Abstract
1. A number of putative endothelin (ET) receptor ligands were synthesized with a view to assessing their relative affinity for human recombinant ET receptors. 2. Human (h) and endothelin ETA and ETB receptor open reading frames were cloned by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction into the mammalian expression vector pcDNA1 and stable cell lines were created by transfection of Chinese hamster ovary cells. 3. Scatchard analyses of saturation isotherms for the specific binding of [125I]-endothelin-1 ([125I]-ET-1) to membranes, prepared from Chinese hamster ovary cells transfected with hETA or hETB receptors, yielded values for equilibrium dissociation constants (Kd) of 20.5 +/- 1.8 pM and 25.5 +/- 5.5 pM, respectively. Hill coefficients did not differ significantly from unity, suggesting binding to homogeneous, non-interacting receptor populations. 4. Pharmacological characterization of the transfected hETA and hETB receptors was undertaken by measuring the relative abilities of ETA and ETB receptor-selective peptide ligands to inhibit binding of [125I]ET-1. For interaction with hETA receptors, the relative order of potency was ET-1 > ET-3 = FR139317 = BQ123 >[Ala1,3,11,15]-ET-1 = sarafotoxin S6c (S6c). In contrast, the relative order of potency, at hETB receptors, was ET-1 = ET-3 = [Ala1,3,11,15]-ET-1 = S6c >> FR139317 = BQ123. 5. The novel non-peptide ligands, Ro 46-2005, SB 209670 and BMS 182874, were found to inhibit [125I]-ET-1 binding to human recombinant ETA and ETB receptors.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF
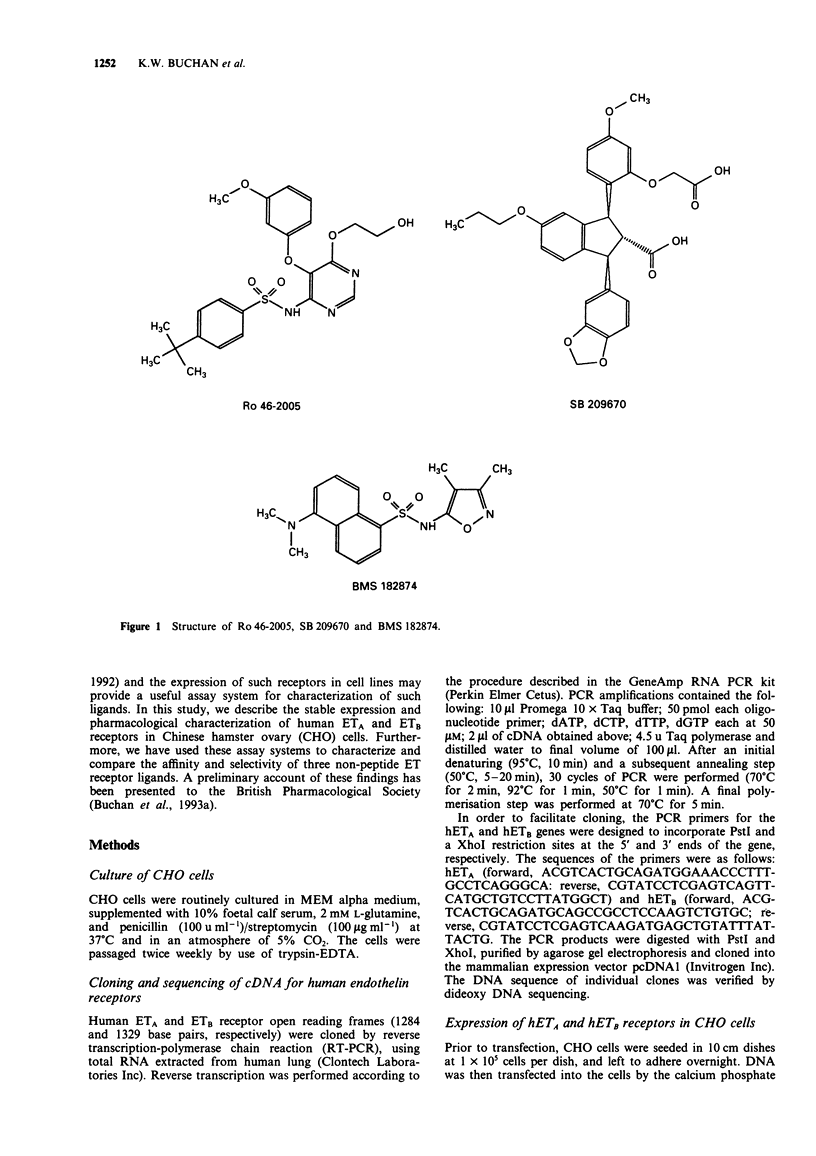

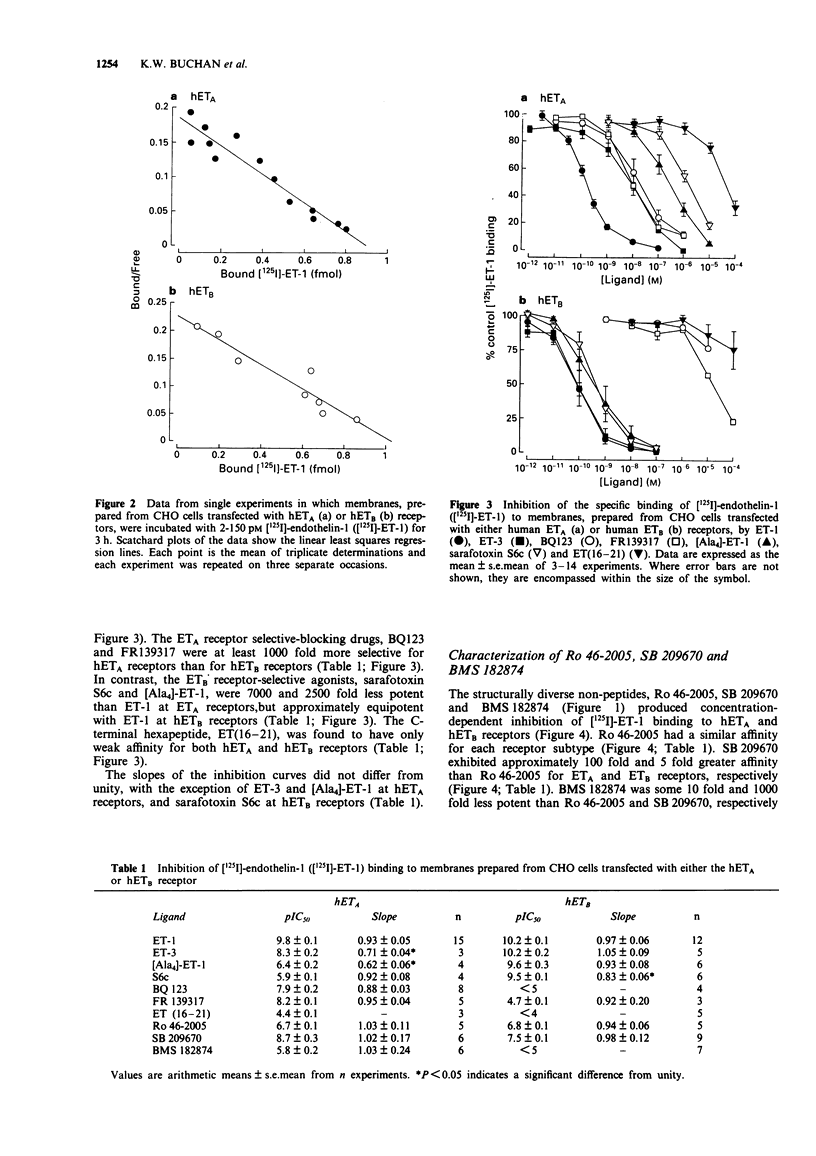
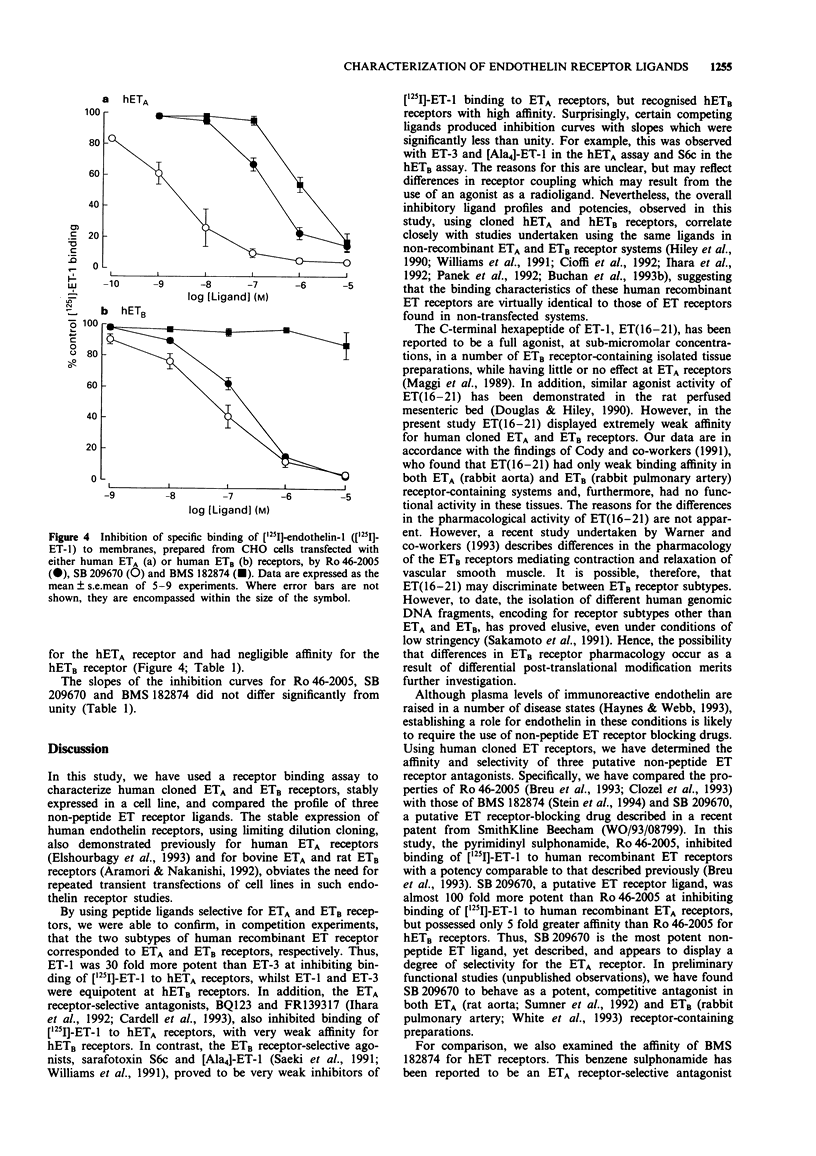


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi M., Yang Y. Y., Furuichi Y., Miyamoto C. Cloning and characterization of cDNA encoding human A-type endothelin receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Nov 14;180(3):1265–1272. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81332-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai H., Hori S., Aramori I., Ohkubo H., Nakanishi S. Cloning and expression of a cDNA encoding an endothelin receptor. Nature. 1990 Dec 20;348(6303):730–732. doi: 10.1038/348730a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aramori I., Nakanishi S. Coupling of two endothelin receptor subtypes to differing signal transduction in transfected Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):12468–12474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breu V., Löffler B. M., Clozel M. In vitro characterization of Ro 46-2005, a novel synthetic non-peptide endothelin antagonist of ETA and ETB receptors. FEBS Lett. 1993 Nov 15;334(2):210–214. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81713-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchan K. W., Sumner M. J., Watts I. S. Human placental membranes contain predominantly ETB receptors. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1993;22 (Suppl 8):S136–S139. doi: 10.1097/00005344-199322008-00037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardell L. O., Uddman R., Edvinsson L. A novel ETA-receptor antagonist, FR 139317, inhibits endothelin-induced contractions of guinea-pig pulmonary arteries, but not trachea. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Feb;108(2):448–452. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb12824.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y., Prusoff W. H. Relationship between the inhibition constant (K1) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Dec 1;22(23):3099–3108. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90196-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cioffi C. L., Neale R. F., Jr, Jackson R. H., Sills M. A. Characterization of rat lung endothelin receptor subtypes which are coupled to phosphoinositide hydrolysis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Aug;262(2):611–618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clozel M., Breu V., Burri K., Cassal J. M., Fischli W., Gray G. A., Hirth G., Löffler B. M., Müller M., Neidhart W. Pathophysiological role of endothelin revealed by the first orally active endothelin receptor antagonist. Nature. 1993 Oct 21;365(6448):759–761. doi: 10.1038/365759a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLean A., Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Simultaneous analysis of families of sigmoidal curves: application to bioassay, radioligand assay, and physiological dose-response curves. Am J Physiol. 1978 Aug;235(2):E97–102. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.235.2.E97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas S. A., Hiley C. R. Endothelium-dependent vascular activities of endothelin-like peptides in the isolated superior mesenteric arterial bed of the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Sep;101(1):81–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12093.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elshourbagy N. A., Korman D. R., Wu H. L., Sylvester D. R., Lee J. A., Nuthalaganti P., Bergsma D. J., Kumar C. S., Nambi P. Molecular characterization and regulation of the human endothelin receptors. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 25;268(6):3873–3879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes W. G., Webb D. J. The endothelin family of peptides: local hormones with diverse roles in health and disease? Clin Sci (Lond) 1993 May;84(5):485–500. doi: 10.1042/cs0840485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiley C. R., Jones C. R., Pelton J. T., Miller R. C. Binding of [125I]-endothelin-1 to rat cerebellar homogenates and its interactions with some analogues. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Oct;101(2):319–324. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12708.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihara M., Noguchi K., Saeki T., Fukuroda T., Tsuchida S., Kimura S., Fukami T., Ishikawa K., Nishikibe M., Yano M. Biological profiles of highly potent novel endothelin antagonists selective for the ETA receptor. Life Sci. 1992;50(4):247–255. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(92)90331-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh H., Hiraoka N., Higuchi H., Ito M., Konishi T., Nakano T. Contractile actions of endothelin-1 in isolated helical strips from rat pulmonary artery: potentiation of serotonin-induced contraction. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1992 Jul;20(1):1–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi C. A., Giuliani S., Patacchini R., Rovero P., Giachetti A., Meli A. The activity of peptides of the endothelin family in various mammalian smooth muscle preparations. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Dec 12;174(1):23–31. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90869-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panek R. L., Major T. C., Hingorani G. P., Doherty A. M., Taylor D. G., Rapundalo S. T. Endothelin and structurally related analogs distinguish between endothelin receptor subtypes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Mar 16;183(2):566–571. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)90519-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saeki T., Ihara M., Fukuroda T., Yamagiwa M., Yano M. [Ala1,3,11,15]endothelin-1 analogs with ETB agonistic activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Aug 30;179(1):286–292. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91367-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto A., Yanagisawa M., Sakurai T., Takuwa Y., Yanagisawa H., Masaki T. Cloning and functional expression of human cDNA for the ETB endothelin receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jul 31;178(2):656–663. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90158-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurai T., Yanagisawa M., Masaki T. Molecular characterization of endothelin receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992 Mar;13(3):103–108. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(92)90038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurai T., Yanagisawa M., Takuwa Y., Miyazaki H., Kimura S., Goto K., Masaki T. Cloning of a cDNA encoding a non-isopeptide-selective subtype of the endothelin receptor. Nature. 1990 Dec 20;348(6303):732–735. doi: 10.1038/348732a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein P. D., Hunt J. T., Floyd D. M., Moreland S., Dickinson K. E., Mitchell C., Liu E. C., Webb M. L., Murugesan N., Dickey J. The discovery of sulfonamide endothelin antagonists and the development of the orally active ETA antagonist 5-(dimethylamino)-N-(3,4-dimethyl-5-isoxazolyl)-1-naphthalenesulf onamide. J Med Chem. 1994 Feb 4;37(3):329–331. doi: 10.1021/jm00029a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumner M. J., Cannon T. R., Mundin J. W., White D. G., Watts I. S. Endothelin ETA and ETB receptors mediate vascular smooth muscle contraction. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Nov;107(3):858–860. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14537.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waggoner W. G., Genova S. L., Rash V. A. Kinetic analyses demonstrate that the equilibrium assumption does not apply to [125I]endothelin-1 binding data. Life Sci. 1992;51(24):1869–1876. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(92)90038-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner T. D., Allcock G. H., Corder R., Vane J. R. Use of the endothelin antagonists BQ-123 and PD 142893 to reveal three endothelin receptors mediating smooth muscle contraction and the release of EDRF. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Oct;110(2):777–782. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13879.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiland G. A., Molinoff P. B. Quantitative analysis of drug-receptor interactions: I. Determination of kinetic and equilibrium properties. Life Sci. 1981 Jul 27;29(4):313–330. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90324-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White D. G., Cannon T. R., Garratt H., Mundin J. W., Sumner M. J., Watts I. S. Endothelin ETA and ETB receptors mediate vascular smooth-muscle contraction. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1993;22 (Suppl 8):S144–S148. doi: 10.1097/00005344-199322008-00039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. L., Jr, Jones K. L., Pettibone D. J., Lis E. V., Clineschmidt B. V. Sarafotoxin S6c: an agonist which distinguishes between endothelin receptor subtypes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Mar 15;175(2):556–561. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91601-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa M., Masaki T. Endothelin, a novel endothelium-derived peptide. Pharmacological activities, regulation and possible roles in cardiovascular control. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 Jun 15;38(12):1877–1883. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90484-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


