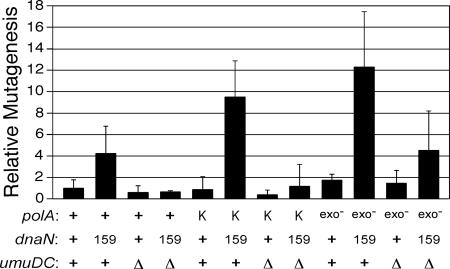
FIG. 4.
Spontaneous mutation frequencies in dnaN+ and dnaN159 strains expressing either Pol I or the Klenow fragment of Pol I. All strains used were derivatives of CJ278 [Δ(gal-bio) thi-1 relA1 spoT1 ΔpolA::kan] and expressed either the polA+ allele, the Klenow fragment of Pol I, or the polA-exo mutant allele from an F′ episome (18). The strains examined were RM137, dnaN+ (F′ polA+); RM138, dnaN159 (F′ polA+); RM139, dnaN+ ΔumuDC595::cat (F′ polA+); RM140, dnaN159 ΔumuDC595::cat (F′ polA+); RM141, dnaN+ (F′ Klenow); RM142, dnaN159 (F′ Klenow); RM143, dnaN+ ΔumuDC596::ermGT (F′ Klenow); RM144, dnaN159 ΔumuDC596::ermGT (F′ Klenow); RM145, dnaN+ (F′ polA-exo mutant); RM146, dnaN159 (F′ polA-exo mutant); RM147, dnaN+ ΔumuDC596::ermGT (F′ polA-exo mutant); RM148, dnaN159 ΔumuDC596::ermGT (F′ polA-exo mutant). The mutation frequency was calculated following growth at 30°C by dividing the number of Rifr colonies by the total number of viable cells, as described previously (29, 38, 40). Mutation frequencies are expressed relative to the dnaN+ polA+ strain (9.7 ± 7.5 Rifr CFU/109 total viable cells), which was set equal to 1.0, and are the averages of at least five independent determinations. The error bars represent the standard deviations. Abbreviations: +, polA+, dnaN+, or umuD+C+, as indicated; exo−, Pol I exo mutant; K, Klenow fragment; 159, dnaN159; Δ, ΔumuDC596::ermGT or ΔumuDC595::cat.