Abstract
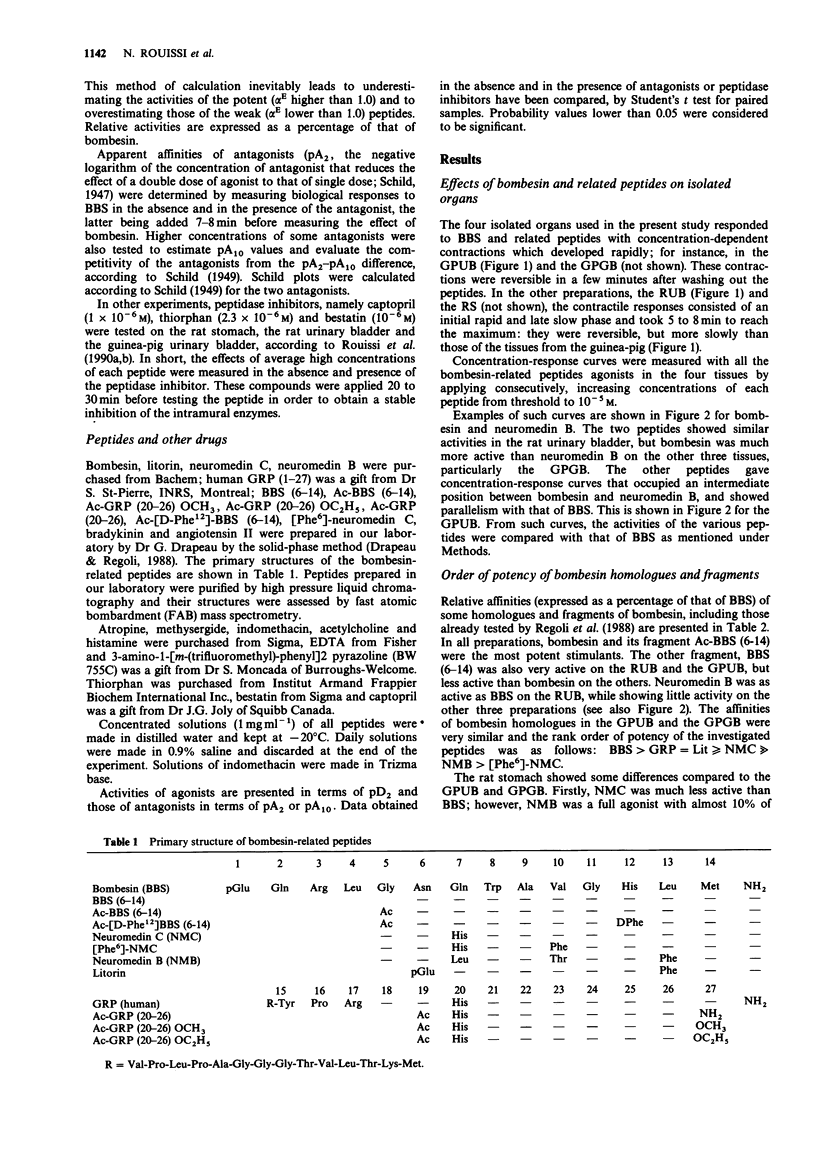
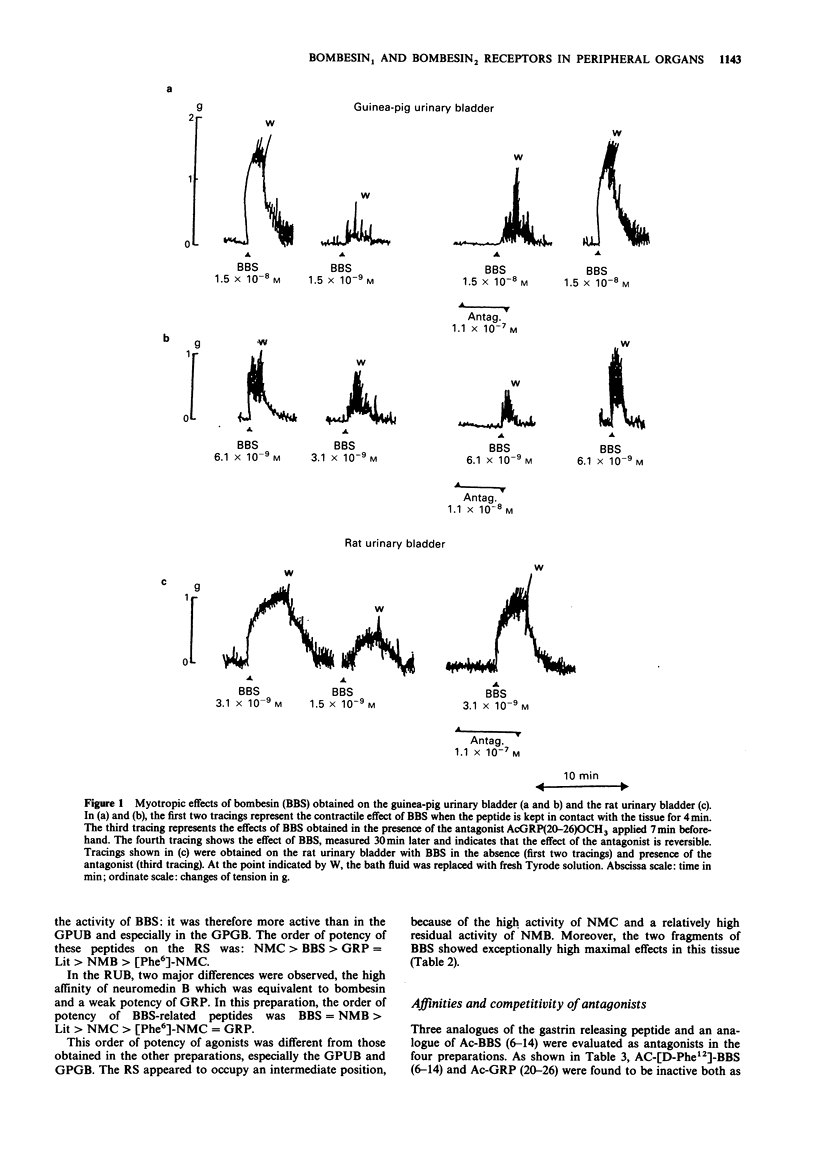
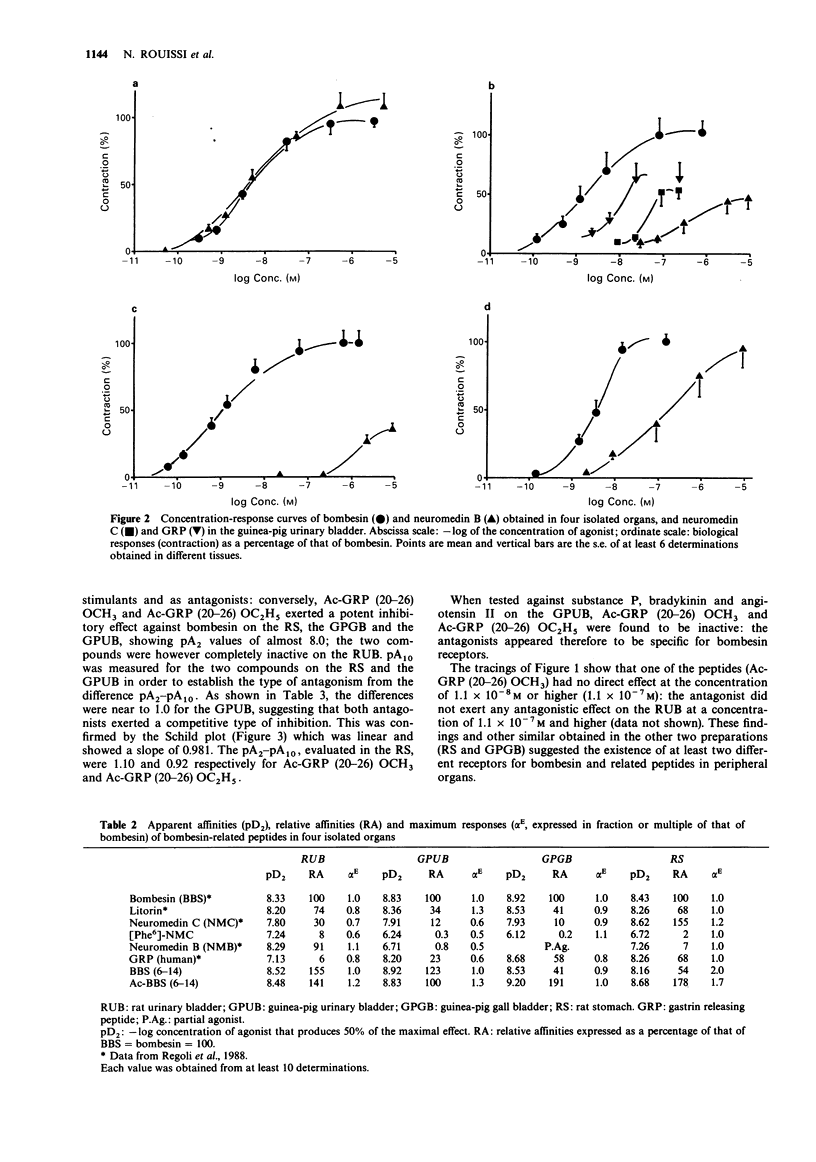
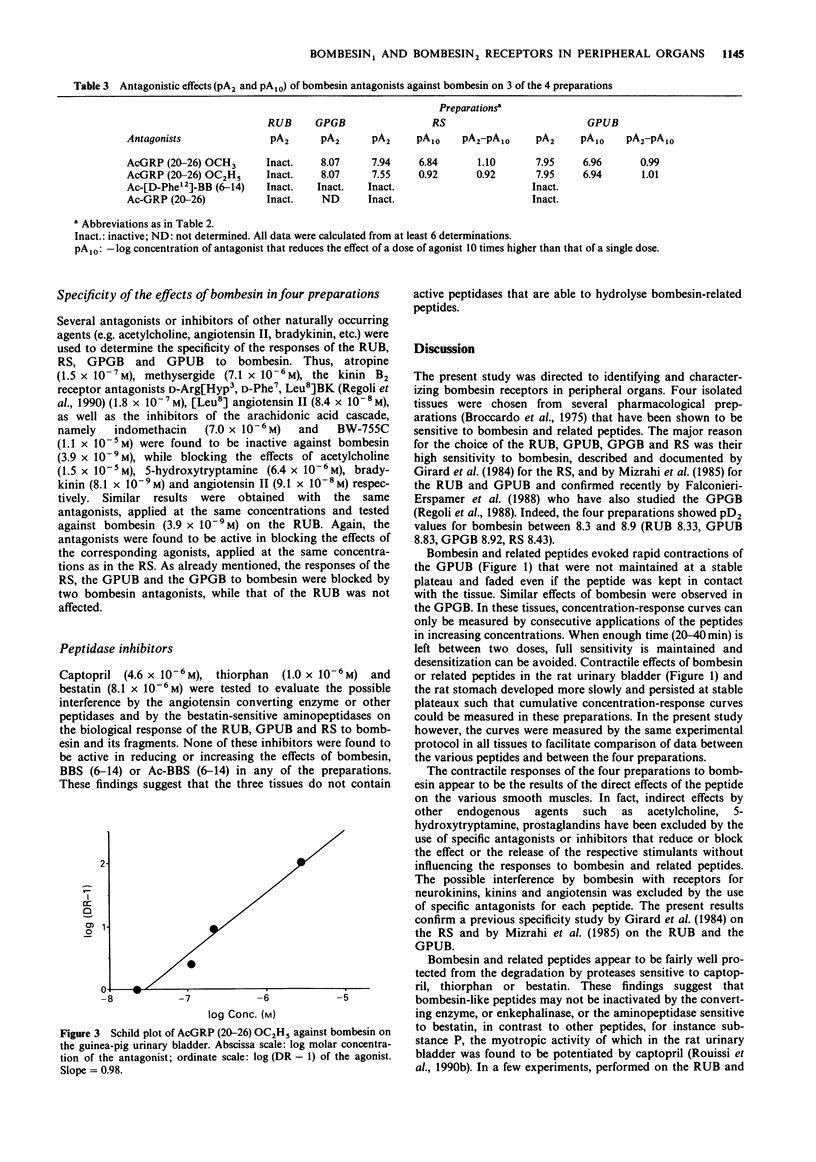
1 Guinea-pig and rat urinary bladders, rat stomach and the guinea-pig gall bladder, four isolated organs that show high sensitivity to bombesin, were used to characterize bombesin receptors in peripheral organs. 2 The order of potency of agonists was determined with several naturally occurring peptides of the bombesin series, namely bombesin (BBS), litorin (Lit), neuromedin B (NMB), the gastrin-releasing peptide (GRP 18-27), neuromedin C (NMC) and with some bombesin fragments. It was found that bombesin, neuromedin C, litorin and two bombesin fragments, BBS (6-14) and AcBBS (6-14) had similar activities in the four preparations, while neuromedin B and [Phe6]-neuromedin C were more active on the rat urinary bladder than on the other tissues. 3 The order of potency of agonists determined in the rat urinary bladder was as follows: BBS = NMB greater than Lit greater than NMC greater than [Phe6]NMC = GRP and it was found to be different from that observed in the other preparations: BBS greater than GRP = Lit greater than or equal to NMC much greater than NMB greater than [Phe6]NMC, suggesting the existence of two different bombesin receptors, BBS1 and BBS2. 4 This interpretation was convalidated by the finding that bombesin antagonists, namely Ac.GRP(20-26)OCH3 and Ac.GRP(20-26)OC2H5 reduced or blocked the effects of bombesin-related peptides on BBS2 receptor systems while being completely inactive on the rat urinary bladder (BBS1 system).
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anastasi A., Erspamer V., Bucci M. Isolation and structure of bombesin and alytesin, 2 analogous active peptides from the skin of the European amphibians Bombina and Alytes. Experientia. 1971 Feb 15;27(2):166–167. doi: 10.1007/BF02145873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anastasi A., Erspamer V., Endean R. Aminoacid composition and sequence of litorin, a bombesin-like nonapeptide from the skin of the Australian leptodactylid frog Litoria aurea. Experientia. 1975 May 15;31(5):510–511. doi: 10.1007/BF01932427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertaccini G., Erspamer V., Impicciatore M. The actions of bombesin on gastric secretion of the dog and the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1973 Nov;49(3):437–444. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1973.tb17254.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broccardo M., Falconieri Erspamer G., Melchiorri P., Negri L., de Castiglione R. Relative potency of bombesin-like peptides. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 Oct;55(2):221–227. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1975.tb07631.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapeau G., Regoli D. Synthesis of bradykinin analogs. Methods Enzymol. 1988;163:263–272. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)63025-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erspamer V., Erpamer G. F., Inselvini M. Some pharmacological actions of alytesin and bombesin. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1970 Nov;22(11):875–876. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1970.tb08465.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falconieri Erspamer G., Severini C., Erspamer V., Melchiorri P., Delle Fave G., Nakajima T. Parallel bioassay of 27 bombesin-like peptides on 9 smooth muscle preparations. Structure-activity relationships and bombesin receptor subtypes. Regul Pept. 1988 May;21(1-2):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(88)90085-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girard F., Bachelard H., St-Pierre S., Rioux F. The contractile effect of bombesin, gastrin releasing peptide and various fragments in the rat stomach strip. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Jul 20;102(3-4):489–497. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90570-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heimbrook D. C., Saari W. S., Balishin N. L., Friedman A., Moore K. S., Reimen M. W., Kiefer D. M., Rotberg N. S., Wallen J. W., Oliff A. Carboxyl-terminal modification of a gastrin releasing peptide derivative generates potent antagonists. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 5;264(19):11258–11262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen R. T., Coy D. H., Saeed Z. A., Heinz-Erian P., Mantey S., Gardner J. D. Interaction of bombesin and related peptides with receptors on pancreatic acinar cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;547:138–149. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb23882.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen R. T., Heinz-Erian P., Mantey S., Jones S. W., Gardner J. D. Characterization of ability of various substance P antagonists to inhibit action of bombesin. Am J Physiol. 1988 Jun;254(6 Pt 1):G883–G890. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1988.254.6.G883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen R. T., Jones S. W., Folkers K., Gardner J. D. A synthetic peptide that is a bombesin receptor antagonist. Nature. 1984 May 3;309(5963):61–63. doi: 10.1038/309061a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald T. J., Jörnvall H., Nilsson G., Vagne M., Ghatei M., Bloom S. R., Mutt V. Characterization of a gastrin releasing peptide from porcine non-antral gastric tissue. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Sep 12;90(1):227–233. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91614-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minamino N., Kangawa K., Matsuo H. Neuromedin B: a novel bombesin-like peptide identified in porcine spinal cord. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jul 29;114(2):541–548. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90814-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minamino N., Kangawa K., Matsuo H. Neuromedin C: a bombesin-like peptide identified in porcine spinal cord. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Feb 29;119(1):14–20. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91611-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizrahi J., Dion S., D'Orléans-Juste P., Regoli D. Activities and antagonism of bombesin on urinary smooth muscles. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 May 20;111(3):339–345. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90640-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsuki M., Fujii M., Nakamura T., Tani S., Oka T., Baba S., Yajima H. Actions of neuromedin-B and neuromedin-C on amylase release from isolated rat pancreatic acini. Pancreas. 1987;2(3):252–257. doi: 10.1097/00006676-198705000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoli D., Dion S., Rhaleb N. E., Drapeau G., Rouissi N., D'Orléans-Juste P. Receptors for neurokinins, tachykinins, and bombesin: a pharmacological study. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;547:158–173. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb23884.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoli D., Rhaleb N. E., Dion S., Drapeau G. New selective bradykinin receptor antagonists and bradykinin B2 receptor characterization. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Apr;11(4):156–161. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90067-I. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouissi N., Nantel F., Drapeau G., Rhaleb N. E., Dion S., Regoli D. Inhibitors of peptidases: how they influence the biological activities of substance P, neurokinins, bradykinin and angiotensin in guinea pig, hamster and rat urinary bladders. Pharmacology. 1990;40(4):196–204. doi: 10.1159/000138659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouissi N., Nantel F., Drapeau G., Rhaleb N. E., Dion S., Regoli D. Inhibitors of peptidases: how they influence the biological activities of substance P, neurokinins, kinins and angiotensins in isolated vessels. Pharmacology. 1990;40(4):185–195. doi: 10.1159/000138658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Severi C., Grider J. R., Makhlouf G. M. Identification of separate bombesin and substance P receptors on isolated muscle cells from canine gallbladder. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Apr;245(1):195–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VANE J. R. A sensitive method for the assay of 5-hydroxytryptamine. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1957 Sep;12(3):344–349. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1957.tb00146.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Schrenck T., Heinz-Erian P., Moran T., Mantey S. A., Gardner J. D., Jensen R. T. Neuromedin B receptor in esophagus: evidence for subtypes of bombesin receptors. Am J Physiol. 1989 Apr;256(4 Pt 1):G747–G758. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1989.256.4.G747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


