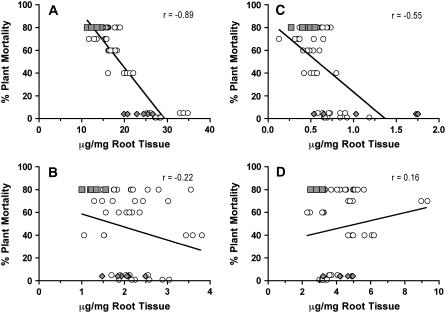
Figure 3.
Relationship between preformed whole-root suberin and soybean partial resistance to P. sojae. Ten-day-old roots from nine independent soybean genotypes were subjected to solvent extraction, BF3/MeOH transesterification, and alkaline NBO (see “Materials and Methods” for details). Data obtained for aliphatic suberin (A), esterified phenolic (B), phenolic suberin (C), and suberin-associated (D) wax components were plotted against plant mortality data obtained from plantings of the same genotypes in fields naturally infested with P. sojae. Genotypes used (% mortality) were ‘Westag 97’ (1%), ‘Conrad’ (4%), ‘Elgin’ (5%), ‘Williams’ (40%), ‘Steele’ (60%), ‘Sloan’ (70%), ‘Haro(1-7)1’ (80%), ‘OX20-8’ (80%), and OX760-6 (80%). The data for ‘Conrad’ (diamonds) and OX760-6 (squares) are highlighted. Each data point represents an independent estimate of the suberin component measured. Regression lines are shown to indicate trends. The r values are Pearson's correlation coefficients.