Abstract
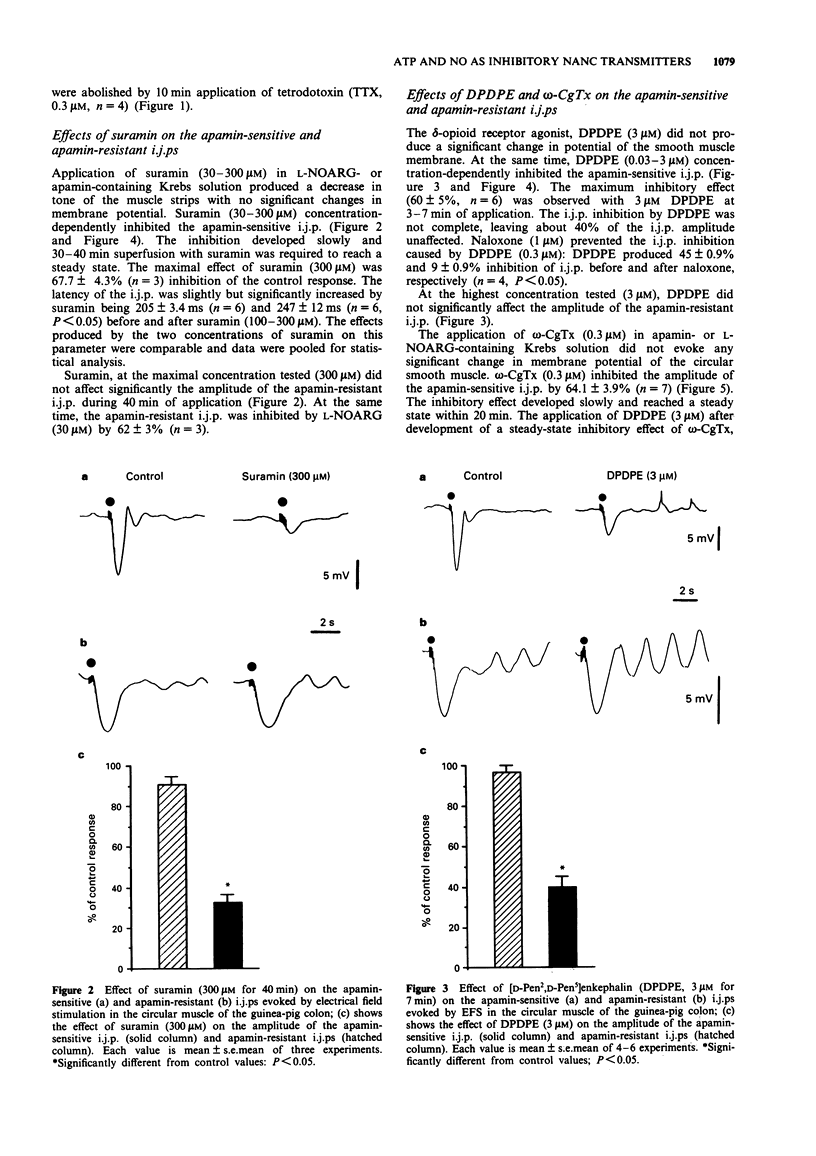
1. The effect of the P2-purinoceptor antagonist, suramin, the specific N-type voltage-dependent calcium channel blocker, omega-conotoxin GVIA (omega-CgTx) and the delta-opioid receptor agonist [D-Pen2,D-Pen5] enkephalin (DPDPE) on the apamin-sensitive and apamin-resistant inhibitory junction potentials (i.j.ps) produced by electrical field stimulation (EFS) were investigated by means of a sucrose-gap technique in the circular muscle of the guinea-pig colon. 2. After incubation of muscle strips in either atropine (1 microM), guanethidine (3 microM) and NG-nitro-L-arginine (L-NOARG, 30 microM) or atropine, guanethidine and apamin (0.3 microM), the addition of the NK1 receptor antagonist, SR 140,333 (1 microM) abolished the non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic (NANC) excitatory junction potential (e.j.p.) and unmasked a pure apamin-sensitive i.j.p. (in the presence of L-NOARG) or a pure apamin-resistant i.j.p. (in the presence of apamin). Both types of i.j.p. were abolished by tetrodotoxin. 3. Suramin (30-300 microM) concentration-dependently inhibited the apamin-sensitive i.j.p., while the apamin-resistant i.j.p. was not significantly affected by suramin (up to 300 microM). L-NOARG (30 microM) markedly reduced the apamin-resistant i.j.p. 4. The delta-opioid receptor agonist, DPDPE (0.03-3 microM) concentration-dependently reduced the apamin-sensitive i.j.p., while leaving the apamin-resistant i.j.p. unaffected. Naloxone (1 microM) prevented the i.j.p. inhibition evoked by DPDPE (0.3 microM). 5. omega-CgTx (0.3 microM) markedly reduced the apamin-sensitive but not the apamin-resistant i.j.p.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akins P. T., McCleskey E. W. Characterization of potassium currents in adult rat sensory neurons and modulation by opioids and cyclic AMP. Neuroscience. 1993 Oct;56(3):759–769. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(93)90372-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artemenko D. P., Buryi V. A., Vladimirova I. A., Shuba M. F. Modifikatsiia metoda odinarnogo sakharoznogo mostika. Fiziol Zh. 1982 May;28(3):374–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeckxstaens G. E., De Man J. G., Pelckmans P. A., Cromheeke K. M., Herman A. G., Van Maercke Y. M. Ca2+ dependency of the release of nitric oxide from non-adrenergic non-cholinergic nerves. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Dec;110(4):1329–1334. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13964.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeckxstaens G. E., Pelckmans P. A., Bult H., De Man J. G., Herman A. G., Van Maercke Y. M. Non-adrenergic non-cholinergic relaxation mediated by nitric oxide in the canine ileocolonic junction. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov 6;190(1-2):239–246. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)94132-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Hwang P. M., Snyder S. H. Localization of nitric oxide synthase indicating a neural role for nitric oxide. Nature. 1990 Oct 25;347(6295):768–770. doi: 10.1038/347768a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G. Review lecture. Neurotransmitters and trophic factors in the autonomic nervous system. J Physiol. 1981;313:1–35. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa M., Furness J. B., Pompolo S., Brookes S. J., Bornstein J. C., Bredt D. S., Snyder S. H. Projections and chemical coding of neurons with immunoreactivity for nitric oxide synthase in the guinea-pig small intestine. Neurosci Lett. 1992 Dec 14;148(1-2):121–125. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(92)90819-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crist J. R., He X. D., Goyal R. K. Both ATP and the peptide VIP are inhibitory neurotransmitters in guinea-pig ileum circular muscle. J Physiol. 1992 Feb;447:119–131. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp018994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Luca A., Li C. G., Rand M. J., Reid J. J., Thaina P., Wong-Dusting H. K. Effects of omega-conotoxin GVIA on autonomic neuroeffector transmission in various tissues. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Oct;101(2):437–447. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12727.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emonds-Alt X., Doutremepuich J. D., Heaulme M., Neliat G., Santucci V., Steinberg R., Vilain P., Bichon D., Ducoux J. P., Proietto V. In vitro and in vivo biological activities of SR140333, a novel potent non-peptide tachykinin NK1 receptor antagonist. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Dec 21;250(3):403–413. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90027-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grider J. R., Murthy K. S., Jin J. G., Makhlouf G. M. Stimulation of nitric oxide from muscle cells by VIP: prejunctional enhancement of VIP release. Am J Physiol. 1992 Apr;262(4 Pt 1):G774–G778. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1992.262.4.G774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grider J. R., Rivier J. R. Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) as transmitter of inhibitory motor neurons of the gut: evidence from the use of selective VIP antagonists and VIP antiserum. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 May;253(2):738–742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross R. A., Macdonald R. L. Dynorphin A selectively reduces a large transient (N-type) calcium current of mouse dorsal root ganglion neurons in cell culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5469–5473. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He X. D., Goyal R. K. Nitric oxide involvement in the peptide VIP-associated inhibitory junction potential in the guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1993 Feb;461:485–499. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyle C. H. A modified single sucrose gap. Junction potentials and electrotonic potentials in gastrointestinal smooth muscles. J Pharmacol Methods. 1987 Nov;18(3):219–226. doi: 10.1016/0160-5402(87)90072-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyle C. H., Kamm M. A., Burnstock G., Lennard-Jones J. E. Enkephalins modulate inhibitory neuromuscular transmission in circular muscle of human colon via delta-opioid receptors. J Physiol. 1990 Dec;431:465–478. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyle C. H., Knight G. E., Burnstock G. Suramin antagonizes responses to P2-purinoceptor agonists and purinergic nerve stimulation in the guinea-pig urinary bladder and taenia coli. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Mar;99(3):617–621. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12979.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosterlitz H. W. The Wellcome Foundation lecture, 1982. Opioid peptides and their receptors. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1985 Jul 22;225(1238):27–40. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1985.0048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. G., Rand M. J. Nitric oxide and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide mediate non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic inhibitory transmission to smooth muscle of the rat gastric fundus. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Dec 4;191(3):303–309. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)94162-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi C. A., Giuliani S. Multiple inhibitory mechanisms mediate non-adrenergic non-cholinergic relaxation in the circular muscle of the guinea-pig colon. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1993 Jun;347(6):630–634. doi: 10.1007/BF00166946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi C. A., Patacchini R., Santicioli P., Lippe I. T., Giuliani S., Geppetti P., Del Bianco E., Selleri S., Meli A. The effect of omega conotoxin GVIA, a peptide modulator of the N-type voltage sensitive calcium channels, on motor responses produced by activation of efferent and sensory nerves in mammalian smooth muscle. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1988 Aug;338(2):107–113. doi: 10.1007/BF00174856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marino F., Marcoli M., De Ponti F., Lecchini S., Castelletti C. M., Frigo G. M. Inhibition of endogenous acetylcholine release by blockade of voltage-dependent calcium channels in enteric neurons of the guinea-pig colon. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1993 May;45(5):449–452. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1993.tb05574.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. J. Multiple calcium channels and neuronal function. Science. 1987 Jan 2;235(4784):46–52. doi: 10.1126/science.2432656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Williams J. T., Surprenant A., Christie M. J. Mu and delta receptors belong to a family of receptors that are coupled to potassium channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5487–5491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno N., Ito K. M., Yamamoto Y., Suzuki H. Suramin selectively inhibits the non-adrenergic non-cholinergic inhibitory junction potential in the guinea-pig stomach. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Nov 2;249(1):121–123. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90671-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders K. M., Ward S. M. Nitric oxide as a mediator of nonadrenergic noncholinergic neurotransmission. Am J Physiol. 1992 Mar;262(3 Pt 1):G379–G392. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1992.262.3.G379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vladimirova I. A., Shuba M. F. Sinapticheskie protsessy v gladkikh myshtsakh. Neirofiziologiia. 1984;16(3):307–319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zagorodniuk V. P., Shuba M. F. Priroda neadrenergicheskogo tormozhaniia v gladkikh myshtsakh kishechnika cheloveka. Neirofiziologiia. 1986;18(3):373–381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zagorodnyuk V. P., Vladimirova I. A., Vovk E. V., Shuba M. F. Studies of the inhibitory non-adrenergic neuromuscular transmission in the smooth muscle of the normal human intestine and from a case of Hirschsprung's disease. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1989 Feb;26(1):51–60. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(89)90107-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- den Hertog A., Nelemans A., Van den Akker J. The inhibitory action of suramin on the P2-purinoceptor response in smooth muscle cells of guinea-pig taenia caeci. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Aug 3;166(3):531–534. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90370-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


