Abstract
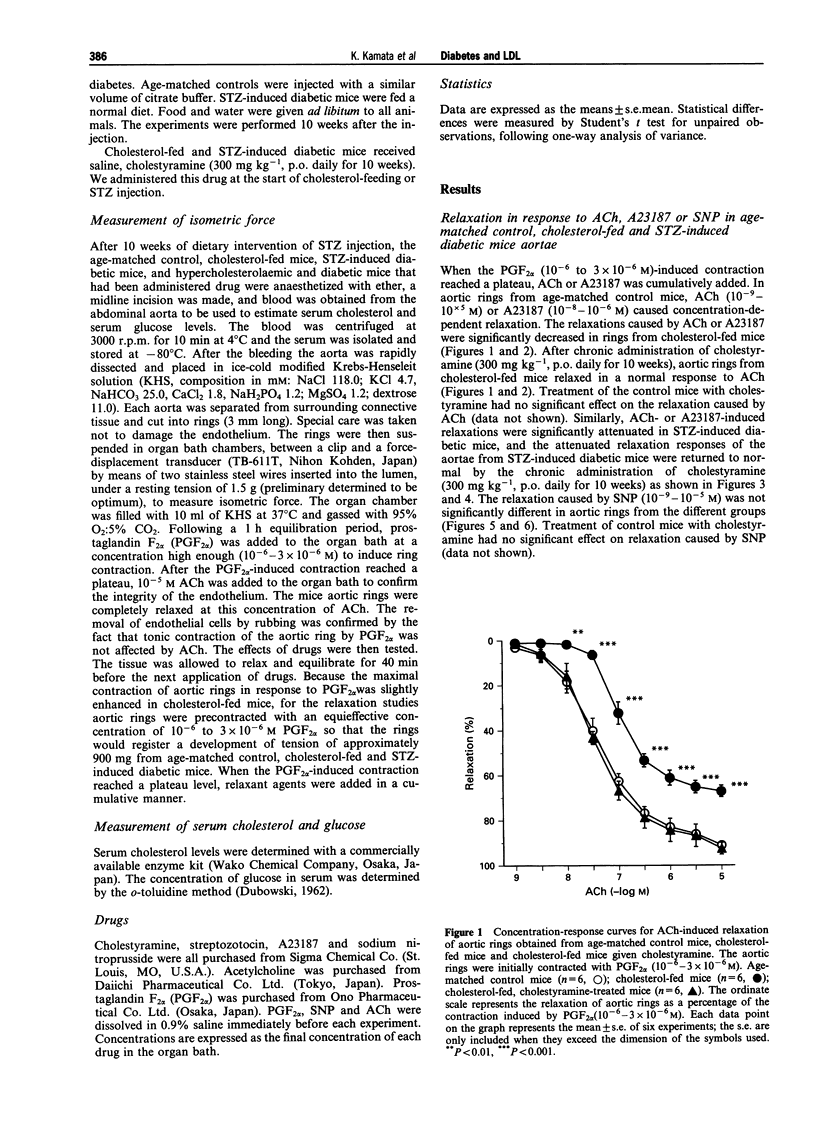
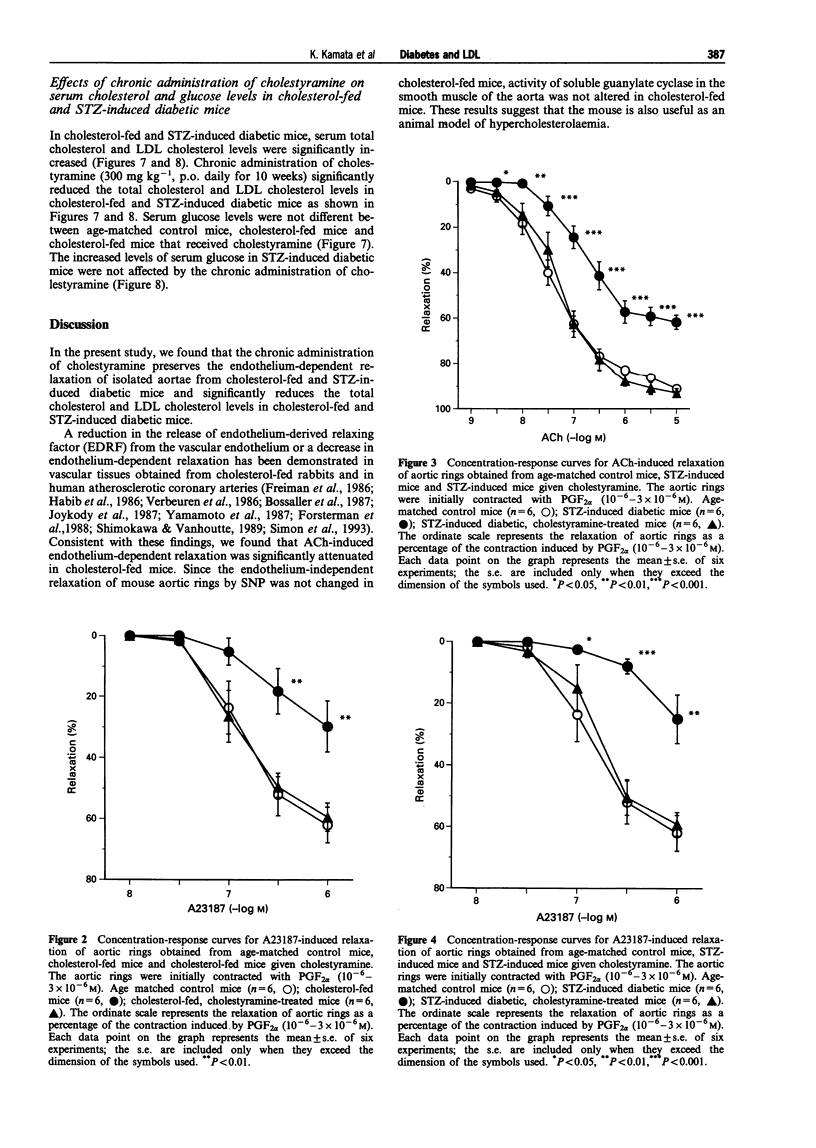
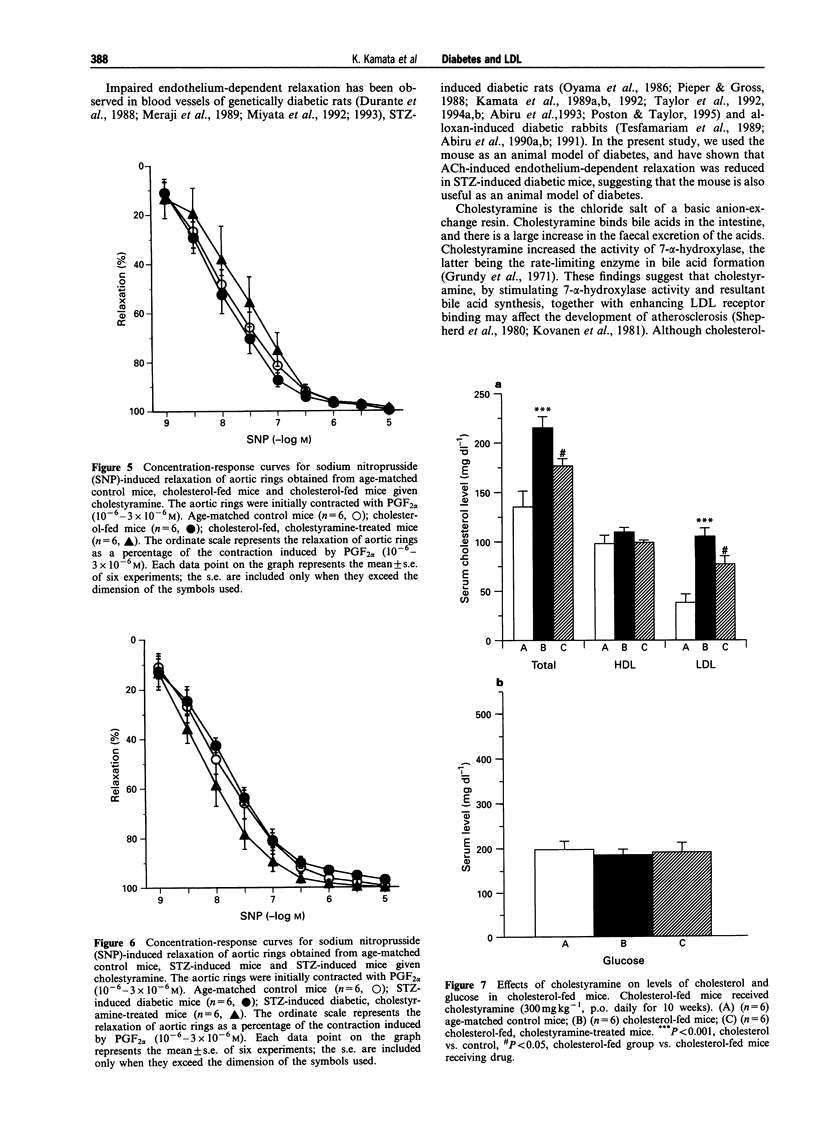
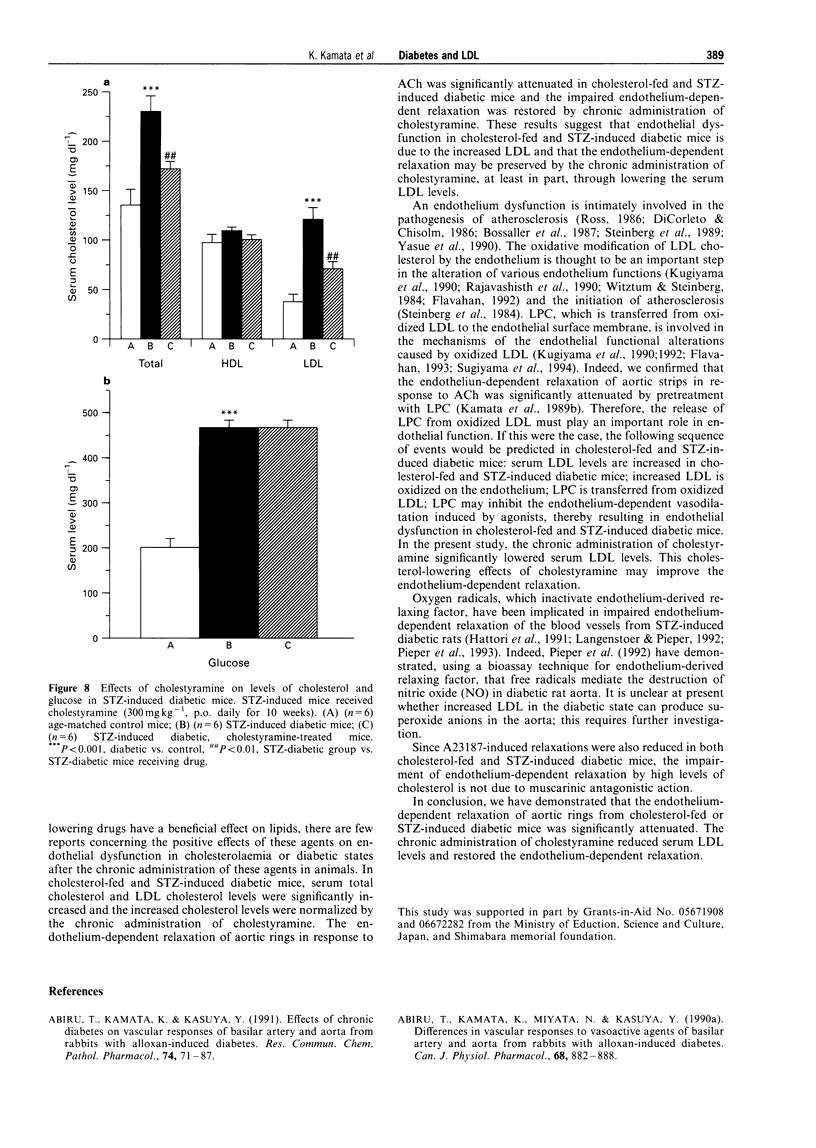
1. Experiments were designed to investigate the effects of the low density lipoprotein (LDL)-lowering drugs cholestyramine on serum LDL levels and endothelium-dependent relaxation to acetylcholine (ACh) in cholesterol-fed or streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic mice. 2. In aortic rings from control mice, ACh or A23187 caused concentration-dependent relaxation. The relaxations caused by ACh or A23187 were significantly attenuated in aortic rings from cholesterol-fed and STZ-diabetic mice. The attenuated vasodilatation in both cholesterol-fed and diabetic mice was returned to normal by chronic administration of cholestyramine. The endothelium-independent relaxations of aortic rings induced by sodium nitroprusside (SNP) were not significantly different between control, cholesterol-fed and STZ-induced diabetic mice. 3. The increased LDL levels in cholesterol-fed and diabetic mice were returned to normal by the chronic administration of cholestyramine. Chronic administration of cholestyramine had no effects on serum glucose levels. 4. These results suggest that attenuated endothelium-dependent vasodilatations in both cholesterol-fed and STZ-diabetic mice are improved by the chronic administration of cholestyramine, and these effects are, at least in part, due to lowering serum LDL levels.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abiru T., Kamata K., Kasuya Y. Effects of chronic diabetes on vascular responses of basilar artery and aorta from rabbits with alloxan-induced diabetes. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1991 Oct;74(1):71–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abiru T., Kamata K., Miyata N., Kasuya Y. Differences in vascular responses to vasoactive agents of basilar artery and aorta from rabbits with alloxan-induced diabetes. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1990 Jul;68(7):882–888. doi: 10.1139/y90-134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abiru T., Watanabe Y., Kamata K., Miyata N., Kasuya Y. Decrease in endothelium-dependent relaxation and levels of cyclic nucleotides in aorta from rabbits with alloxan-induced diabetes. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1990 Apr;68(1):13–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal D. K., McNeill J. H. Vascular responses to agonists in rat mesenteric artery from diabetic rats. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1987 Jul;65(7):1484–1490. doi: 10.1139/y87-232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berliner J. A., Territo M. C., Sevanian A., Ramin S., Kim J. A., Bamshad B., Esterson M., Fogelman A. M. Minimally modified low density lipoprotein stimulates monocyte endothelial interactions. J Clin Invest. 1990 Apr;85(4):1260–1266. doi: 10.1172/JCI114562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bossaller C., Habib G. B., Yamamoto H., Williams C., Wells S., Henry P. D. Impaired muscarinic endothelium-dependent relaxation and cyclic guanosine 5'-monophosphate formation in atherosclerotic human coronary artery and rabbit aorta. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jan;79(1):170–174. doi: 10.1172/JCI112779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christlieb A. R. Diabetes and hypertensive vascular disease. Mechanisms and treatment. Am J Cardiol. 1973 Sep 20;32(4):592–606. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(73)80051-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBOWSKI K. M. An o-toluidine method for body-fluid glucose determination. Clin Chem. 1962 May-Jun;8:215–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiCorleto P. E., Chisolm G. M., 3rd Participation of the endothelium in the development of the atherosclerotic plaque. Prog Lipid Res. 1986;25(1-4):365–374. doi: 10.1016/0163-7827(86)90074-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durante W., Sen A. K., Sunahara F. A. Impairment of endothelium-dependent relaxation in aortae from spontaneously diabetic rats. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Jun;94(2):463–468. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11548.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flavahan N. A. Atherosclerosis or lipoprotein-induced endothelial dysfunction. Potential mechanisms underlying reduction in EDRF/nitric oxide activity. Circulation. 1992 May;85(5):1927–1938. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.85.5.1927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flavahan N. A. Lysophosphatidylcholine modifies G protein-dependent signaling in porcine endothelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1993 Mar;264(3 Pt 2):H722–H727. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1993.264.3.H722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freiman P. C., Mitchell G. G., Heistad D. D., Armstrong M. L., Harrison D. G. Atherosclerosis impairs endothelium-dependent vascular relaxation to acetylcholine and thrombin in primates. Circ Res. 1986 Jun;58(6):783–789. doi: 10.1161/01.res.58.6.783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Förstermann U., Mügge A., Alheid U., Haverich A., Frölich J. C. Selective attenuation of endothelium-mediated vasodilation in atherosclerotic human coronary arteries. Circ Res. 1988 Feb;62(2):185–190. doi: 10.1161/01.res.62.2.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundy S. M., Ahrens E. H., Jr, Salen G. Interruption of the enterohepatic circulation of bile acids in man: comparative effects of cholestyramine and ileal exclusion on cholesterol metabolism. J Lab Clin Med. 1971 Jul;78(1):94–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habib J. B., Bossaller C., Wells S., Williams C., Morrisett J. D., Henry P. D. Preservation of endothelium-dependent vascular relaxation in cholesterol-fed rabbit by treatment with the calcium blocker PN 200110. Circ Res. 1986 Feb;58(2):305–309. doi: 10.1161/01.res.58.2.305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris K. H., MacLeod K. M. Influence of the endothelium on contractile responses of arteries from diabetic rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Aug 9;153(1):55–64. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90587-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori Y., Kawasaki H., Abe K., Kanno M. Superoxide dismutase recovers altered endothelium-dependent relaxation in diabetic rat aorta. Am J Physiol. 1991 Oct;261(4 Pt 2):H1086–H1094. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1991.261.4.H1086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs M., Plane F., Bruckdorfer K. R. Native and oxidized low-density lipoproteins have different inhibitory effects on endothelium-derived relaxing factor in the rabbit aorta. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 May;100(1):21–26. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12045.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayakody L., Senaratne M., Thomson A., Kappagoda T. Endothelium-dependent relaxation in experimental atherosclerosis in the rabbit. Circ Res. 1987 Feb;60(2):251–264. doi: 10.1161/01.res.60.2.251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamata K., Kojima S., Sugiura M., Kasuya Y. Preservation of endothelium-dependent vascular relaxation in cholesterol-fed mice by the chronic administration of prazosin or pravastatin. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1996 Feb;70(2):149–156. doi: 10.1254/jjp.70.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamata K., Miyata N., Abiru T., Kasuya Y. Functional changes in vascular smooth muscle and endothelium of arteries during diabetes mellitus. Life Sci. 1992;50(19):1379–1387. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(92)90256-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamata K., Miyata N., Kasuya Y. Impairment of endothelium-dependent relaxation and changes in levels of cyclic GMP in aorta from streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Jun;97(2):614–618. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11993.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamata K., Miyata N., Kasuya Y. Involvement of endothelial cells in relaxation and contraction responses of the aorta to isoproterenol in naive and streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Jun;249(3):890–894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovanen P. T., Bilheimer D. W., Goldstein J. L., Jaramillo J. J., Brown M. S. Regulatory role for hepatic low density lipoprotein receptors in vivo in the dog. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kugiyama K., Kerns S. A., Morrisett J. D., Roberts R., Henry P. D. Impairment of endothelium-dependent arterial relaxation by lysolecithin in modified low-density lipoproteins. Nature. 1990 Mar 8;344(6262):160–162. doi: 10.1038/344160a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kugiyama K., Ohgushi M., Sugiyama S., Murohara T., Fukunaga K., Miyamoto E., Yasue H. Lysophosphatidylcholine inhibits surface receptor-mediated intracellular signals in endothelial cells by a pathway involving protein kinase C activation. Circ Res. 1992 Dec;71(6):1422–1428. doi: 10.1161/01.res.71.6.1422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langenstroer P., Pieper G. M. Regulation of spontaneous EDRF release in diabetic rat aorta by oxygen free radicals. Am J Physiol. 1992 Jul;263(1 Pt 2):H257–H265. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1992.263.1.H257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludmer P. L., Selwyn A. P., Shook T. L., Wayne R. R., Mudge G. H., Alexander R. W., Ganz P. Paradoxical vasoconstriction induced by acetylcholine in atherosclerotic coronary arteries. N Engl J Med. 1986 Oct 23;315(17):1046–1051. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198610233151702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meraji S., Jayakody L., Senaratne M. P., Thomson A. B., Kappagoda T. Endothelium-dependent relaxation in aorta of BB rat. Diabetes. 1987 Aug;36(8):978–981. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.8.978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyata N., Tsuchida K., Okuyama S., Otomo S., Kamata K., Kasuya Y. Age-related changes in endothelium-dependent relaxation in aorta from genetically diabetic WBN/Kob rats. Am J Physiol. 1992 Apr;262(4 Pt 2):H1104–H1109. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1992.262.4.H1104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyata N., Yamaura H., Tsuchida K., Okuyama S., Otomo S., Kamata K., Kasuya Y. Impairment of endothelium-dependent relaxation of superior mesenteric artery in genetically diabetic WBN/Kob rats. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1993 Mar-Apr;71(3-4):297–300. doi: 10.1139/y93-046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oyama Y., Kawasaki H., Hattori Y., Kanno M. Attenuation of endothelium-dependent relaxation in aorta from diabetic rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Dec 2;132(1):75–78. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90013-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieper G. M., Gross G. J. Oxygen free radicals abolish endothelium-dependent relaxation in diabetic rat aorta. Am J Physiol. 1988 Oct;255(4 Pt 2):H825–H833. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1988.255.4.H825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieper G. M., Langenstroer P., Gross G. J. Hydroxyl radicals mediate injury to endothelium-dependent relaxation in diabetic rat. Mol Cell Biochem. 1993 May 26;122(2):139–145. doi: 10.1007/BF01076098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieper G. M., Mei D. A., Langenstroer P., O'Rourke S. T. Bioassay of endothelium-derived relaxing factor in diabetic rat aorta. Am J Physiol. 1992 Sep;263(3 Pt 2):H676–H680. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1992.263.3.H676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poston L., Taylor P. D. Glaxo/MRS Young Investigator Prize. Endothelium-mediated vascular function in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Clin Sci (Lond) 1995 Mar;88(3):245–255. doi: 10.1042/cs0880245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn M. T., Parthasarathy S., Fong L. G., Steinberg D. Oxidatively modified low density lipoproteins: a potential role in recruitment and retention of monocyte/macrophages during atherogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2995–2998. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajavashisth T. B., Andalibi A., Territo M. C., Berliner J. A., Navab M., Fogelman A. M., Lusis A. J. Induction of endothelial cell expression of granulocyte and macrophage colony-stimulating factors by modified low-density lipoproteins. Nature. 1990 Mar 15;344(6263):254–257. doi: 10.1038/344254a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis--an update. N Engl J Med. 1986 Feb 20;314(8):488–500. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198602203140806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd J., Packard C. J., Bicker S., Lawrie T. D., Morgan H. G. Cholestyramine promotes receptor-mediated low-density-lipoprotein catabolism. N Engl J Med. 1980 May 29;302(22):1219–1222. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198005293022202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimokawa H., Vanhoutte P. M. Impaired endothelium-dependent relaxation to aggregating platelets and related vasoactive substances in porcine coronary arteries in hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis. Circ Res. 1989 May;64(5):900–914. doi: 10.1161/01.res.64.5.900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon B. C., Haudenschild C. C., Cohen R. A. Preservation of endothelium-dependent relaxation in atherosclerotic rabbit aorta by probucol. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1993 Jun;21(6):893–901. doi: 10.1097/00005344-199306000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg D., Parthasarathy S., Carew T. E., Khoo J. C., Witztum J. L. Beyond cholesterol. Modifications of low-density lipoprotein that increase its atherogenicity. N Engl J Med. 1989 Apr 6;320(14):915–924. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198904063201407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinbrecher U. P., Parthasarathy S., Leake D. S., Witztum J. L., Steinberg D. Modification of low density lipoprotein by endothelial cells involves lipid peroxidation and degradation of low density lipoprotein phospholipids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3883–3887. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama S., Kugiyama K., Ohgushi M., Fujimoto K., Yasue H. Lysophosphatidylcholine in oxidized low-density lipoprotein increases endothelial susceptibility to polymorphonuclear leukocyte-induced endothelial dysfunction in porcine coronary arteries. Role of protein kinase C. Circ Res. 1994 Apr;74(4):565–575. doi: 10.1161/01.res.74.4.565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor P. D., McCarthy A. L., Thomas C. R., Poston L. Endothelium-dependent relaxation and noradrenaline sensitivity in mesenteric resistance arteries of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Oct;107(2):393–399. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb12757.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor P. D., Oon B. B., Thomas C. R., Poston L. Prevention by insulin treatment of endothelial dysfunction but not enhanced noradrenaline-induced contractility in mesenteric resistance arteries from streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Jan;111(1):35–41. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb14020.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor P. D., Wickenden A. D., Mirrlees D. J., Poston L. Endothelial function in the isolated perfused mesentery and aortae of rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes: effect of treatment with the aldose reductase inhibitor, ponalrestat. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Jan;111(1):42–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb14021.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tesfamariam B., Jakubowski J. A., Cohen R. A. Contraction of diabetic rabbit aorta caused by endothelium-derived PGH2-TxA2. Am J Physiol. 1989 Nov;257(5 Pt 2):H1327–H1333. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1989.257.5.H1327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbeuren T. J., Jordaens F. H., Zonnekeyn L. L., Van Hove C. E., Coene M. C., Herman A. G. Effect of hypercholesterolemia on vascular reactivity in the rabbit. I. Endothelium-dependent and endothelium-independent contractions and relaxations in isolated arteries of control and hypercholesterolemic rabbits. Circ Res. 1986 Apr;58(4):552–564. doi: 10.1161/01.res.58.4.552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witztum J. L., Steinberg D. Role of oxidized low density lipoprotein in atherogenesis. J Clin Invest. 1991 Dec;88(6):1785–1792. doi: 10.1172/JCI115499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto Y., Tomoike H., Egashira K., Nakamura M. Attenuation of endothelium-related relaxation and enhanced responsiveness of vascular smooth muscle to histamine in spastic coronary arterial segments from miniature pigs. Circ Res. 1987 Dec;61(6):772–778. doi: 10.1161/01.res.61.6.772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasue H., Matsuyama K., Matsuyama K., Okumura K., Morikami Y., Ogawa H. Responses of angiographically normal human coronary arteries to intracoronary injection of acetylcholine by age and segment. Possible role of early coronary atherosclerosis. Circulation. 1990 Feb;81(2):482–490. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.81.2.482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama M., Hirata K., Miyake R., Akita H., Ishikawa Y., Fukuzaki H. Lysophosphatidylcholine: essential role in the inhibition of endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation by oxidized low density lipoprotein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Apr 16;168(1):301–308. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91708-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


