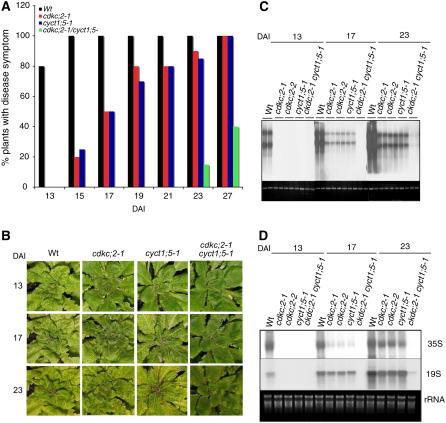
Figure 1.
Enhanced Resistance of cdkc;2 and cyct1;5 Mutants to CaMV.
(A) Disease symptom development in mechanically inoculated plants. Forty wild-type, cdkc;2-1, and cyct1;5-1 single or double mutant plants were mechanically inoculated with partially purified CaMV virons (0.5 mg protein/mL), and plants with CaMV mosaic symptoms were scored at the indicated DAI.
(B) Disease symptom development in plants inoculated by bombardment of the infectious CaMV DNA clone pCa122. Photographs of representative plants were taken at the indicated DAI. Disease symptom development in the cdkc;2-2 mutant was the same as in the cdkc;2-1 mutant.
(C) Viral DNA accumulation. Wild-type and mutant plants were inoculated by bombardment of pCa122, and total DNA was isolated from leaf tissues harvested at the indicated DAI and probed with the P6 open reading frame of CaMV. Ethidium bromide staining of genomic DNA is shown as a loading control.
(D) Viral RNA accumulation. Total RNA was isolated from inoculated plants and first probed with the P3 open reading frame of CaMV for detection of the 35S RNA. The blot was stripped and reprobed with the P6 open reading frame of CaMV for detection of the 19S RNA. Ethidium bromide staining of rRNA is shown for the assessment of equal loading.