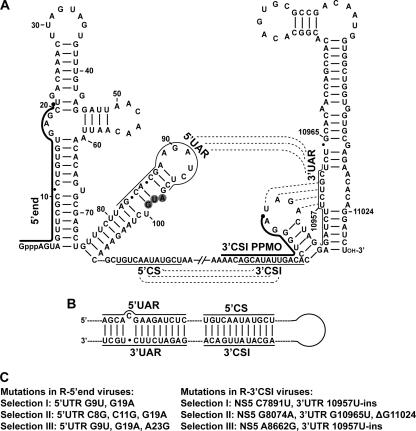
FIG. 1.
Sequences and structures of the PPMO-targeted WNV RNA regions. (A) Terminal stem-loop structures and potential RNA-RNA interactions within the WNV genome. Secondary structures formed by the 5′- and 3′-terminal sequences of the WNV genome are depicted. Two PPMOs, the 5′-end PPMO and the 3′ CSI PPMO, are indicated as thick lines with filled circles (representing an Arg-rich peptide [11]) at the 5′ ends. The AUG initiation codon of the open reading frame is shaded in gray. Three RNA interactions are denoted by dashed lines, the 5′ UAR-3′ UAR and 5′ CS-3′ CSI interactions and a pseudoknot base pairing (located at the 3′-terminal stem-loops). The sequences involved in the 5′ UAR-3′ UAR and 5′ CS-3′ CSI interactions are indicated by thin lines. Nucleotide positions are numbered based on the full-length sequence of the WNV genome. Gppp indicates a gap structure of viral genome. (B) Potential genome cyclization of WNV through the 5′ UAR-3′ UAR and 5′ CS-3′ CSI base pairings. (C) Adaptive mutations derived from viruses resistant to the 5′-end PPMO (left panel) or the 3′ CSI PPMO (right panel).