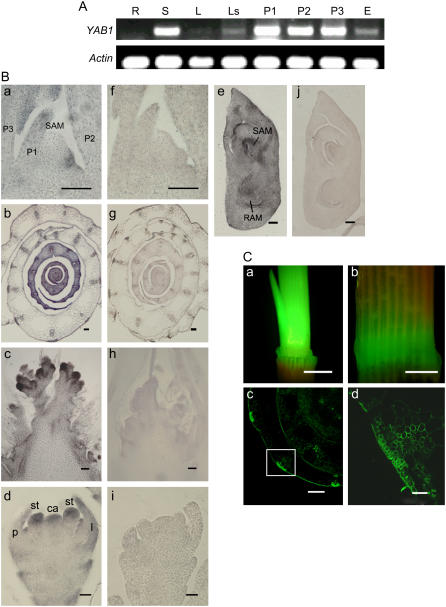
Figure 1.
Expression pattern of YAB1. A, Detection of YAB1 transcript by semiquantitative RT-PCR in roots (R), shoots (S), mature leaves (L), leaf sheaths (Ls), and panicles at three developmental stages (P1–P3; P1, primary panicle branch primordia; P2, secondary branch primordia; P3, stamen and carpel primordia) and developing embryo (E). B, In situ hybridization detection of YAB1 transcripts in leaf primordia (a and f), young leaves (b and g), rachis meristem (c and h), floral meristem (d and i), and developing embryo (e and j) with antisense (a–e) or sense (f and g) cDNA of YAB1 as probes. Bars in a, f, c, and h = 5 μm; bars in e and j = 10 μm; bars in b, g, and d, I = 20 μm. C, Detection of GFP expression under the control of the YAB1 promoter (−1,662 to 1) in the elongating stem (a) and the leaf sheath (b). c, Cross section of sheaths showing GFP expression in sclerenchyma, vascular bundles, and epidermal cells. d, Enlargement of the boxed area in c. Bars in a and b = 1 cm, in c = 30 μm, in d = 100 μm. ca, Carpel primordium; l, lemma; p, palea; P1 to P3, leaf primordium; RAM, root apical meristem; st, stamen primordium.