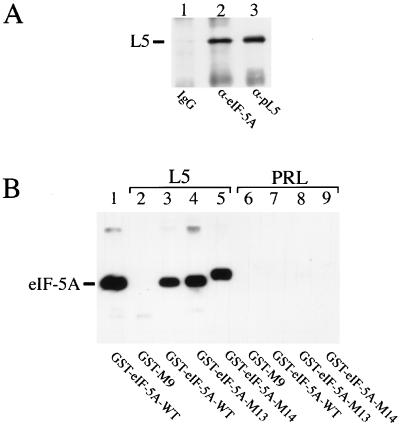
Figure 3.
Binding of L5 to eIF-5A in vivo and in vitro. (A) Coprecipitation of eIF-5A and ribosomal protein L5 using total cell lysate. Equal amounts of HeLa cell extracts were subjected to immunoprecipitation analyses with preimmune IgG (lane 1, negative control), anti-eIF-5A antibodies (lane 2, α-eIF–5A), or anti-L5 antibodies (α-pL5, lane 3, positive control). The precipitated complexes were resolved on SDS/polyacrylamide gels, immobilized on membranes, and subjected to Western blot analysis with anti-L5 antibodies (α-pL5). The location of L5 protein is indicated on the left. (B) Specific interaction of recombinant His-tagged L5 with GST–eIF-5A fusion proteins. Bacterial S100 extracts containing either His-tagged L5 (lanes 2–5) or His-tagged prolactin (PRL, lanes 6–9) protein were incubated in vitro with various GST fusion proteins (indicated at the bottom). The binding reactions were then immobilized with metal affinity resin and eluted with imidazole. Eluted proteins were separated on SDS/polyacrylamide gels, blotted, and subjected to Western blot analysis with anti-GST antibodies. For comparison, recombinant GST–eIF-5A wild-type protein (WT) was loaded directly in lane 1 of the SDS/polyacrylamide gel (indicated at the left). The GST–M9 (49, 50) protein served as negative control (lanes 2 and 6).