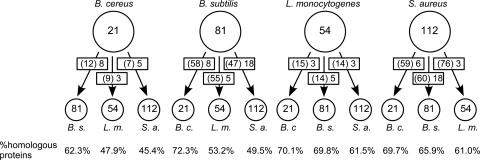
FIG. 4.
Conservation of genes from the σB regulon in B. cereus, B. subtilis, L. monocytogenes, and S. aureus. The number of genes that are directly regulated by σB in a given organism is shown in the large circle. The conservation of σB-dependent genes from this organism in three other gram-positive bacteria (B. c., B. cereus; B. s., B. subtilis; L. m., L. monocytogenes; S. a., S. aureus) was determined with TIGR's Multi-Genome Homology Comparison tool (http://cmr.tigr.org/tigr-scripts/CMR/shared/MakeFrontPages.cgi?page=circular_display) with a cutoff for significance of a P value of ≤1.0 × 10−5. The numbers of conserved genes of the σB regulon are indicated in the arrows toward the small circles. The numbers in parentheses are the numbers of genes from the σB regulon of the query organism that have a homolog in the target organism. The second number in the arrow indicates the number of genes from this group, which are dependent on σB for their expression in both organisms. For comparative purposes, the conservation of all protein-coding genes between the genomes is indicated at the bottom of the figure.