Abstract
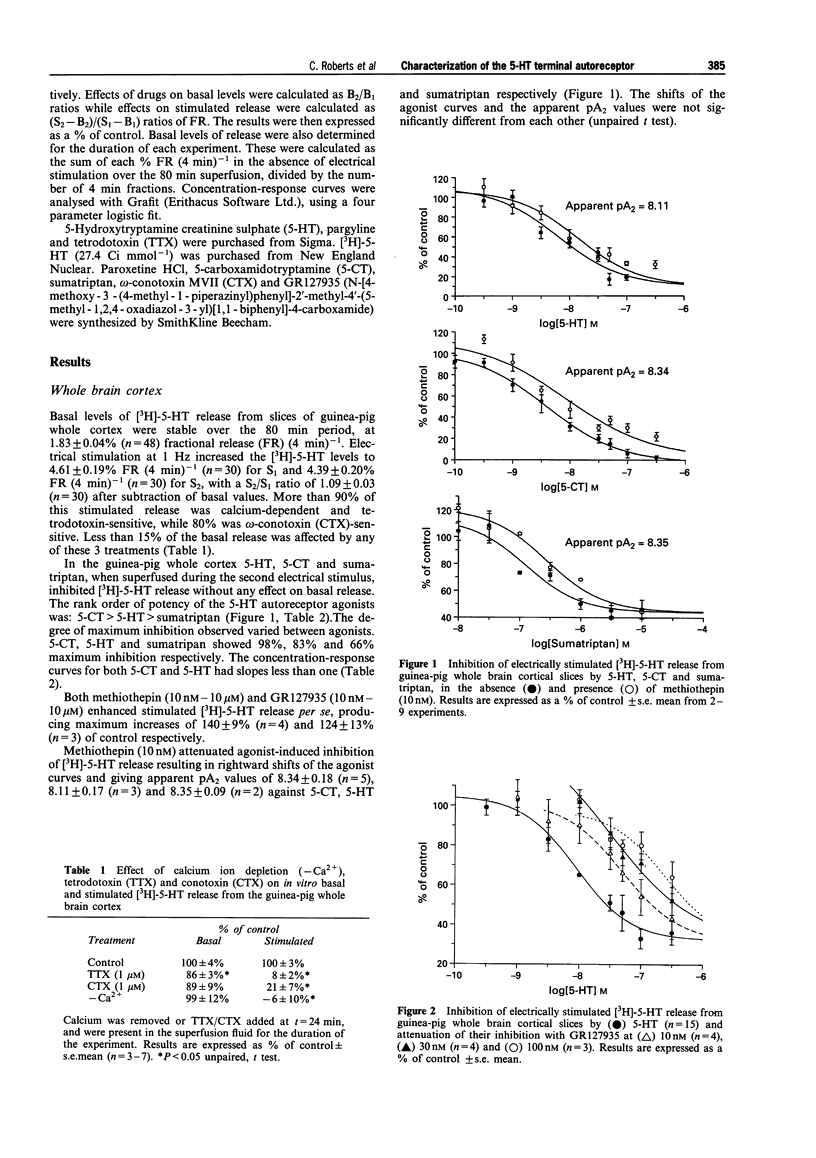
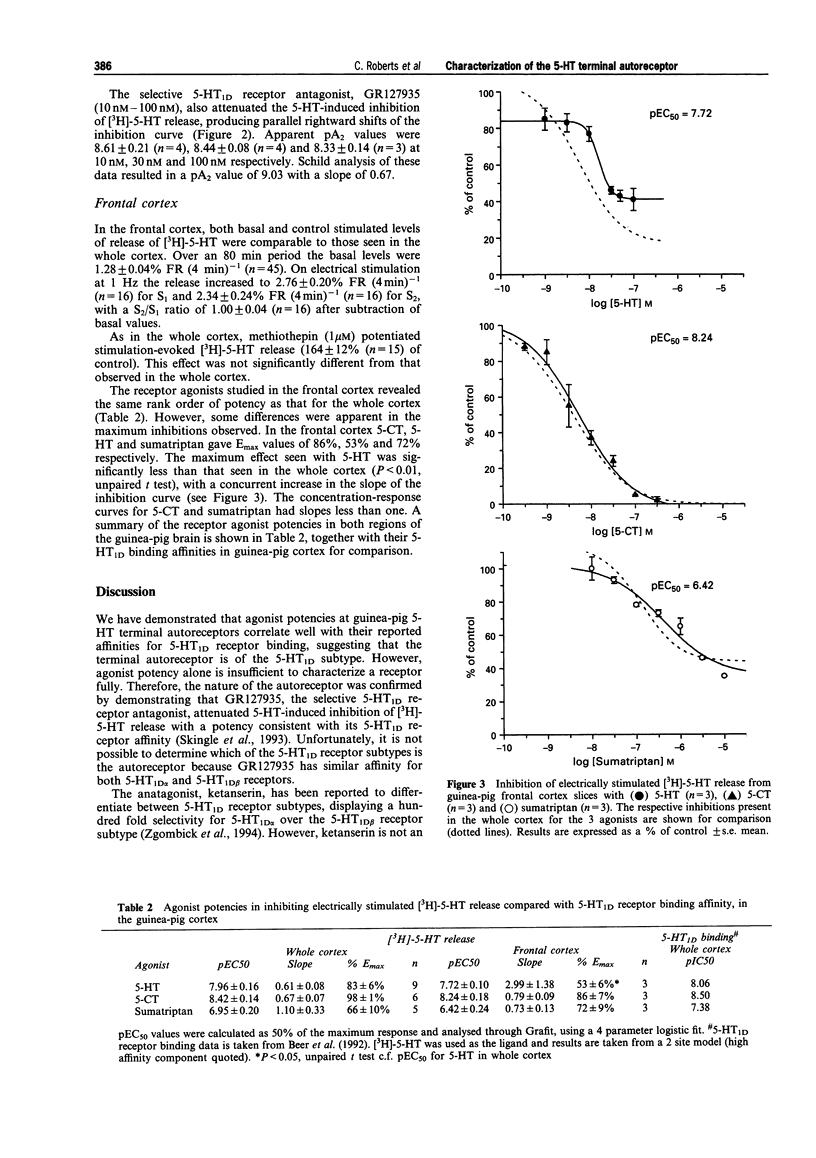
1 In guinea-pig cerebral cortical slices in vitro we have shown that the rank order of potency of 5-hydroxytrptamine (5-HT), 5-carboxamidotryptamine and sumatriptan for inhibition of electrically stimulated [3H]-5-HT release correlates well with published data on their 5-HT1D receptor binding affinities. 2 Both the non-selective 5-HT1D receptor antagonist, methiothepin and the selective 5-HT1D receptor antagonist, N-[4-methoxy-3-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl]phenyl]-2'-methyl-4'- (5-methyl-1,2,4-oxadiazole-3-yl) [1,1-biphenyl]4-carboxamide (GR127935) increased stimulated [3H]-5-HT release per se and also attenuated agonist-induced inhibition of [3H]-5-HT release. GR127935 (10 nM-100 nM) produced a pA2 of 9.0 against 5-HT, which is consistent with its 5-HT1D receptor binding affinity. 3 From these findings we conclude that, in guinea-pig cerebral cortex, the 5-HT terminal autoreceptor is of the 5-HT1D receptor subtype. However, three observations suggest the presence of multiple terminal autoreceptors: shallow inhibition curves to the agonists; a shallow Schild slope of GR127935 antagonism and differences in the maximal responses to 5-HT between whole cortex and frontal cortex.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adham N., Kao H. T., Schecter L. E., Bard J., Olsen M., Urquhart D., Durkin M., Hartig P. R., Weinshank R. L., Branchek T. A. Cloning of another human serotonin receptor (5-HT1F): a fifth 5-HT1 receptor subtype coupled to the inhibition of adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):408–412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adham N., Romanienko P., Hartig P., Weinshank R. L., Branchek T. The rat 5-hydroxytryptamine1B receptor is the species homologue of the human 5-hydroxytryptamine1D beta receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Jan;41(1):1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amlaiky N., Ramboz S., Boschert U., Plassat J. L., Hen R. Isolation of a mouse "5HT1E-like" serotonin receptor expressed predominantly in hippocampus. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 5;267(28):19761–19764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beer M. S., Stanton J. A., Bevan Y., Chauhan N. S., Middlemiss D. N. An investigation of the 5-HT1D receptor binding affinity of 5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-carboxyamidotryptamine and sumatriptan in the central nervous system of seven species. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Mar 24;213(2):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90681-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blier P., Serrano A., Scatton B. Differential responsiveness of the rat dorsal and median raphe 5-HT systems to 5-HT1 receptor agonists and p-chloroamphetamine. Synapse. 1990;5(2):120–133. doi: 10.1002/syn.890050206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruinvels A. T., Landwehrmeyer B., Gustafson E. L., Durkin M. M., Mengod G., Branchek T. A., Hoyer D., Palacios J. M. Localization of 5-HT1B, 5-HT1D alpha, 5-HT1E and 5-HT1F receptor messenger RNA in rodent and primate brain. Neuropharmacology. 1994 Mar-Apr;33(3-4):367–386. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(94)90067-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlander M. G., Lovenberg T. W., Baron B. M., de Lecea L., Danielson P. E., Racke M., Slone A. L., Siegel B. W., Foye P. E., Cannon K. Two members of a distinct subfamily of 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors differentially expressed in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3452–3456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink K., Schlicker E., Betz R., Göthert M. Identification of presynaptic 5-HT1 autoreceptors in pig brain cortex synaptosomes and slices. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1988 Jul;338(1):14–18. doi: 10.1007/BF00168806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamblin M. W., Metcalf M. A. Primary structure and functional characterization of a human 5-HT1D-type serotonin receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Aug;40(2):143–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer D., Middlemiss D. N. Species differences in the pharmacology of terminal 5-HT autoreceptors in mammalian brain. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Apr;10(4):130–132. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90159-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosofsky B. E., Molliver M. E. The serotoninergic innervation of cerebral cortex: different classes of axon terminals arise from dorsal and median raphe nuclei. Synapse. 1987;1(2):153–168. doi: 10.1002/syn.890010204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limberger N., Deicher R., Starke K. Species differences in presynaptic serotonin autoreceptors: mainly 5-HT1B but possibly in addition 5-HT1D in the rat, 5-HT1D in the rabbit and guinea-pig brain cortex. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1991 Apr;343(4):353–364. doi: 10.1007/BF00179039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovenberg T. W., Baron B. M., de Lecea L., Miller J. D., Prosser R. A., Rea M. A., Foye P. E., Racke M., Slone A. L., Siegel B. W. A novel adenylyl cyclase-activating serotonin receptor (5-HT7) implicated in the regulation of mammalian circadian rhythms. Neuron. 1993 Sep;11(3):449–458. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90149-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovenberg T. W., Erlander M. G., Baron B. M., Racke M., Slone A. L., Siegel B. W., Craft C. M., Burns J. E., Danielson P. E., Sutcliffe J. G. Molecular cloning and functional expression of 5-HT1E-like rat and human 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2184–2188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthes H., Boschert U., Amlaiky N., Grailhe R., Plassat J. L., Muscatelli F., Mattei M. G., Hen R. Mouse 5-hydroxytryptamine5A and 5-hydroxytryptamine5B receptors define a new family of serotonin receptors: cloning, functional expression, and chromosomal localization. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Mar;43(3):313–319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maura G., Thellung S., Andrioli G. C., Ruelle A., Raiteri M. Release-regulating serotonin 5-HT1D autoreceptors in human cerebral cortex. J Neurochem. 1993 Mar;60(3):1179–1182. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb03274.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middlemiss D. N., Hutson P. H. The 5-HT1B receptors. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;600:132–348. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb16878.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monsma F. J., Jr, Shen Y., Ward R. P., Hamblin M. W., Sibley D. R. Cloning and expression of a novel serotonin receptor with high affinity for tricyclic psychotropic drugs. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Mar;43(3):320–327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlicker E., Fink K., Göthert M., Hoyer D., Molderings G., Roschke I., Schoeffter P. The pharmacological properties of the presynaptic serotonin autoreceptor in the pig brain cortex conform to the 5-HT1D receptor subtype. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1989 Jul;340(1):45–51. doi: 10.1007/BF00169206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K., Göthert M., Kilbinger H. Modulation of neurotransmitter release by presynaptic autoreceptors. Physiol Rev. 1989 Jul;69(3):864–989. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1989.69.3.864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- To Z. P., Bonhaus D. W., Eglen R. M., Jakeman L. B. Characterization and distribution of putative 5-ht7 receptors in guinea-pig brain. Br J Pharmacol. 1995 May;115(1):107–116. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb16327.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinshank R. L., Zgombick J. M., Macchi M. J., Branchek T. A., Hartig P. R. Human serotonin 1D receptor is encoded by a subfamily of two distinct genes: 5-HT1D alpha and 5-HT1D beta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3630–3634. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson L. O., Middlemiss D. N. Metitepine distinguishes two receptors mediating inhibition of [3H]-5-hydroxytryptamine release in guinea pig hippocampus. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1992 Jun;345(6):696–699. doi: 10.1007/BF00164585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisden W., Parker E. M., Mahle C. D., Grisel D. A., Nowak H. P., Yocca F. D., Felder C. C., Seeburg P. H., Voigt M. M. Cloning and characterization of the rat 5-HT5B receptor. Evidence that the 5-HT5B receptor couples to a G protein in mammalian cell membranes. FEBS Lett. 1993 Oct 25;333(1-2):25–31. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80368-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


