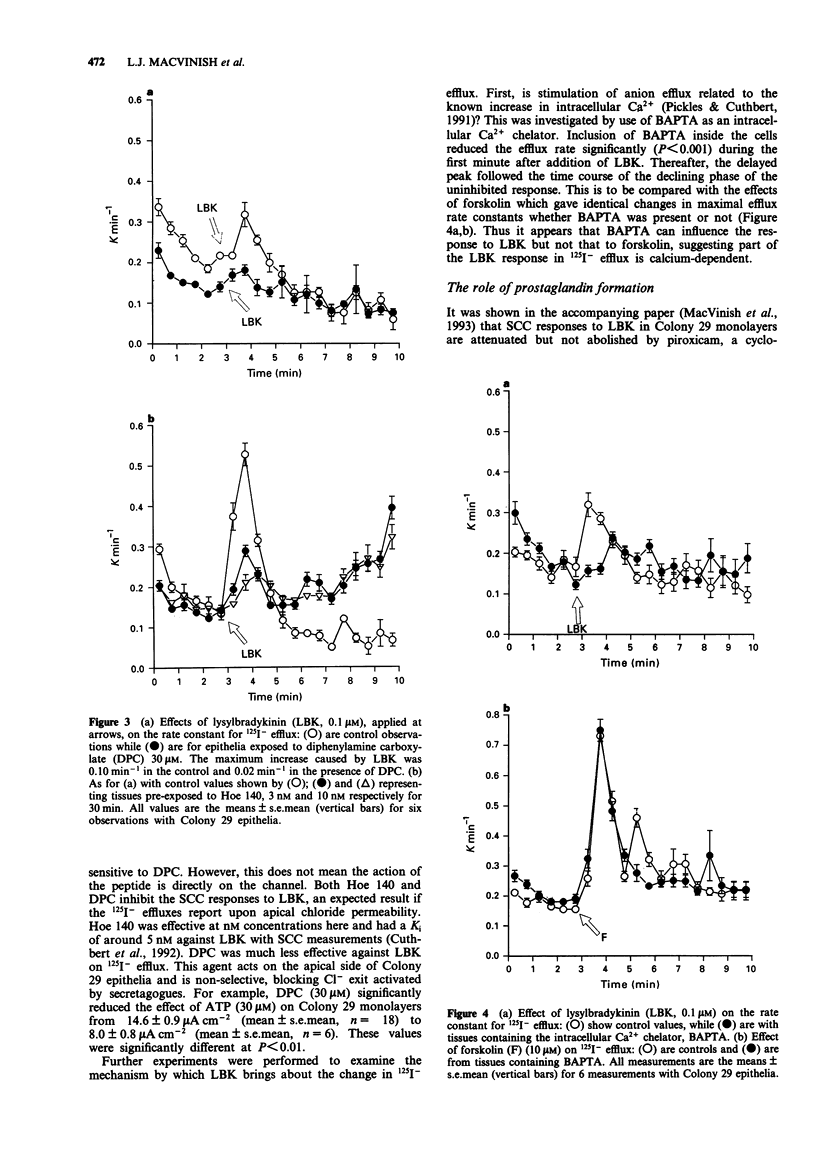
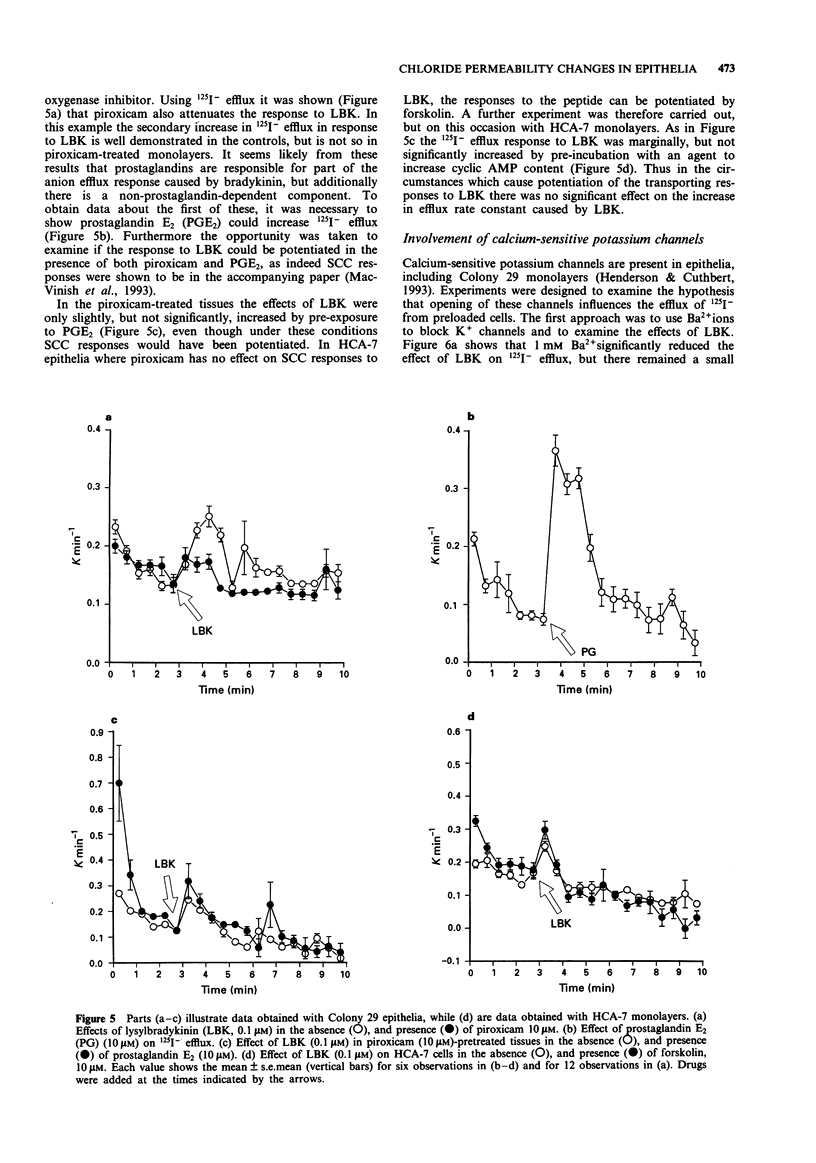
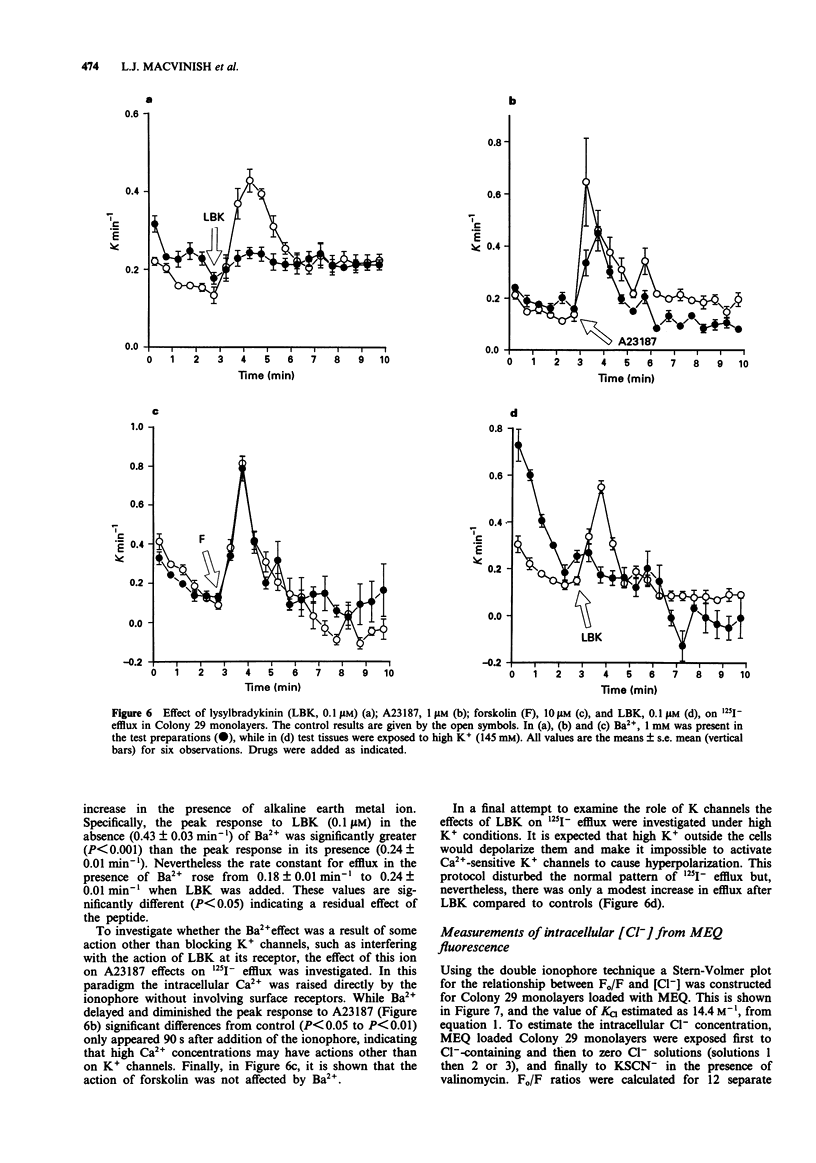
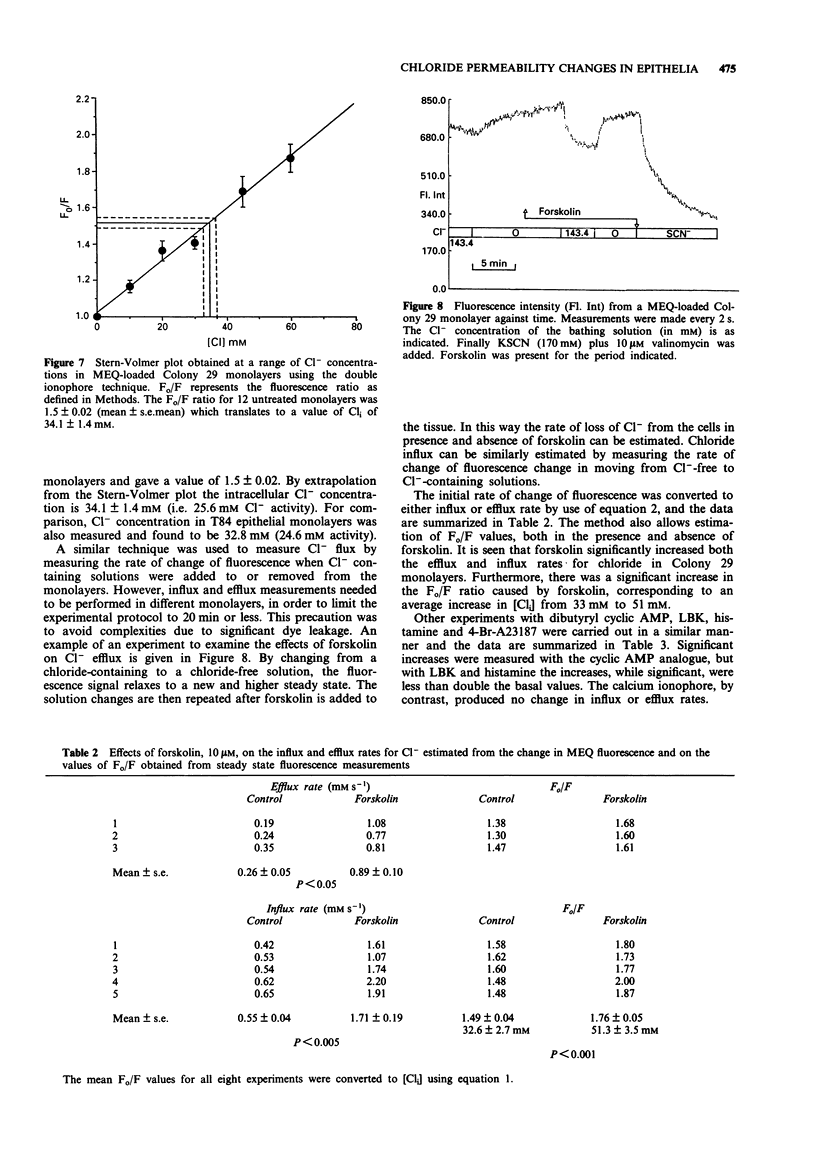
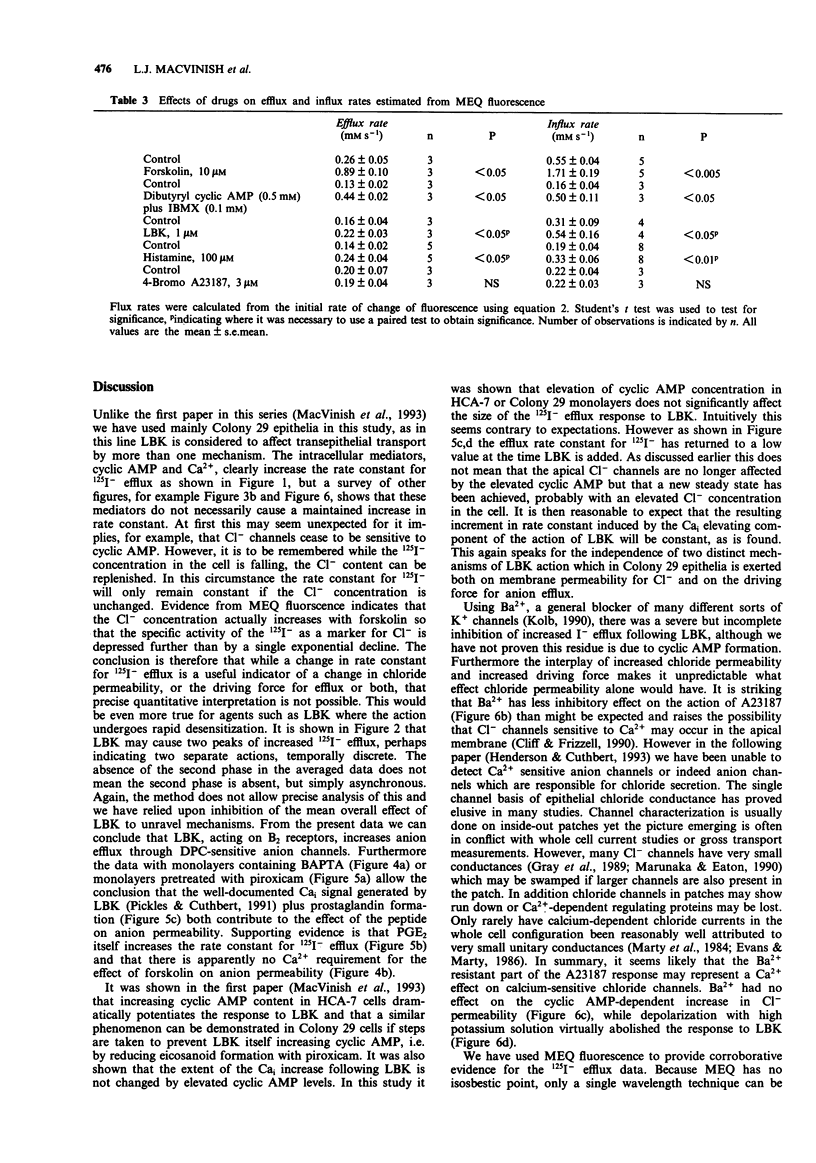
1. The changes in apical Cl- permeability of Colony 29 human colonic epithelial monolayers were estimated from the rate constant of 125I- efflux from tissues loaded with the isotope. 2. Forskolin was used to increase intracellular concentrations of adenosine 3:5' cyclic-monophosphate (cyclic AMP), and A23187 to increase intracellular free Ca2+ (Cai). Both treatments increased the rate constant for 125I- efflux, indicating an increase in apical Cl- permeability. 3. Lysylbradykinin (LBK) also increased the rate constant for 125I- efflux, sometimes biphasically. Chelation of intracellular Ca2+ with BAPTA or prevention of prostaglandin formation with piroxicam, attenuated but did not eliminate the effect of LBK. It is concluded that LBK affects 125I- efflux through the agency of both cyclic AMP and Ca2+. 4. Ba2+ attenuated the effect of LBK and A23187 on 125I- efflux, but had no effect on the action of forskolin. It is concluded that Ca2+ has a major effect on K+ channels, the resulting hyperpolarization increasing the driving force for 125I- efflux. A secondary effect on Ca(2+)-sensitive Cl- channels is possible. By contrast, cyclic AMP exerts it major effect on apical Cl- channels. 5. Using a Cl- sensitive fluorescent dye, MEQ, the intracellular chloride concentration, Cli was estimated to be around 30 mM, which was increased to around 50 mM by forskolin, suggesting cyclic AMP could activate the Na-K-2Cl co-transporter. 6. MEQ fluorescence was used to estimate Cl- influx and efflux rates of epithelial cells. These were increased three fold by forskolin and dibutyryl cyclic AMP and two fold by LBK and histamine.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biwersi J., Verkman A. S. Cell-permeable fluorescent indicator for cytosolic chloride. Biochemistry. 1991 Aug 13;30(32):7879–7883. doi: 10.1021/bi00246a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao A. C., Dix J. A., Sellers M. C., Verkman A. S. Fluorescence measurement of chloride transport in monolayer cultured cells. Mechanisms of chloride transport in fibroblasts. Biophys J. 1989 Dec;56(6):1071–1081. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82755-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao A. C., Widdicombe J. H., Verkman A. S. Chloride conductive and cotransport mechanisms in cultures of canine tracheal epithelial cells measured by an entrapped fluorescent indicator. J Membr Biol. 1990 Feb;113(3):193–202. doi: 10.1007/BF01870071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clancy J. P., McCann J. D., Li M., Welsh M. J. Calcium-dependent regulation of airway epithelial chloride channels. Am J Physiol. 1990 Feb;258(2 Pt 1):L25–L32. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1990.258.2.L25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cliff W. H., Frizzell R. A. Separate Cl- conductances activated by cAMP and Ca2+ in Cl(-)-secreting epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):4956–4960. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.4956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuthbert A. W., Egléme C., Greenwood H., Hickman M. E., Kirkland S. C., MacVinish L. J. Calcium- and cyclic AMP-dependent chloride secretion in human colonic epithelia. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Jul;91(3):503–515. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11243.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuthbert A. W., MacVinish L. J., Pickles R. J. Antagonism of kinin effects on epithelial by Hoe 140: apparently competitive and non-competitive interactions. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Nov;107(3):797–802. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14526.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalmark M., Wieth J. O. Temperature dependence of chloride, bromide, iodide, thiocyanate and salicylate transport in human red cells. J Physiol. 1972 Aug;224(3):583–610. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Stefano A., Wittner M., Schlatter E., Lang H. J., Englert H., Greger R. Diphenylamine-2-carboxylate, a blocker of the Cl(-)-conductive pathway in Cl(-)-transporting epithelia. Pflugers Arch. 1985;405 (Suppl 1):S95–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00581787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. G., Marty A. Calcium-dependent chloride currents in isolated cells from rat lacrimal glands. J Physiol. 1986 Sep;378:437–460. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray M. A., Harris A., Coleman L., Greenwell J. R., Argent B. E. Two types of chloride channel on duct cells cultured from human fetal pancreas. Am J Physiol. 1989 Aug;257(2 Pt 1):C240–C251. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.257.2.C240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halm D. R., Rechkemmer G. R., Schoumacher R. A., Frizzell R. A. Apical membrane chloride channels in a colonic cell line activated by secretory agonists. Am J Physiol. 1988 Apr;254(4 Pt 1):C505–C511. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1988.254.4.C505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R. M., Ashford M. L., MacVinish L. J., Cuthbert A. W. Chloride channels and anion fluxes in a human colonic epithelium (HCA-7). Br J Pharmacol. 1992 May;106(1):109–114. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14301.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R. M., Cuthbert A. W. Activation of ion channels by lysylbradykinin in the HCA-7 colony 29 human adenocarcinoma cell line. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Feb;108(2):479–483. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb12828.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hock F. J., Wirth K., Albus U., Linz W., Gerhards H. J., Wiemer G., Henke S., Breipohl G., König W., Knolle J. Hoe 140 a new potent and long acting bradykinin-antagonist: in vitro studies. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;102(3):769–773. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12248.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb H. A. Potassium channels in excitable and non-excitable cells. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1990;115:51–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krapf R., Berry C. A., Verkman A. S. Estimation of intracellular chloride activity in isolated perfused rabbit proximal convoluted tubules using a fluorescent indicator. Biophys J. 1988 Jun;53(6):955–962. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83176-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacVinish L. J., Pickles R. J., Cuthbert A. W. Cyclic AMP and Ca2+ interactions affecting epithelial chloride secretion in human cultured colonic epithelia. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Feb;108(2):462–468. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb12826.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marty A., Tan Y. P., Trautmann A. Three types of calcium-dependent channel in rat lacrimal glands. J Physiol. 1984 Dec;357:293–325. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marunaka Y., Eaton D. C. Chloride channels in the apical membrane of a distal nephron A6 cell line. Am J Physiol. 1990 Feb;258(2 Pt 1):C352–C368. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.258.2.C352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Grady S. M., Palfrey H. C., Field M. Characteristics and functions of Na-K-Cl cotransport in epithelial tissues. Am J Physiol. 1987 Aug;253(2 Pt 1):C177–C192. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.2.C177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulais M., Turner R. J. Beta-adrenergic upregulation of the Na(+)-K(+)-2Cl- cotransporter in rat parotid acinar cells. J Clin Invest. 1992 Apr;89(4):1142–1147. doi: 10.1172/JCI115695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pewitt E. B., Hegde R. S., Haas M., Palfrey H. C. The regulation of Na/K/2Cl cotransport and bumetanide binding in avian erythrocytes by protein phosphorylation and dephosphorylation. Effects of kinase inhibitors and okadaic acid. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 5;265(34):20747–20756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickles R. J., Cuthbert A. W. Relation of anion secretory activity to intracellular Ca2+ in response to lysylbradykinin and histamine in a cultured human colonic epithelium. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Jun 18;199(1):77–91. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90639-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roscher A. A., Manganiello V. C., Jelsema C. L., Moss J. Autoregulation of bradykinin receptors and bradykinin-induced prostacyclin formation in human fibroblasts. J Clin Invest. 1984 Aug;74(2):552–558. doi: 10.1172/JCI111452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venglarik C. J., Bridges R. J., Frizzell R. A. A simple assay for agonist-regulated Cl and K conductances in salt-secreting epithelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1990 Aug;259(2 Pt 1):C358–C364. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.259.2.C358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verkman A. S. Development and biological applications of chloride-sensitive fluorescent indicators. Am J Physiol. 1990 Sep;259(3 Pt 1):C375–C388. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.259.3.C375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolsing D. H., Rosenbaum J. S. Bradykinin-stimulated inositol phosphate production in NG108-15 cells is mediated by a small population of binding sites which rapidly desensitize. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 May;257(2):621–633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


