Abstract
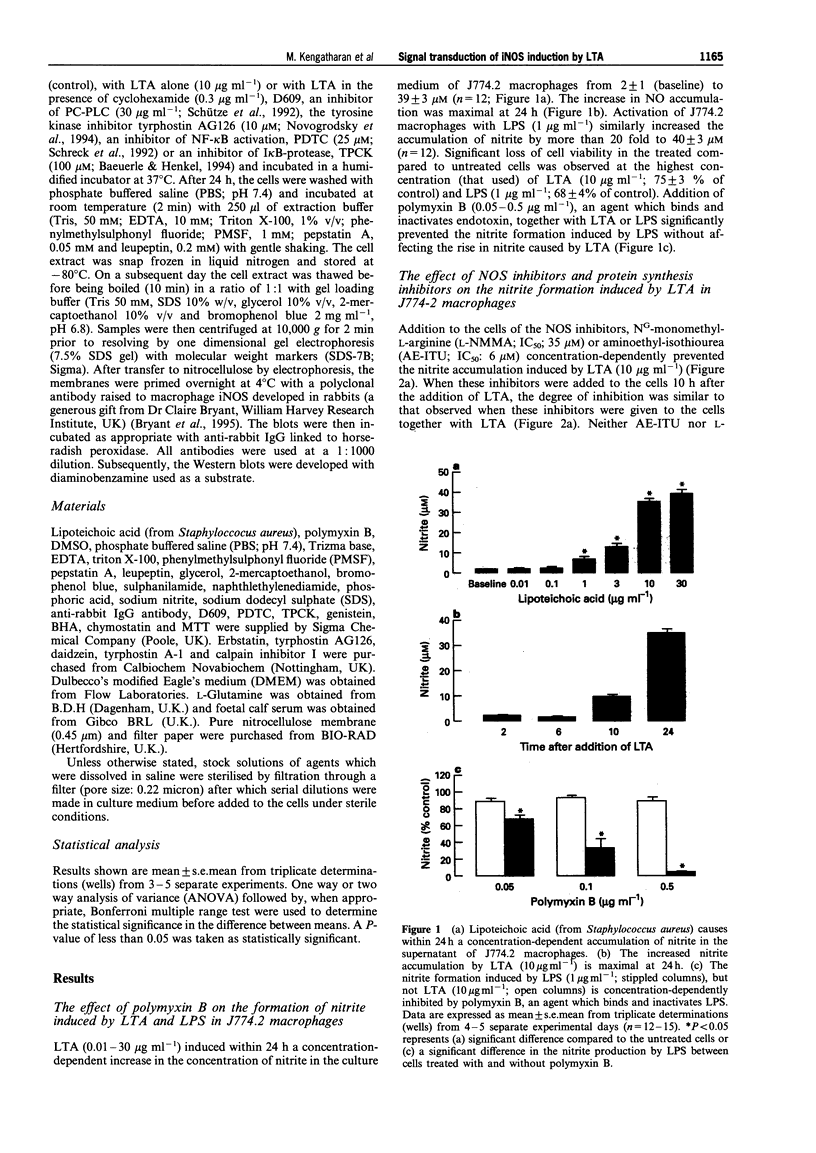
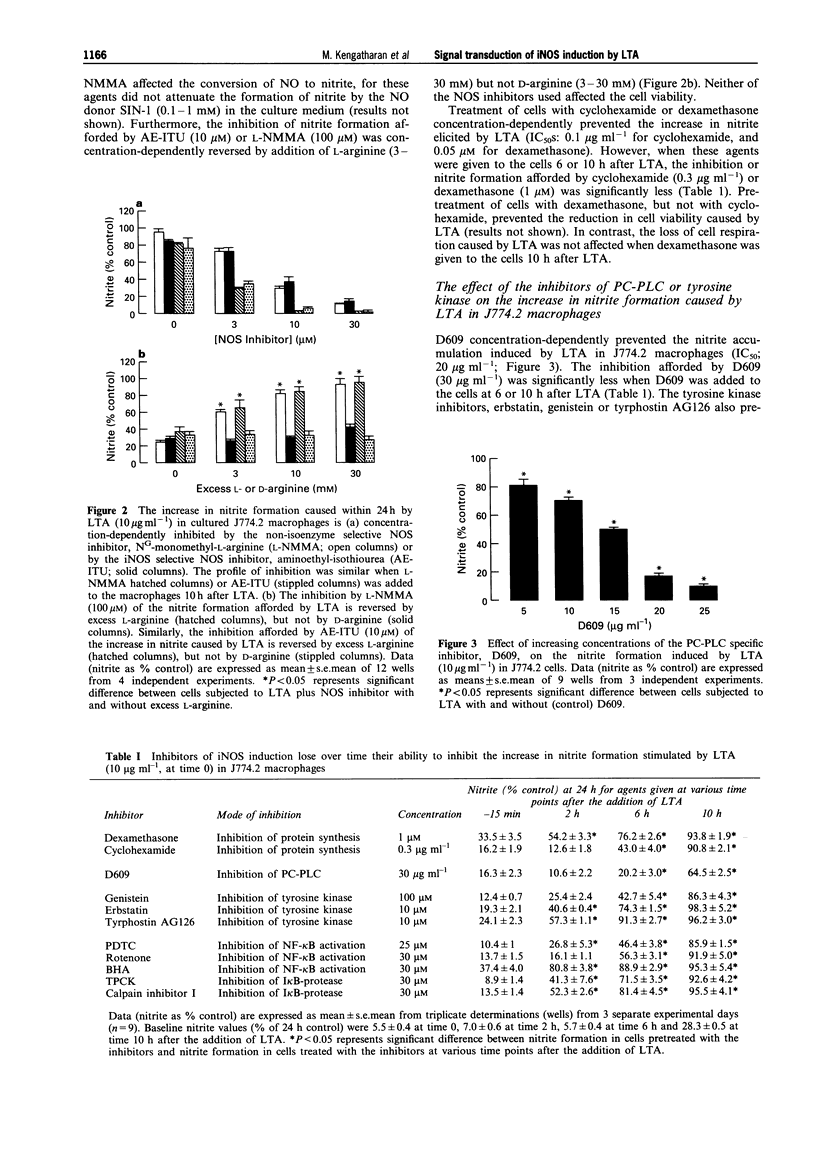
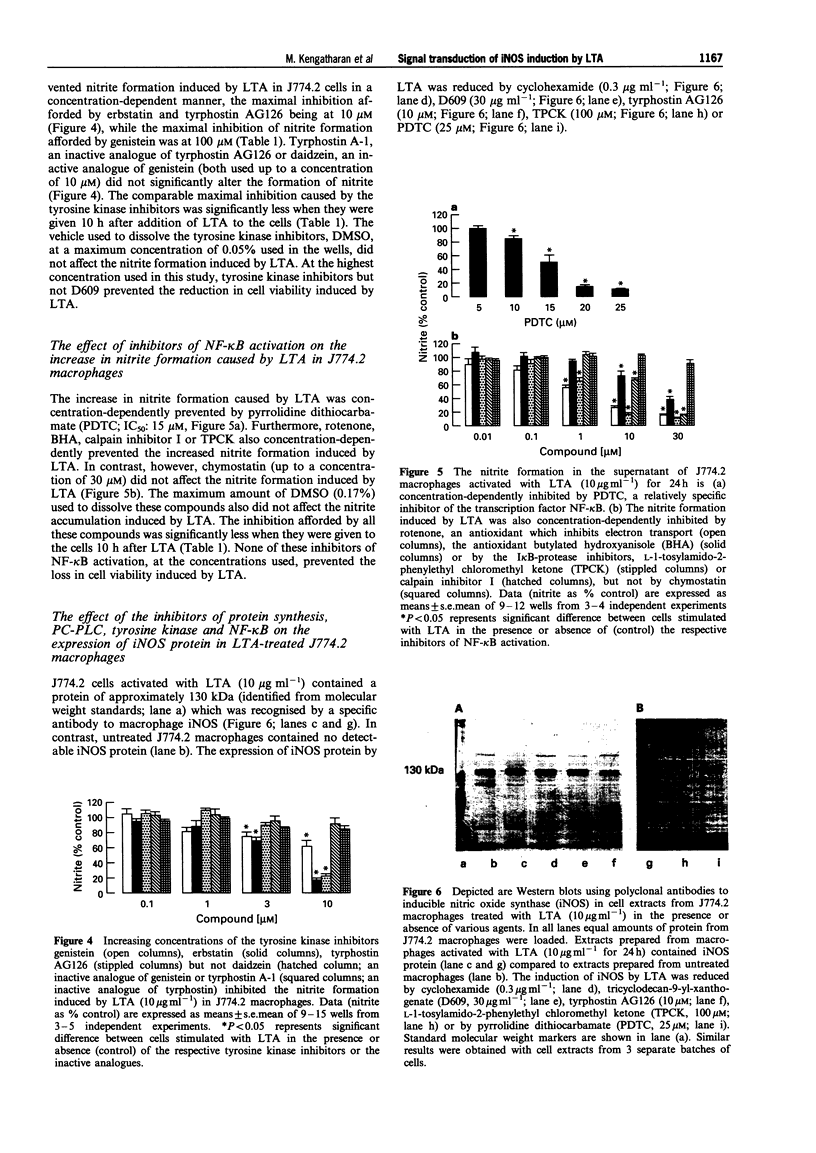
1. This study investigates the signal transduction mechanisms leading to the enhanced formation of nitric oxide (NO) due to the induction of NO synthase (iNOS) in murine J774.2 macrophages in culture activated with lipoteichoic acid (LTA), a cell wall component of the gram-positive bacterium Staphylococcus aureus. 2. LTA (10 microgram ml-1) caused within 24 h an enhanced accumulation of nitrite (an indicator of NO biosynthesis) in the supernatant of J774.2 macrophages which was prevented by the non-selective NOS inhibitor NG-monomethyl-L-arginine (L-NMMA; IC50: 35 microM) or by the iNOS-selective NOS inhibitor, aminoethyl-isothiourea (AE-ITU; IC50: 6 microM). The inhibition of nitrite formation afforded by these agents was prevented by excess L-arginine (3-30 mM), but not by D-arginine (3-30 mM). Furthermore, the degree of iNOS inhibition was similar when these NOS inhibitors were added to the macrophages 10 h after LTA. 3. Pretreatment of J774.2 macrophages with cyclohexamide or dexamethasone prevented the enhanced formation of nitrite caused by LTA. This inhibition did not occur when dexamethasone or cyclohexamide were added to the cells 10 h after LTA. The increase in nitrite formation stimulated by LTA (10 micrograms ml-1) was not affected by polymyxin B (0.05-0.5 microgram ml-1), an agent which binds and inactivates endotoxin. 4. A specific inhibitor of phosphatidylcholine-phospholipase C (PC-PLC), D609, prevented the increase in nitrite formation (IC50 = 20 micrograms ml-1) caused by LTA. The inhibition afforded by D609 was significantly smaller when this agent was added to the cells 10 h after LTA. 5. The structurally distinct tyrosine kinase inhibitors, erbstatin, genistein, and tyrphostin AG126 prevented the formation of nitrite caused by LTA. The inhibition afforded by these compounds was significantly attenuated when they were added to the cells 10 h after LTA. In contrast, daidzein or tyrphostin A-1, which are inactive analogues of genistein and tyrphostin (up to a concentration of 10 microM) did not affect the nitrite formation caused by LTA. 6. Inhibitors of the activation of the nuclear transcription factor NF-kappa B such as pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate (PDTC; an antioxidant and a metal chelator), butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA; an antioxidant), L-1-tosylamido-2-phenylethyl chloromethyl ketone (TPCK), calpain inhibitor I (both I kappa B-protease inhibitors), or rotenone (an antioxidant which inhibits electron transport) prevented the nitrite formation stimulated by LTA. The inhibition afforded by these agents was significantly smaller when they were added to the macrophages 10 h after LTA. 7. Incubation of J774.2 cells with LTA over 24 h resulted in the expression of iNOS protein (130 kDa) as identified by Western blot analysis. The expression of iNOS protein by LTA was significantly attenuated by cyclohexamide, D609, tyrphostin AG126, PDTC or by TPCK. 8. Thus, the signal transduction leading to the expression of iNOS protein and activity caused by LTA in murine J774.2 macrophages involves (i) the activation of PC-PLC, (ii) phosphorylation of tyrosine kinase, and (iii) the activation of the transcription factor NF-kappa B.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akarasereenont P., Mitchell J. A., Appleton I., Thiemermann C., Vane J. R. Involvement of tyrosine kinase in the induction of cyclo-oxygenase and nitric oxide synthase by endotoxin in cultured cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Dec;113(4):1522–1528. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb17169.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akarasereenont P., Mitchell J. A., Bakhle Y. S., Thiemermann C., Vane J. R. Comparison of the induction of cyclooxygenase and nitric oxide synthase by endotoxin in endothelial cells and macrophages. Eur J Pharmacol. 1995 Jan 24;273(1-2):121–128. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(94)00680-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auguet M., Lonchampt M. O., Delaflotte S., Goulin-Schulz J., Chabrier P. E., Braquet P. Induction of nitric oxide synthase by lipoteichoic acid from Staphylococcus aureus in vascular smooth muscle cells. FEBS Lett. 1992 Feb 3;297(1-2):183–185. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80356-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A., Henkel T. Function and activation of NF-kappa B in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:141–179. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.12.040194.001041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bone R. C. Gram-positive organisms and sepsis. Arch Intern Med. 1994 Jan 10;154(1):26–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant C. E., Tomlinson A., Mitchell J. A., Thiemermann C., Willoughby D. A. Nitric oxide synthase in the rat fallopian tube is regulated during the oestrous cycle. J Endocrinol. 1995 Jul;146(1):149–157. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1460149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casnellie J. E. Protein kinase inhibitors: probes for the functions of protein phosphorylation. Adv Pharmacol. 1991;22:167–205. doi: 10.1016/s1054-3589(08)60035-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho H. J., Xie Q. W., Calaycay J., Mumford R. A., Swiderek K. M., Lee T. D., Nathan C. Calmodulin is a subunit of nitric oxide synthase from macrophages. J Exp Med. 1992 Aug 1;176(2):599–604. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.2.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunha F. Q., Moss D. W., Leal L. M., Moncada S., Liew F. Y. Induction of macrophage parasiticidal activity by Staphylococcus aureus and exotoxins through the nitric oxide synthesis pathway. Immunology. 1993 Apr;78(4):563–567. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Kimpe S. J., Hunter M. L., Bryant C. E., Thiemermann C., Vane J. R. Delayed circulatory failure due to the induction of nitric oxide synthase by lipoteichoic acid from Staphylococcus aureus in anaesthetized rats. Br J Pharmacol. 1995 Mar;114(6):1317–1323. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb13349.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinerman J. L., Lowenstein C. J., Snyder S. H. Molecular mechanisms of nitric oxide regulation. Potential relevance to cardiovascular disease. Circ Res. 1993 Aug;73(2):217–222. doi: 10.1161/01.res.73.2.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapier J. C., Wietzerbin J., Hibbs J. B., Jr Interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor induce the L-arginine-dependent cytotoxic effector mechanism in murine macrophages. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Oct;18(10):1587–1592. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830181018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dziarski R. Cell-bound albumin is the 70-kDa peptidoglycan-, lipopolysaccharide-, and lipoteichoic acid-binding protein on lymphocytes and macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 12;269(32):20431–20436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberhardt W., Kunz D., Pfeilschifter J. Pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate differentially affects interleukin 1 beta- and cAMP-induced nitric oxide synthase expression in rat renal mesangial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Apr 15;200(1):163–170. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. D. Specific commitment of different pre-mRNAs to splicing by single SR proteins. Nature. 1993 Sep 2;365(6441):82–85. doi: 10.1038/365082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garvey E. P., Oplinger J. A., Tanoury G. J., Sherman P. A., Fowler M., Marshall S., Harmon M. F., Paith J. E., Furfine E. S. Potent and selective inhibition of human nitric oxide synthases. Inhibition by non-amino acid isothioureas. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 28;269(43):26669–26676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm S., Baeuerle P. A. The inducible transcription factor NF-kappa B: structure-function relationship of its protein subunits. Biochem J. 1993 Mar 1;290(Pt 2):297–308. doi: 10.1042/bj2900297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross S. S., Stuehr D. J., Aisaka K., Jaffe E. A., Levi R., Griffith O. W. Macrophage and endothelial cell nitric oxide synthesis: cell-type selective inhibition by NG-aminoarginine, NG-nitroarginine and NG-methylarginine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jul 16;170(1):96–103. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91245-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imoto M., Umezawa K., Isshiki K., Kunimoto S., Sawa T., Takeuchi T., Umezawa H. Kinetic studies of tyrosine kinase inhibition by erbstatin. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1987 Oct;40(10):1471–1473. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.40.1471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwasaki T., Uehara Y., Graves L., Rachie N., Bomsztyk K. Herbimycin A blocks IL-1-induced NF-kappa B DNA-binding activity in lymphoid cell lines. FEBS Lett. 1992 Feb 24;298(2-3):240–244. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80067-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitzki A., Gilon C. Tyrphostins as molecular tools and potential antiproliferative drugs. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1991 May;12(5):171–174. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(91)90538-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. C., Brown K., Siebenlist U. Activation of NF-kappa B requires proteolysis of the inhibitor I kappa B-alpha: signal-induced phosphorylation of I kappa B-alpha alone does not release active NF-kappa B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jan 17;92(2):552–556. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.2.552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowenstein C. J., Glatt C. S., Bredt D. S., Snyder S. H. Cloned and expressed macrophage nitric oxide synthase contrasts with the brain enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):6711–6715. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.6711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons C. R., Orloff G. J., Cunningham J. M. Molecular cloning and functional expression of an inducible nitric oxide synthase from a murine macrophage cell line. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):6370–6374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marczin N., Papapetropoulos A., Catravas J. D. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors suppress endotoxin- and IL-1 beta-induced NO synthesis in aortic smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol. 1993 Sep;265(3 Pt 2):H1014–H1018. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1993.265.3.H1014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto S., Maki M., Schmitt M. J., Hatanaka M., Verma I. M. Tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced phosphorylation of I kappa B alpha is a signal for its degradation but not dissociation from NF-kappa B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Dec 20;91(26):12740–12744. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.26.12740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Higgs A. The L-arginine-nitric oxide pathway. N Engl J Med. 1993 Dec 30;329(27):2002–2012. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199312303292706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Palmer R. M., Higgs E. A. Nitric oxide: physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev. 1991 Jun;43(2):109–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Dec 16;65(1-2):55–63. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90303-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novogrodsky A., Vanichkin A., Patya M., Gazit A., Osherov N., Levitzki A. Prevention of lipopolysaccharide-induced lethal toxicity by tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Science. 1994 May 27;264(5163):1319–1322. doi: 10.1126/science.8191285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radomski M. W., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. Glucocorticoids inhibit the expression of an inducible, but not the constitutive, nitric oxide synthase in vascular endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):10043–10047. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.10043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read M. A., Cordle S. R., Veach R. A., Carlisle C. D., Hawiger J. Cell-free pool of CD14 mediates activation of transcription factor NF-kappa B by lipopolysaccharide in human endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 1;90(21):9887–9891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.21.9887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees D. D., Cellek S., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. Dexamethasone prevents the induction by endotoxin of a nitric oxide synthase and the associated effects on vascular tone: an insight into endotoxin shock. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Dec 14;173(2):541–547. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80068-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schieven G. L., Kirihara J. M., Myers D. E., Ledbetter J. A., Uckun F. M. Reactive oxygen intermediates activate NF-kappa B in a tyrosine kinase-dependent mechanism and in combination with vanadate activate the p56lck and p59fyn tyrosine kinases in human lymphocytes. Blood. 1993 Aug 15;82(4):1212–1220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreck R., Baeuerle P. A. A role for oxygen radicals as second messengers. Trends Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;1(2-3):39–42. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(91)90072-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze-Osthoff K., Bakker A. C., Vanhaesebroeck B., Beyaert R., Jacob W. A., Fiers W. Cytotoxic activity of tumor necrosis factor is mediated by early damage of mitochondrial functions. Evidence for the involvement of mitochondrial radical generation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 15;267(8):5317–5323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schütze S., Potthoff K., Machleidt T., Berkovic D., Wiegmann K., Krönke M. TNF activates NF-kappa B by phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C-induced "acidic" sphingomyelin breakdown. Cell. 1992 Nov 27;71(5):765–776. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90553-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman M. P., Aeberhard E. E., Wong V. Z., Griscavage J. M., Ignarro L. J. Pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate inhibits induction of nitric oxide synthase activity in rat alveolar macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Mar 31;191(3):1301–1308. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southan G. J., Szabó C., Thiemermann C. Isothioureas: potent inhibitors of nitric oxide synthases with variable isoform selectivity. Br J Pharmacol. 1995 Jan;114(2):510–516. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb13256.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabó C., Mitchell J. A., Gross S. S., Thiemermann C., Vane J. R. Nifedipine inhibits the induction of nitric oxide synthase by bacterial lipopolysaccharide. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 May;265(2):674–680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada H., Kawabata Y., Arakaki R., Kusumoto S., Fukase K., Suda Y., Yoshimura T., Kokeguchi S., Kato K., Komuro T. Molecular and structural requirements of a lipoteichoic acid from Enterococcus hirae ATCC 9790 for cytokine-inducing, antitumor, and antigenic activities. Infect Immun. 1995 Jan;63(1):57–65. doi: 10.1128/iai.63.1.57-65.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiemermann C. The role of the L-arginine: nitric oxide pathway in circulatory shock. Adv Pharmacol. 1994;28:45–79. doi: 10.1016/s1054-3589(08)60493-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschaikowsky K., Meisner M., Schönhuber F., Rügheimer E. Induction of nitric oxide synthase activity in phagocytic cells inhibited by tricyclodecan-9-yl-xanthogenate (D609). Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Nov;113(3):664–668. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb17043.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Ramos R. A., Tobias P. S., Ulevitch R. J., Mathison J. C. CD14, a receptor for complexes of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and LPS binding protein. Science. 1990 Sep 21;249(4975):1431–1433. doi: 10.1126/science.1698311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. C., Croxtall J. D., Perretti M., Bryant C. E., Thiemermann C., Flower R. J., Vane J. R. Lipocortin 1 mediates the inhibition by dexamethasone of the induction by endotoxin of nitric oxide synthase in the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Apr 11;92(8):3473–3477. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.8.3473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie Q. W., Kashiwabara Y., Nathan C. Role of transcription factor NF-kappa B/Rel in induction of nitric oxide synthase. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 18;269(7):4705–4708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]