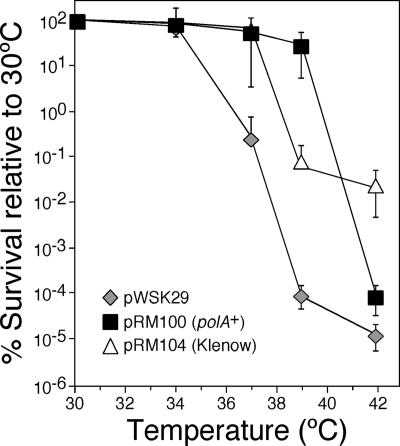
FIG. 1.
Elevated levels of Pol I partially suppress the temperature-sensitive growth phenotype of the dnaN159 strain. Strain MS105 [thr-1 araD139 Δ(gpt-proA)62 lacY1 tsx-33 glnV44(AS) galK2(Oc) hisG4(Oc) rpsL31 xylA5 mtl-1 argE3(Oc) thi-1 sulA211 lexA51(Def) tnaA300::Tn10 dnaN159] was transformed with either pWSK29 (control), pRM100 (polA+), or pRM104 (Klenow). We used strain MS105 for this experiment because it displays a more pronounced temperature-sensitive phenotype than many other dnaN159 strains, thus increasing the range in which we could observe an effect by Pol I or Klenow. Temperature sensitivity was measured by plating out dilutions of overnight cultures grown at 30°C onto M9 minimal medium, followed by incubation at the indicated temperature overnight. The number of CFU observed at each indicated temperature is expressed as a percentage of that observed for the same strain at 30°C, which was set equal to 100%. The error bars indicate standard deviations. MS105 bearing pWSK29 had an average titer of 5.1 × 108 viable cells/ml, MS105 bearing pRM100 had an average titer of 1.5 × 108 viable cells/ml, and MS105 bearing pRM104 had an average titer of 0.1 × 107 viable cells/ml.