Abstract
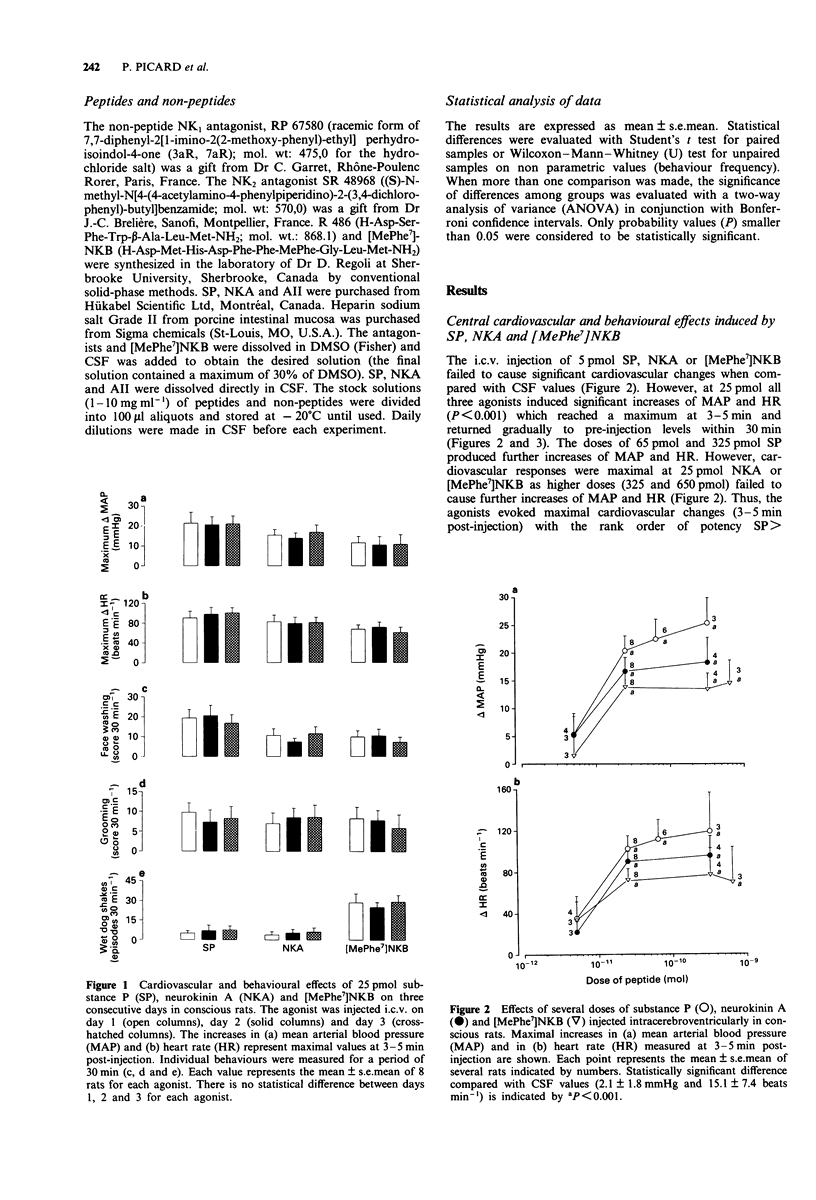
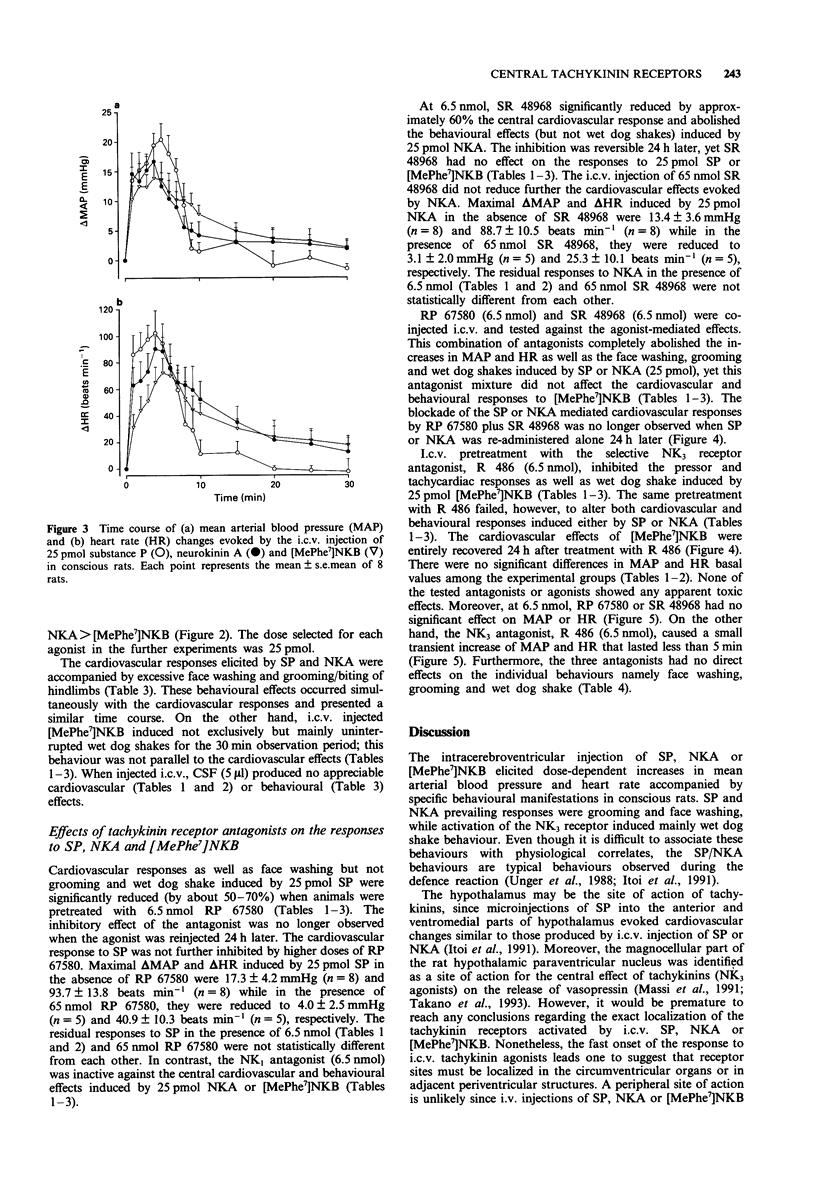
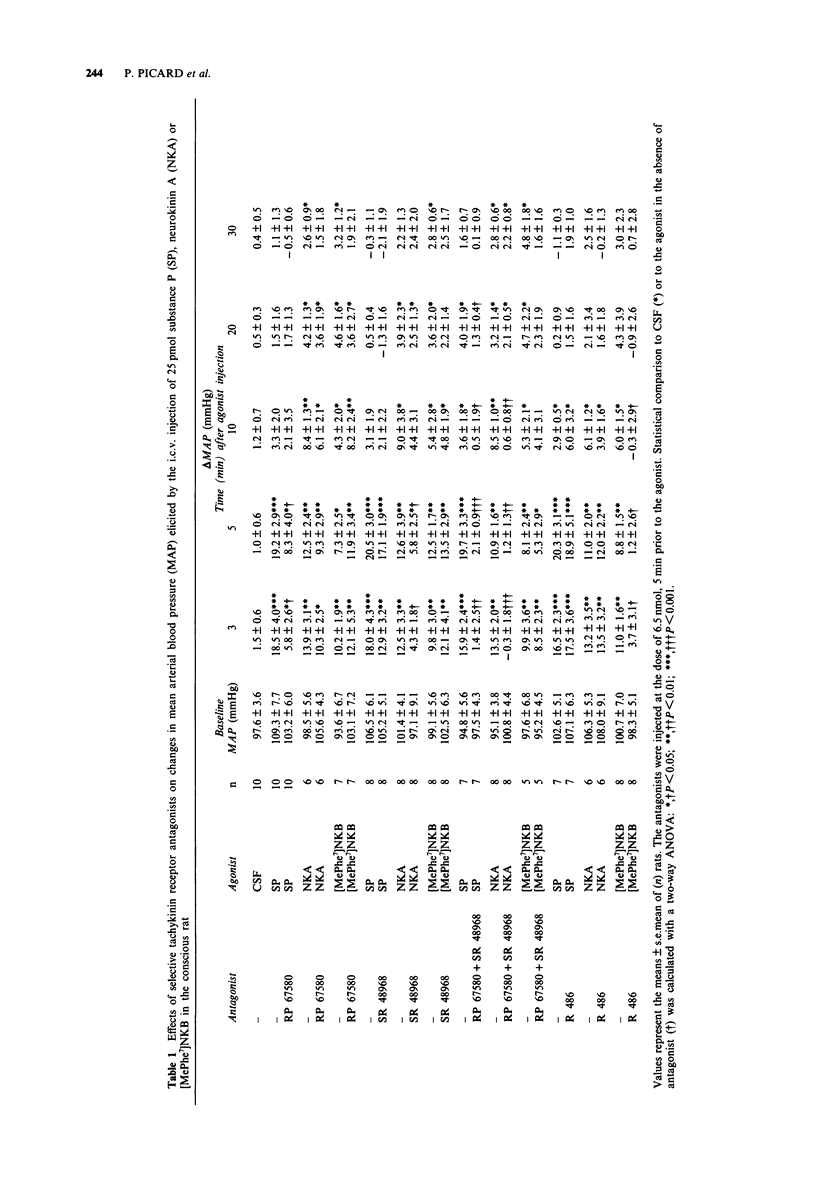
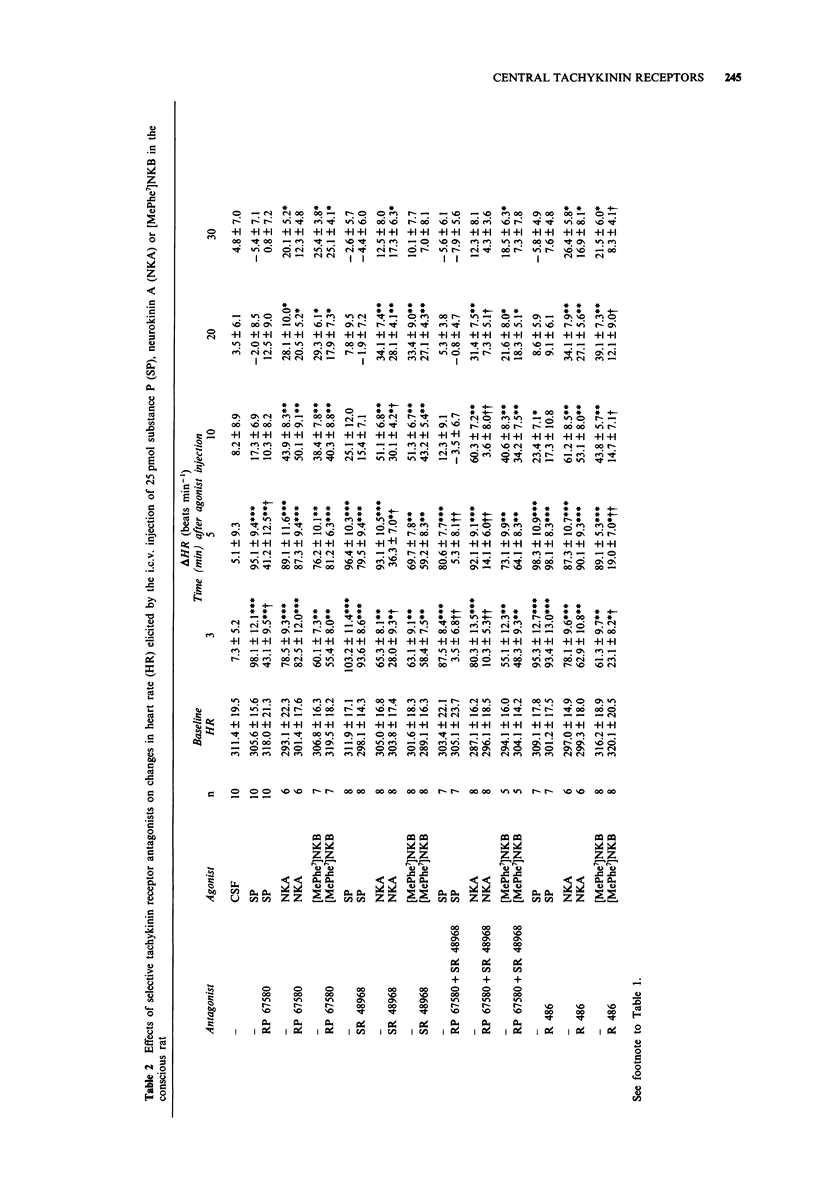
1. The effects of intracerebroventricular (i.c.v.) injection of selective and potent NK1 (RP 67580), NK2 (SR 48968) and NK3 (R 486, [Trp7, beta-Ala8]NKA(4-10)) receptor antagonists were assessed on the cardiovascular and behavioural responses elicited by the i.c.v. injection of substance P (SP), neurokinin A (NKA) or [MePhe7]neurokinin B ([MePhe7]NKB) in the conscious freely moving rat. 2. SP, NKA and [MePhe7]NKB (5-650 pmol) evoked dose-dependent increases in mean arterial blood pressure (MAP) and heart rate (HR) with the rank order of potency SP > NKA > [MePhe7]NKB. The cardiovascular responses were accompanied by excessive face washing, grooming and wet dog shakes. 3. The cardiovascular effects and face washing behaviour induced by SP (25 pmol) were significantly reduced by the pre-injection (i.c.v., 5 min earlier) of RP 67580 (6.5 nmol). However, this antagonist failed to affect the central effects of 25 pmol NKA or [MePhe7]NKB. 4. The cardiovascular and behavioural responses (except for wet dog shakes) elicited by NKA (25 pmol) were significantly reduced by 6.5 nmol SR 48968. However, the latter antagonist had no effect on the SP or [MePhe7]NKB-mediated responses. 5. Both cardiovascular and behavioural effects produced by either SP or NKA (25 pmol) were completely abolished when rats were pretreated with a combination of RP 67580 (6.5 nmol) and SR 48968 (6.5 nmol), yet this combination of antagonists failed to modify the central effects of [MePhe7]NKB. 6. R 486 (6.5 nmol) inhibited the cardiovascular effects as well as wet dog shakes produced by [MePhe7]NKB, but it was inactive against the responses induced by either SP or NKA.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF

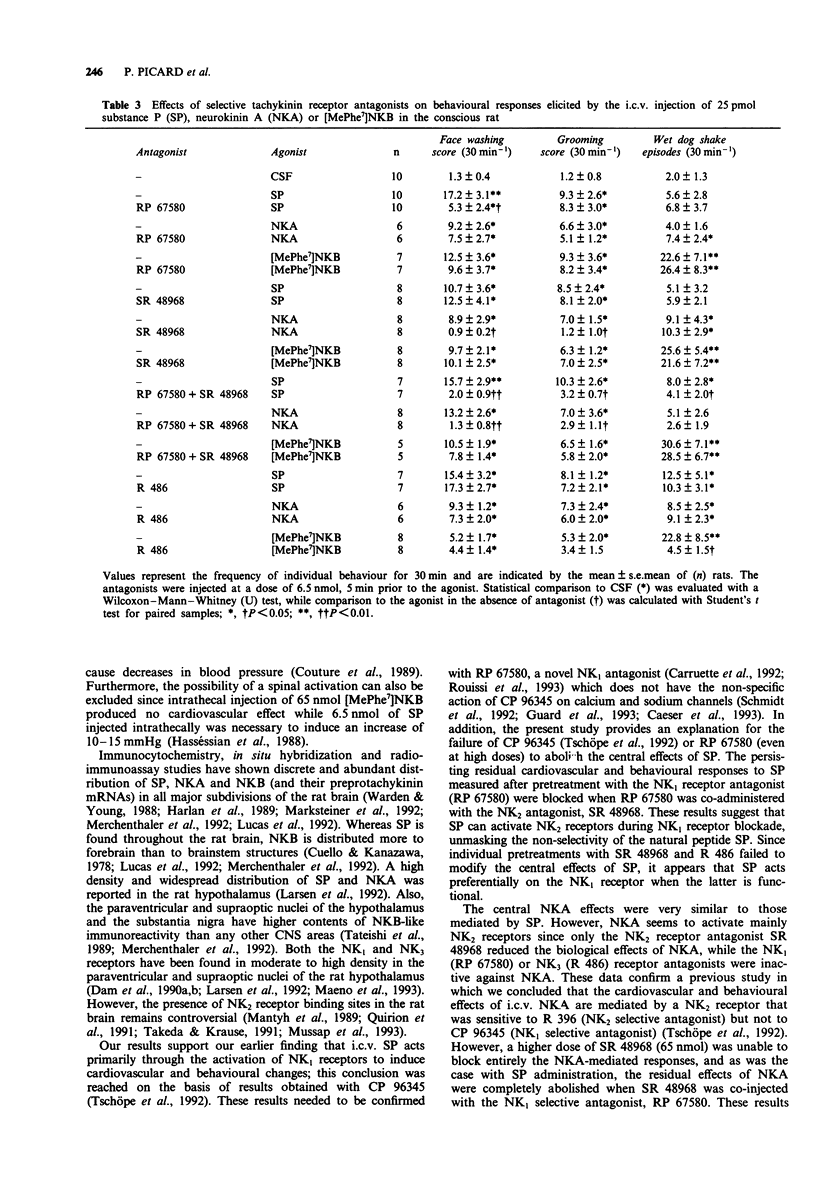
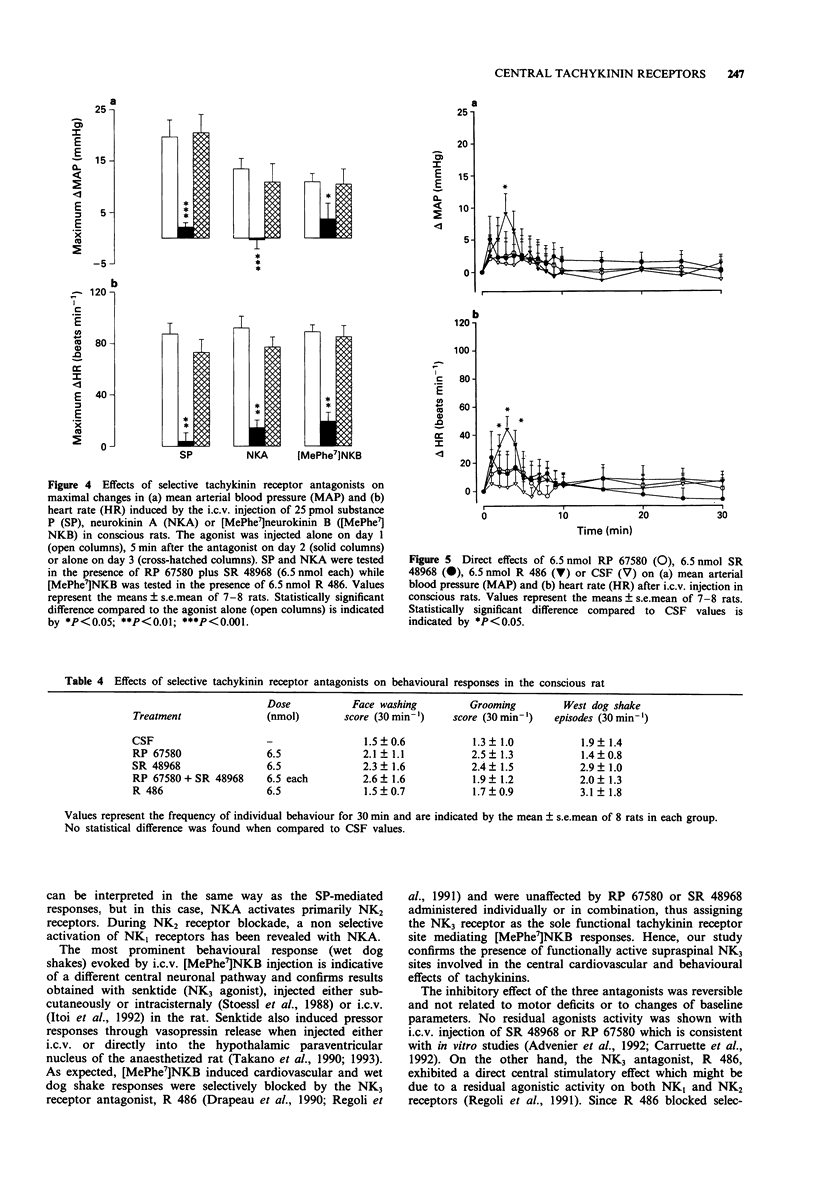


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Advenier C., Rouissi N., Nguyen Q. T., Emonds-Alt X., Breliere J. C., Neliat G., Naline E., Regoli D. Neurokinin A (NK2) receptor revisited with SR 48968, a potent non-peptide antagonist. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 May 15;184(3):1418–1424. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80041-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caeser M., Seabrook G. R., Kemp J. A. Block of voltage-dependent sodium currents by the substance P receptor antagonist (+/-)-CP-96,345 in neurones cultured from rat cortex. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Aug;109(4):918–924. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13708.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carruette A., Moussaoui S. M., Champion A., Cottez D., Goniot P., Garret C. Comparison in different tissue preparations of the in vitro pharmacological profile of RP 67580, a new non-peptide substance P antagonist. Neuropeptides. 1992 Dec;23(4):245–250. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(92)90131-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couture R., Boucher S., Picard P., Regoli D. Receptor characterization of the spinal action of neurokinins on nociception: a three receptor hypothesis. Regul Pept. 1993 Jul 2;46(1-2):426–429. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(93)90109-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couture R., Laneuville O., Guimond C., Drapeau G., Regoli D. Characterization of the peripheral action of neurokinins and neurokinin receptor selective agonists on the rat cardiovascular system. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1989 Nov;340(5):547–557. doi: 10.1007/BF00260610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuello A. C., Kanazawa I. The distribution of substance P immunoreactive fibers in the rat central nervous system. J Comp Neurol. 1978 Mar 1;178(1):129–156. doi: 10.1002/cne.901780108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dam T. V., Escher E., Quirion R. Visualization of neurokinin-3 receptor sites in rat brain using the highly selective ligand [3H]senktide. Brain Res. 1990 Jan 1;506(1):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)91218-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dam T. V., Martinelli B., Quirion R. Autoradiographic distribution of brain neurokinin-1/substance P receptors using a highly selective ligand [3H]-[Sar9,Met(O2)11]-substance P. Brain Res. 1990 Oct 29;531(1-2):333–337. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)90796-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapeau G., Rouissi N., Nantel F., Rhaleb N. E., Tousignant C., Regoli D. Antagonists for the neurokinin NK-3 receptor evaluated in selective receptor systems. Regul Pept. 1990 Nov 15;31(2):125–135. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(90)90115-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emonds-Alt X., Vilain P., Goulaouic P., Proietto V., Van Broeck D., Advenier C., Naline E., Neliat G., Le Fur G., Brelière J. C. A potent and selective non-peptide antagonist of the neurokinin A (NK2) receptor. Life Sci. 1992;50(15):PL101–PL106. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(92)90352-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garret C., Carruette A., Fardin V., Moussaoui S., Peyronel J. F., Blanchard J. C., Laduron P. M. RP 67580, un antagoniste, non peptidique, puissant et sélectif de la substance P. C R Acad Sci III. 1992;314(5):199–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gispen W. H., Wiegant V. M., Greven H. M., de Wied D. The induction of excessive grooming in the rat by intraventricular application of peptides derived from ACTH: structure-activity studies. Life Sci. 1975 Aug 15;17(4):645–652. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90103-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guard S., Boyle S. J., Tang K. W., Watling K. J., McKnight A. T., Woodruff G. N. The interaction of the NK1 receptor antagonist CP-96,345 with L-type calcium channels and its functional consequences. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Sep;110(1):385–391. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13821.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlan R. E., Garcia M. M., Krause J. E. Cellular localization of substance P- and neurokinin A-encoding preprotachykinin mRNA in the female rat brain. J Comp Neurol. 1989 Sep 8;287(2):179–212. doi: 10.1002/cne.902870204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasséssian H., Drapeau G., Couture R. Spinal action of neurokinins producing cardiovascular responses in the conscious freely moving rat: evidence for a NK-1 receptor mechanism. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1988 Dec;338(6):649–654. doi: 10.1007/BF00165629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoi K., Jost N., Badoer E., Tschöpe C., Culman J., Unger T. Localization of the substance P-induced cardiovascular responses in the rat hypothalamus. Brain Res. 1991 Aug 30;558(1):123–126. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)90727-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoi K., Tschöpe C., Jost N., Culman J., Lebrun C., Stauss B., Unger T. Identification of the central tachykinin receptor subclass involved in substance P-induced cardiovascular and behavioral responses in conscious rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Sep 4;219(3):435–444. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90485-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen P. J., Jessop D. S., Chowdrey H. S., Mikkelsen J. D., Lightman S. L. Osmotic regulation of substance P and neurokinin A peptide content and substance P binding sites in distinct hypothalamic nuclei of the rat. Peptides. 1992 Jul-Aug;13(4):705–712. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(92)90176-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas L. R., Hurley D. L., Krause J. E., Harlan R. E. Localization of the tachykinin neurokinin B precursor peptide in rat brain by immunocytochemistry and in situ hybridization. Neuroscience. 1992 Nov;51(2):317–345. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90318-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeno H., Kiyama H., Tohyama M. Distribution of the substance P receptor (NK-1 receptor) in the central nervous system. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1993 Apr;18(1-2):43–58. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(93)90172-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi C. A., Patacchini R., Giuliani S., Giachetti A. In vivo and in vitro pharmacology of SR 48,968, a non-peptide tachykinin NK2 receptor antagonist. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Mar 30;234(1):83–90. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90709-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi C. A., Patacchini R., Rovero P., Giachetti A. Tachykinin receptors and tachykinin receptor antagonists. J Auton Pharmacol. 1993 Feb;13(1):23–93. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1993.tb00396.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantyh P. W., Gates T., Mantyh C. R., Maggio J. E. Autoradiographic localization and characterization of tachykinin receptor binding sites in the rat brain and peripheral tissues. J Neurosci. 1989 Jan;9(1):258–279. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-01-00258.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marksteiner J., Sperk G., Krause J. E. Distribution of neurons expressing neurokinin B in the rat brain: immunohistochemistry and in situ hybridization. J Comp Neurol. 1992 Mar 22;317(4):341–356. doi: 10.1002/cne.903170403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massi M., Saija A., Polidori C., Perfumi M., Gentili L., Costa G., de Caro G. The hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus is a site of action for the central effect of tachykinins on plasma vasopressin. Brain Res Bull. 1991 Jan;26(1):149–154. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(91)90200-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merchenthaler I., Maderdrut J. L., O'Harte F., Conlon J. M. Localization of neurokinin B in the central nervous system of the rat. Peptides. 1992 Jul-Aug;13(4):815–829. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(92)90192-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mussap C. J., Geraghty D. P., Burcher E. Tachykinin receptors: a radioligand binding perspective. J Neurochem. 1993 Jun;60(6):1987–2009. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb03484.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka M., Yoshioka K. Neurotransmitter functions of mammalian tachykinins. Physiol Rev. 1993 Apr;73(2):229–308. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1993.73.2.229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard P., Boucher S., Regoli D., Gitter B. D., Howbert J. J., Couture R. Use of non-peptide tachykinin receptor antagonists to substantiate the involvement of NK1 and NK2 receptors in a spinal nociceptive reflex in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Mar 2;232(2-3):255–261. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90782-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polidori C., Saija A., Perfumi M., Costa G., de Caro G., Massi M. Vasopressin release induced by intracranial injection of tachykinins is due to activation of central neurokinin-3 receptors. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Sep 11;103(3):320–325. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90120-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quirion R., Dam T. V., Guard S. Selective neurokinin receptor radioligands. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1991;632:137–144. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1991.tb33102.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoli D., Nantel F., Tousignant C., Jukic D., Rouissi N., Rhaleb N. E., Télémaque S., Drapeau G., d'Orléans-Juste P. Neurokinin agonists and antagonists. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1991;632:170–183. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1991.tb33105.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouissi N., Claing A., Nicolau M., Jukic D., D'Orléans-Juste P., Regoli D. Substance P (NK-1 receptor) antagonists: in vivo and in vitro activities in rats and guinea pigs. Life Sci. 1993;52(13):1141–1147. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(93)90436-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoessl A. J., Dourish C. T., Iversen S. D. The NK-3 tachykinin receptor agonist senktide elicits 5-HT-mediated behaviour following central or peripheral administration in mice and rats. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Jun;94(2):285–287. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11527.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takano Y., Nagashima A., Hagio T., Tateishi K., Kamiya H. Role of central tachykinin peptides in cardiovascular regulation in rats. Brain Res. 1990 Oct 1;528(2):231–237. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)91662-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takano Y., Nakayama Y., Matsumoto T., Saito R., Kamiya H. O. The mechanism of central pressor actions of tachykinin NK-3 receptor in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus in rats. Regul Pept. 1993 Jul 2;46(1-2):360–363. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(93)90086-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y., Krause J. E. Pharmacological and molecular biological studies on the diversity of rat tachykinin NK-2 receptor subtypes in rat CNS, duodenum, vas deferens, and urinary bladder. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1991;632:479–482. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1991.tb33163.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tateishi K., Matsuoka Y., Hamaoka T. Establishment of highly specific radioimmunoassays for neurokinin A and neurokinin B and determination of tissue distribution of these peptides in rat central nervous system. Regul Pept. 1989 Mar;24(3):245–257. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(89)90221-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thunhorst R. L., Johnson A. K. Effects of arterial pressure on drinking and urinary responses to intracerebroventricular angiotensin II. Am J Physiol. 1993 Jan;264(1 Pt 2):R211–R217. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1993.264.1.R211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschöpe C., Picard P., Culman J., Prat A., Itoi K., Regoli D., Unger T., Couture R. Use of selective antagonists to dissociate the central cardiovascular and behavioural effects of tachykinins on NK1 and NK2 receptors in the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Nov;107(3):750–755. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14518.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger T., Carolus S., Demmert G., Ganten D., Lang R. E., Maser-Gluth C., Steinberg H., Veelken R. Substance P induces a cardiovascular defense reaction in the rat: pharmacological characterization. Circ Res. 1988 Oct;63(4):812–820. doi: 10.1161/01.res.63.4.812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger T., Rascher W., Schuster C., Pavlovitch R., Schömig A., Dietz R., Ganten D. Central blood pressure effects of substance P and angiotensin II: role of the sympathetic nervous system and vasopressin. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Apr 24;71(1):33–42. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90384-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warden M. K., Young W. S., 3rd Distribution of cells containing mRNAs encoding substance P and neurokinin B in the rat central nervous system. J Comp Neurol. 1988 Jun 1;272(1):90–113. doi: 10.1002/cne.902720107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


