Abstract
1. P1-purinoceptors mediating relaxation of the rat duodenum longitudinal muscle and contraction of the rat duodenum muscularis mucosae were characterized by the use of adenosine and its analogues, 5'-N-ethylcarboxamidoadenosine (NECA), N6-cyclopentyl-adenosine (CPA), N6-(phenylisopropyl)adenosine (R-PIA), 2-chloroadenosine (2-CADO) and 2-p-((carboxyethyl)phenethylamino)-5'-carboxamidoadenosine (CGS21680), as well as the P1-purinoceptor antagonist 8-phenyltheophylline (8-PT) and the A1-selective antagonist, 1,3-dipropyl-8-cyclopentylxanthine (DPCPX). 2. In the rat duodenum longitudinal muscle, the order of potency of the adenosine agonists was CPA > NECA > adenosine > CGS21680. DPCPX antagonized responses to CPA and NECA at a concentration of 1 nM suggesting that they are acting at A1 receptors. A Schild plot versus CPA gave a slope near to unity (slope = 0.955) and a pA2 of 9.8 confirming that CPA was acting via A1 receptors. Schild analysis for DPCPX versus NECA, however, gave a slope of 0.674 suggesting that NECA was acting on both A1 and A2 receptors. CGS21680, a selective A2a agonist, was much less potent than adenosine suggesting that the A2 receptors are of the A2b subtype. 3. In the rat duodenum muscularis mucosae, the order of potency of the adenosine agonists was NECA > or = R-PIA = CPA > 2-CADO > adenosine, and DPCPX antagonized responses to CPA and NECA at a concentration of 1 microM. CGS21680, at a concentration of 10 microM, had no effect on this tissue. This suggests the presence of A2 receptors in this tissue and that they are of the A2b subtype. 4. These results are in agreement with previous studies in the whole duodenum showing the presence of A1 and A2b receptors causing relaxation, and this shows that the longitudinal muscle dominates the response of the whole tissue. In addition, a contractile A2b receptor has been revealed on the muscularis mucosae, the first time this subtype has been reported to elicit an excitatory response in a smooth muscle preparation.
Full text
PDF
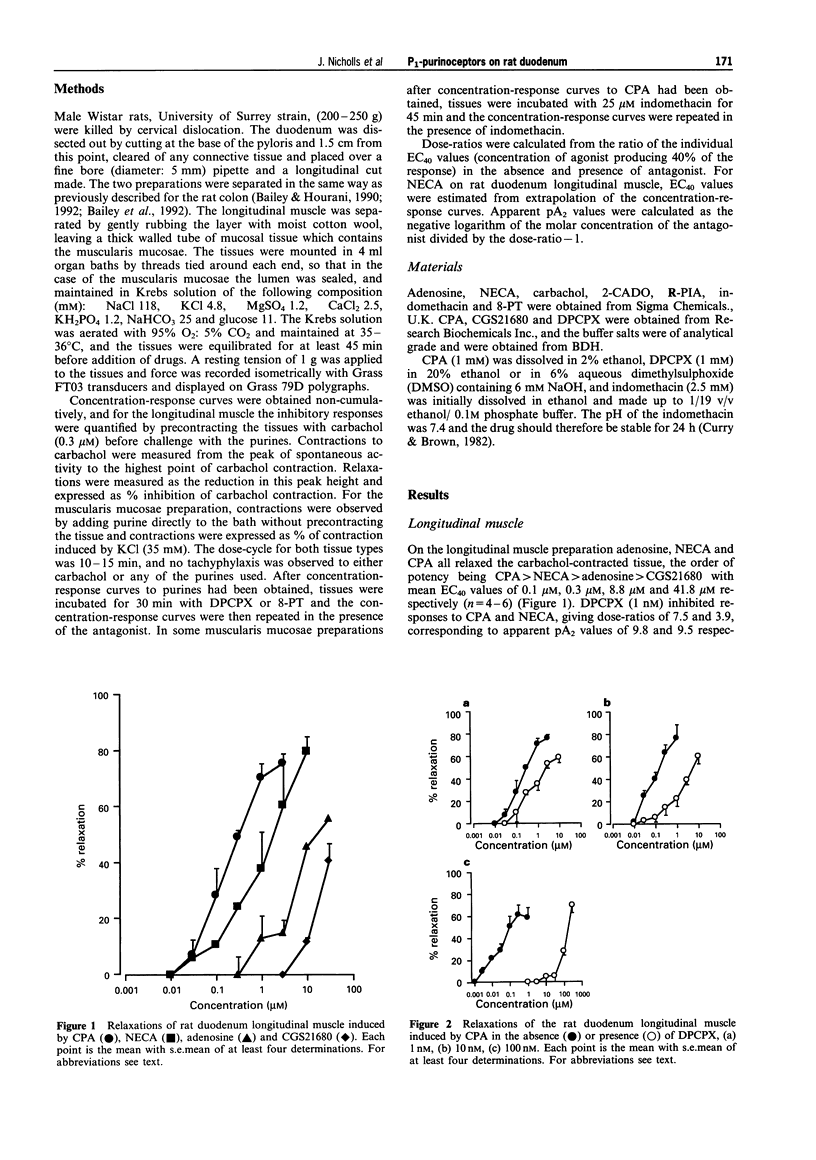
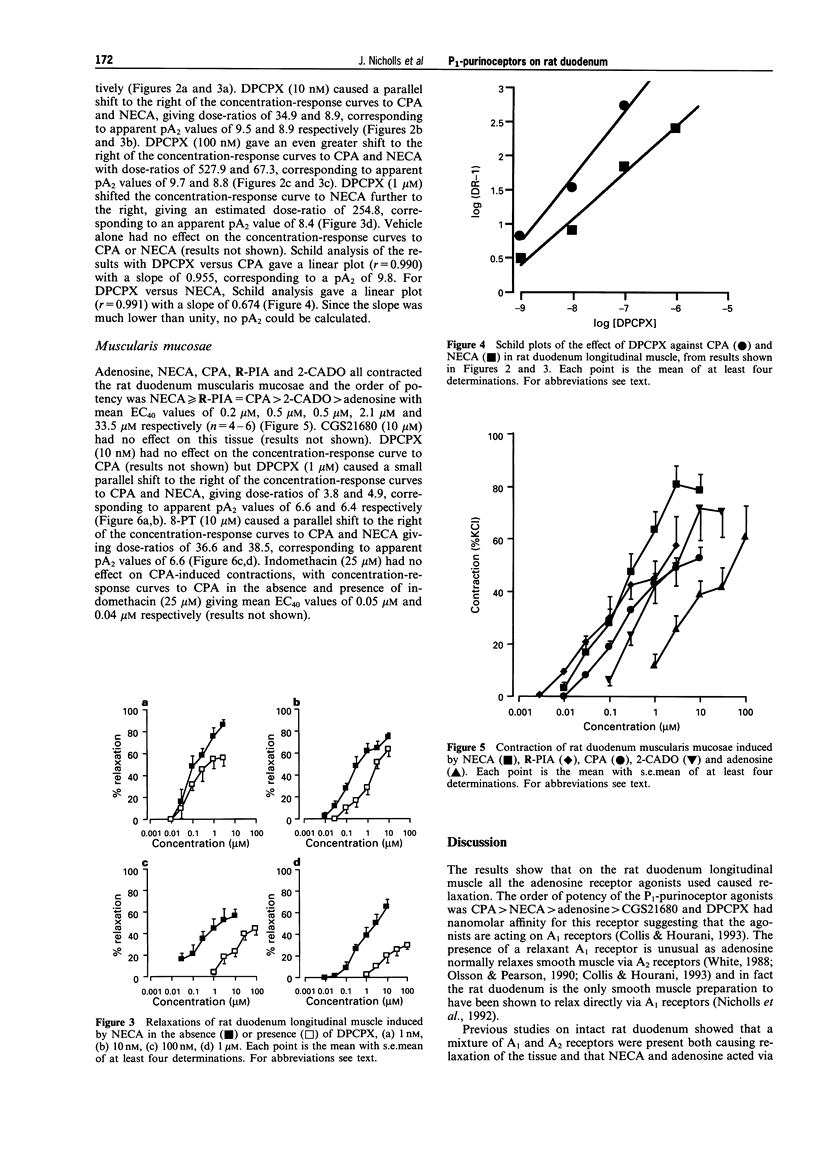
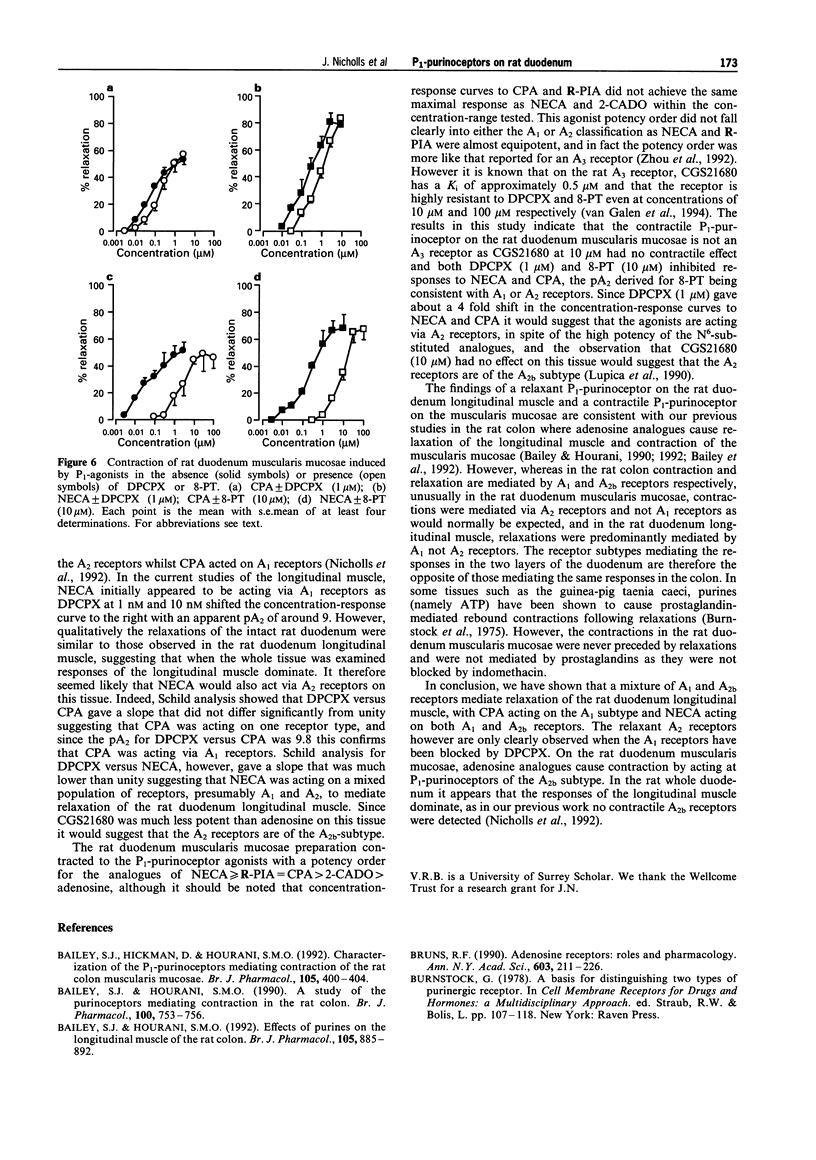

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailey S. J., Hickman D., Hourani S. M. Characterization of the P1-purinoceptors mediating contraction of the rat colon muscularis mucosae. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Feb;105(2):400–404. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14265.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey S. J., Hourani S. M. A study of the purinoceptors mediating contraction in the rat colon. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Aug;100(4):753–756. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14087.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey S. J., Hourani S. M. Effects of purines on the longitudinal muscle of the rat colon. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Apr;105(4):885–892. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb09073.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns R. F. Adenosine receptors. Roles and pharmacology. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;603:211–226. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb37674.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G., Cocks T., Paddle B., Staszewska-Barczak J. Evidence that prostaglandin is responsible for the 'rebound contraction' following stimulation of non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic ('purinergic') inhibitory nerves. Eur J Pharmacol. 1975 Apr;31(2):360–362. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(75)90060-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collis M. G., Hourani S. M. Adenosine receptor subtypes. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1993 Oct;14(10):360–366. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(93)90094-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry S. H., Brown E. A., Kuck H., Cassin S. Preparation and stability of indomethacin solutions. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1982 Jul;60(7):988–992. doi: 10.1139/y82-139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer S. G., Canning B. J., Wilkins D. E. Adenosine receptor-mediated contraction and relaxation of guinea-pig isolated tracheal smooth muscle: effects of adenosine antagonists. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Oct;95(2):371–378. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11655.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredholm B. B., Abbracchio M. P., Burnstock G., Daly J. W., Harden T. K., Jacobson K. A., Leff P., Williams M. Nomenclature and classification of purinoceptors. Pharmacol Rev. 1994 Jun;46(2):143–156. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis M. F., Schulz R., Hutchison A. J., Do U. H., Sills M. A., Williams M. [3H]CGS 21680, a selective A2 adenosine receptor agonist directly labels A2 receptors in rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Dec;251(3):888–893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lupica C. R., Cass W. A., Zahniser N. R., Dunwiddie T. V. Effects of the selective adenosine A2 receptor agonist CGS 21680 on in vitro electrophysiology, cAMP formation and dopamine release in rat hippocampus and striatum. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Mar;252(3):1134–1141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls J., Hourani S. M., Kitchen I. Characterization of P1-purinoceptors on rat duodenum and urinary bladder. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Mar;105(3):639–642. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb09032.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson R. A., Pearson J. D. Cardiovascular purinoceptors. Physiol Rev. 1990 Jul;70(3):761–845. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1990.70.3.761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peachey J. A., Hourani S. M., Kitchen I. The binding of 1,3-[3H]-dipropyl-8-cyclopentylxanthine to adenosine A1 receptors in rat smooth muscle preparations. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Dec;113(4):1249–1256. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb17132.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoggall S. M., Shaw J. S. The coexistence of adenosine A1 and A2 receptors in guinea-pig aorta. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov 13;190(3):329–335. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)94197-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White T. D. Role of adenine compounds in autonomic neurotransmission. Pharmacol Ther. 1988;38(2):129–168. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(88)90095-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Q. Y., Li C., Olah M. E., Johnson R. A., Stiles G. L., Civelli O. Molecular cloning and characterization of an adenosine receptor: the A3 adenosine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7432–7436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Calker D., Müller M., Hamprecht B. Adenosine regulates via two different types of receptors, the accumulation of cyclic AMP in cultured brain cells. J Neurochem. 1979 Nov;33(5):999–1005. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb05236.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Galen P. J., van Bergen A. H., Gallo-Rodriguez C., Melman N., Olah M. E., IJzerman A. P., Stiles G. L., Jacobson K. A. A binding site model and structure-activity relationships for the rat A3 adenosine receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Jun;45(6):1101–1111. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


