Figure 1.
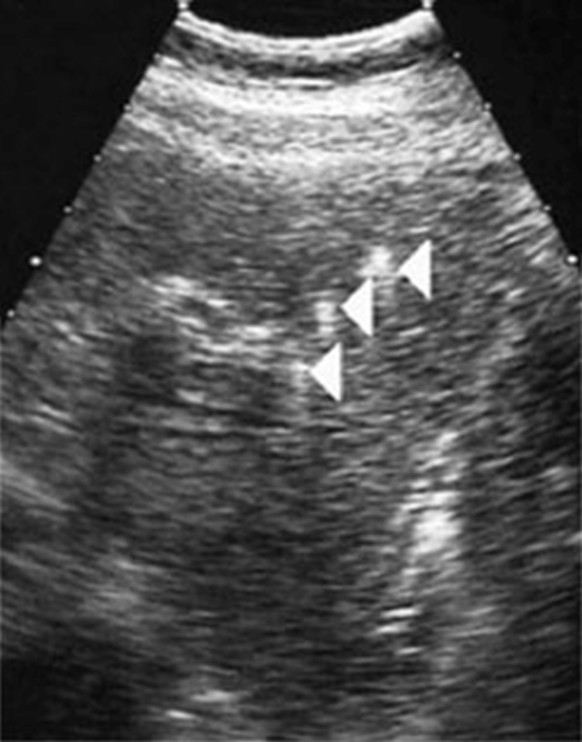
Ultrasound images of intrahepatic hyperechoic foci in patients with the LPAC syndrome. In these patients, a careful US examination detected intrahepatic hyperechoic foci with diffuse topography compatible with lipid deposits along the luminal surface of the intrahepatic biliary tree (Arrows). These multiple dots, less than 1 mm in diameter, cast short echogenic trail without acoustic shadows and looked like comet tails. They were typically distributed along the portal arborizations and may be associated with intrahepatic sludge or microlithiasis casting typical acoustic shadows.
