FIG. 2.
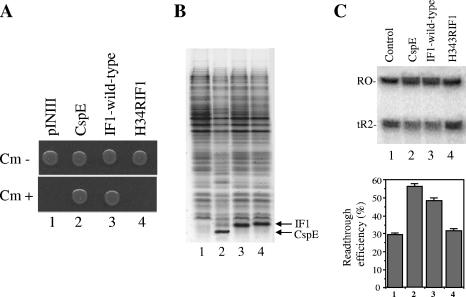
Mutation in IF1 affects its transcription antitermination activity in vivo and in vitro. (A) The in vivo transcription antitermination assay using the RL211 cells was carried out as for the experiment for which results are presented in Fig. 1A. Cells were transformed with the pINIII vector either alone or carrying cspE, wild-type infA, or infA(H34R). Results of cell growth after 1 night (plates without chloramphenicol) and 2 nights (plates with chloramphenicol) are presented. Cm, chloramphenicol. (B) SDS-PAGE analysis of induction patterns of CspE, IF1, and its mutant. Lane 1, cells with pINIII vector alone; lane 2, pINIIIcspE; lane 3, pINIIIInfA; lane 4, pINIIIH34RinfA. Bands corresponding to overexpressed CspE or IF1 are indicated. (C) The in vitro transcription antitermination assay was carried out, using purified CspE or wild-type or mutant IF1, as described for the experiment for which results are presented in Fig. 1B. The products were analyzed by urea-PAGE (7 M urea-10% polyacrylamide). RO and tR2 indicate the runoff and tR2-terminated transcripts, respectively. Mean values calculated from three independent experiments are shown in the bar graph below the gel.