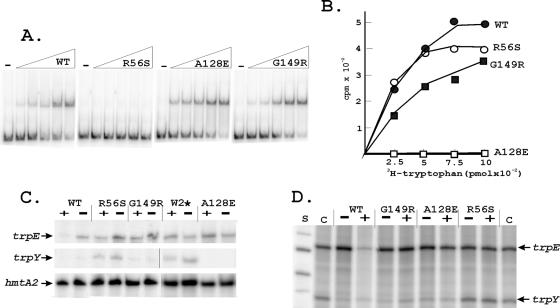
FIG. 2.
DNA and tryptophan binding and transcription regulation by TrpY and TrpY variants. (A) Electrophoretic mobility shift assays of TrpYWT and TrpY variants binding to the trpY-trpE intergenic region. Reaction mixtures contained 32P-labeled DNA (0.5 ng), 50 ng poly(dI·dC) and 0 (−), 1.25, 2.5, 5, 10, or 20 ng of TrpYWT or a TrpY variant. (B) [3H]tryptophan binding by TrpYWT and TrpY variants. (C) Primer extension products generated by reverse transcription of the trpY, trpEGCFBAD (trpE), and hmtA2 transcripts in RNA preparations (17) from wild-type (WT) and TrpY variant-containing M. thermautotrophicus cells grown with (+) or without (−) tryptophan. (D) Runoff trpY and trpE transcripts synthesized in vitro from a template DNA (previously designated T1 [24]) with the entire trpY-trpE intergenic region. Reaction mixtures contained 200 μM (each) ATP, CTP, and GTP; 20 μM UTP plus 10 μCi of [α-32P]UTP; 40 nM M. thermautotrophicus RNA polymerase; 80 nM TFB; 80 nM TBP; and 100 nM TrpYWT or the TrpY variant listed, with (+) or without (−) 24 μM tryptophan (18). After incubation at 60°C for 30 min, the accumulated transcripts were separated by gel electrophoresis and visualized by phosphorimaging, as described in detail previously (24). Control (C) lanes contained the transcripts synthesized in reaction mixtures with no TrpY or TrpY variant added. Single-stranded DNA molecules provided size standards (S).